这个OpenHD改造移植系列的最后一篇文章,这篇文章主要讲如何讲前面说到的全部内容串接起来,讲OSD画面显示和视频画面整合到一起,形成完整的图传地面显示,真正实现PC上直接接收显示图传视频和数据。
OpenHD改造实现廉价高清数字图传(树莓派+PC)—(一)概述_hoopertsau的博客-CSDN博客_openhd
OpenHD改造实现廉价高清数字图传(树莓派+PC)—(二)Wifibroadcast Wifi广播通信_hoopertsau的博客-CSDN博客
OpenHD改造实现廉价高清数字图传(树莓派+PC )—(三)OpenVG和libshapes在PC上的移植_hoopertsau的博客-CSDN博客
OpenHD改造实现廉价高清数字图传(树莓派+PC )—(四)OSD数据传输和画面显示_hoopertsau的博客-CSDN博客
OpenHD改造实现廉价高清数字图传(树莓派+PC)—(五)gstreamer视频采集、传输和显示_hoopertsau的博客-CSDN博客
一、OSD和视频整合显示改造
整合OSD和视频显示核心思路:
在X11window上创建两个窗口,一个用OpenVG来绘制OSD画面,一个用gstreamer来显示视频画面。将OSD画面的背景要设置为透明,并叠加显示在视频窗口上,这样就有浮在视频画面上的效果了。这里主要就在于怎么将OSD的背景设置为透明显示。
这里主要修改的还是openvg目录下的oglinit.c文件,主要是创建窗口这里要修改。
直接看一下代码,如何创建这样的两个窗口。
// 创建X11窗口
VGboolean windowCreate(STATE_T * state, const char* title,
const VGuint width,
const VGuint height)
{
VGint screen, screenWidth, screenHeight;
XSetWindowAttributes windowAttributes;
XSizeHints windowSizeHints;
XVisualInfo* visualInfo;
MY_PFNGLXSWAPINTERVALSGIPROC sgiSwapInterval;
MY_PFNGLXSWAPINTERVALEXTPROC extSwapInterval;
// OpenGL surface configuration
GLXFBConfig fbconfig;
VGint fbConfigsCount = 0;
static int glAttributes[] = {
GLX_RENDER_TYPE, GLX_RGBA_BIT,
GLX_DRAWABLE_TYPE, GLX_WINDOW_BIT,
GLX_DOUBLEBUFFER, True,
GLX_RED_SIZE, 1,
GLX_GREEN_SIZE, 1,
GLX_BLUE_SIZE, 1,
GLX_ALPHA_SIZE, 1,
GLX_DEPTH_SIZE, 1,
None
};
// open a display on the current root window
display = XOpenDisplay(NULL);
if (display == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Unable to open display.\n");
return VG_FALSE;
}
// get the default screen associated with the previously opened display
screen = DefaultScreen(display);
// 根窗口
rootWindow = RootWindow(display, screen);
// get screen bitdepth
screenDepth = DefaultDepth(display, screen);
// run only on a 32bpp display
if ((screenDepth != 24) && (screenDepth != 32)) {
fprintf(stderr, "Cannot find 32bit pixel format on the current display.\n");
XCloseDisplay(display);
return VG_FALSE;
}
// get screen dimensions
screenWidth = DisplayWidth(display, screen);
screenHeight = DisplayHeight(display, screen);
state->screen_width = screenWidth;
state->screen_height = screenHeight;
printf("screen width=%d height=%d\r\n",screenWidth,screenHeight);
unsigned long white = WhitePixel(display,screen);
unsigned long black = BlackPixel(display,screen);
// 再创建透明的OSD显示,在上层
// 找到合适的配置
GLXFBConfig* fbconfigs = glXChooseFBConfig(display, screen, glAttributes, &fbConfigsCount);
int i = 0;
static XRenderPictFormat *pictFormat;
for(i = 0; i<fbConfigsCount; i++) {
visualInfo = (XVisualInfo_CPP*) glXGetVisualFromFBConfig(display, fbconfigs[i]);
if(!visualInfo)
continue;
pictFormat = XRenderFindVisualFormat(display, visualInfo->visual);
if(!pictFormat)
continue;
if(pictFormat->direct.alphaMask > 0) {
fbconfig = fbconfigs[i];
break;
}
}
// initialize window's attribute structure
windowAttributes.colormap = XCreateColormap(display, rootWindow, visualInfo->visual, AllocNone);
windowAttributes.border_pixel = 0;
windowAttributes.background_pixmap = None;
printf("None=%d\r\n",None);
int attr_mask =
CWBackPixmap|
CWColormap|
CWBorderPixel; /* What's in the attr data */
// create the window centered on the screen
state->window_width = width;
state->window_height = height;
// 先创建视频窗口,在底层
video_window = XCreateSimpleWindow(display,
rootWindow,
0, 0, // origin
width, height, // size
1, black, // border
white ); // backgd
// 创建OSD窗口
window = XCreateWindow(display, rootWindow, 0,0, width, height, 1, visualInfo->depth, InputOutput, visualInfo->visual, attr_mask, &windowAttributes);
//if ( window == None )
if (window == None || video_window == None)
{
fprintf(stderr, "Unable to create the window.\n");
XCloseDisplay(display);
return VG_FALSE;
}
// set the window's name
XStoreName(display, window, title);
XStoreName(display, video_window, "video window");
// tell the server to report mouse and key-related events
XSelectInput(display, window, KeyPressMask | KeyReleaseMask | ButtonPressMask | Button1MotionMask | Button2MotionMask | Button3MotionMask | StructureNotifyMask | ExposureMask);
// initialize window's sizehint definition structure
windowSizeHints.flags = PPosition | PMinSize | PMaxSize;
windowSizeHints.x = 0;
windowSizeHints.y = 0;
windowSizeHints.min_width = 1;
// clamp window dimensions according to the maximum surface dimension supported by the OpenVG backend
windowSizeHints.max_width = vgPrivSurfaceMaxDimensionGetMZT();
if (screenWidth < windowSizeHints.max_width) {
windowSizeHints.max_width = screenWidth;
}
windowSizeHints.min_height = 1;
windowSizeHints.max_height = windowSizeHints.max_width;
if (screenHeight < windowSizeHints.max_height) {
windowSizeHints.max_height = screenHeight;
}
// set the window's sizehint 不加这一句话,窗口的位置就不能正确设置
XSetWMNormalHints(display, video_window, &windowSizeHints);
// clear the window
XClearWindow(display, video_window);
// set the window's sizehint
XSetWMNormalHints(display, window, &windowSizeHints);
// clear the window
XClearWindow(display, window);
// create a GLX context for OpenGL rendering
glContext = glXCreateNewContext(display, fbconfig, GLX_RGBA_TYPE, NULL, True);
if (!glContext) {
fprintf(stderr, "Unable to create the GLX context.\n");
XDestroyWindow(display, video_window);
XDestroyWindow(display, window);
XCloseDisplay(display);
return VG_FALSE;
}
// create a GLX window to associate the frame buffer configuration with the created X window
glWindow = glXCreateWindow(display, fbconfig, window, NULL);
// bind the GLX context to the Window
glXMakeContextCurrent(display, glWindow, glWindow, glContext);
// GLX_EXT_swap_control
extSwapInterval = (MY_PFNGLXSWAPINTERVALEXTPROC)glXGetProcAddressARB((const GLubyte *)"glXSwapIntervalEXT");
if (extSwapInterval) {
extSwapInterval(display, glWindow, 0);
}
else {
// GLX_SGI_swap_control
sgiSwapInterval = (MY_PFNGLXSWAPINTERVALSGIPROC)glXGetProcAddressARB((const GLubyte *)"glXSwapIntervalSGI");
if (sgiSwapInterval) {
sgiSwapInterval(0);
}
}
// put the window on top of the others
XMapRaised(display, video_window);
XMapRaised(display, window);
// clear event queue
XFlush(display);
XFree(visualInfo);
/*
// 无边框的效果
Atom window_type = XInternAtom(display, "_NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE", False);
long value = XInternAtom(display, "_NET_WM_WINDOW_TYPE_DOCK", False);
XChangeProperty(display, window, window_type, XA_ATOM, 32, PropModeReplace, (unsigned char *) &value,1 );
*/
// 初始化视频显示
gst_init (NULL,NULL);
printf("gst inited\r\n");
initGst(video_window);
return VG_TRUE;
}
分析一下这个窗口创建的代码,有几个关键的地方。
1、找到合适的显示配置
// 找到合适的配置
GLXFBConfig* fbconfigs = glXChooseFBConfig(display, screen, glAttributes, &fbConfigsCount);
int i = 0;
static XRenderPictFormat *pictFormat;
for(i = 0; i<fbConfigsCount; i++) {
visualInfo = (XVisualInfo_CPP*) glXGetVisualFromFBConfig(display, fbconfigs[i]);
if(!visualInfo)
continue;
pictFormat = XRenderFindVisualFormat(display, visualInfo->visual);
if(!pictFormat)
continue;
if(pictFormat->direct.alphaMask > 0) {
fbconfig = fbconfigs[i];
break;
}
}
2、窗口的属性设置
// initialize window's attribute structure
windowAttributes.colormap = XCreateColormap(display, rootWindow, visualInfo->visual, AllocNone);
windowAttributes.border_pixel = 0;
windowAttributes.background_pixmap = None;
int attr_mask =
CWBackPixmap|
CWColormap|
CWBorderPixel; /* What's in the attr data */
要将背景设置为None,并且mask中要设置背景标志
3、创建两个窗口
// 先创建视频窗口,在底层
video_window = XCreateSimpleWindow(display,
rootWindow,
0, 0, // origin
width, height, // size
1, black, // border
white ); // backgd
// 创建OSD窗口
window = XCreateWindow(display, rootWindow, 0,0, width, height, 1, visualInfo->depth, InputOutput, visualInfo->visual,attr_mask, &windowAttributes);
一个是用于显示视频的video_window ,一个是用于显示osd的
注意:
这两个的父窗口都是rootWindow,我尝试将osd的父窗口设置为视频,这样背景就不透明了。但是如果将视频窗口也设置为透明,gstreamer就显示不正常了,相互之间有影响。所以就干脆分开两个窗口,互不影响。
4、设置窗口的位置
// set the window's sizehint, 不加这一句话,窗口的位置就不能正确设置
XSetWMNormalHints(display, video_window, &windowSizeHints);
// clear the window
XClearWindow(display, video_window);
如果不设置的话,窗口的初始位置可能会有错位,导致两个窗口不能叠加在一起。
5、初始化gstreamer并绑定GUI
// 初始化gstreamer库
gst_init (NULL,NULL);
// 创建视频处理的管道,并绑定到视频显示窗口video_window
initGst(video_window);
这个与上一篇文章的内容类似,就不再详细描述了,直接看之前的代码。
看一下最终效果,叠在一起显示 
二、总结
通过将OpenHD深度的剥离改造,可以实现在普通的PC上显示图传,大大降低我们的成本,不需要再买地面端的树莓派了。同时,OpenHD里面有大量“无用”的脚本和代码,过于复杂。
其实用到的主要就是四个软件:
1、wifibroadcast,提供底层的通信
2、openvg,提供osd绘图的支撑
3、gstreamer,osd调用并用来解析视频用的
4、osd,接收解析并绘制视频和叠加显示信息
当然OpenHD提供的是一揽子解决方案,直接烧写镜像即可开机使用,比较适合不会开发的航模玩家,可以直接上手使用。
三、后续
考虑到天空端的树莓派Zero也开始涨价了,当前价格大概在500块左右(2022年9月30日),为了进一步降低成本,我还考虑将天空端移植到国产的PI上。
这里有几个可选的PI,后续再讲如何往这些国产化的PI上进行迁移,进一步降低成本。
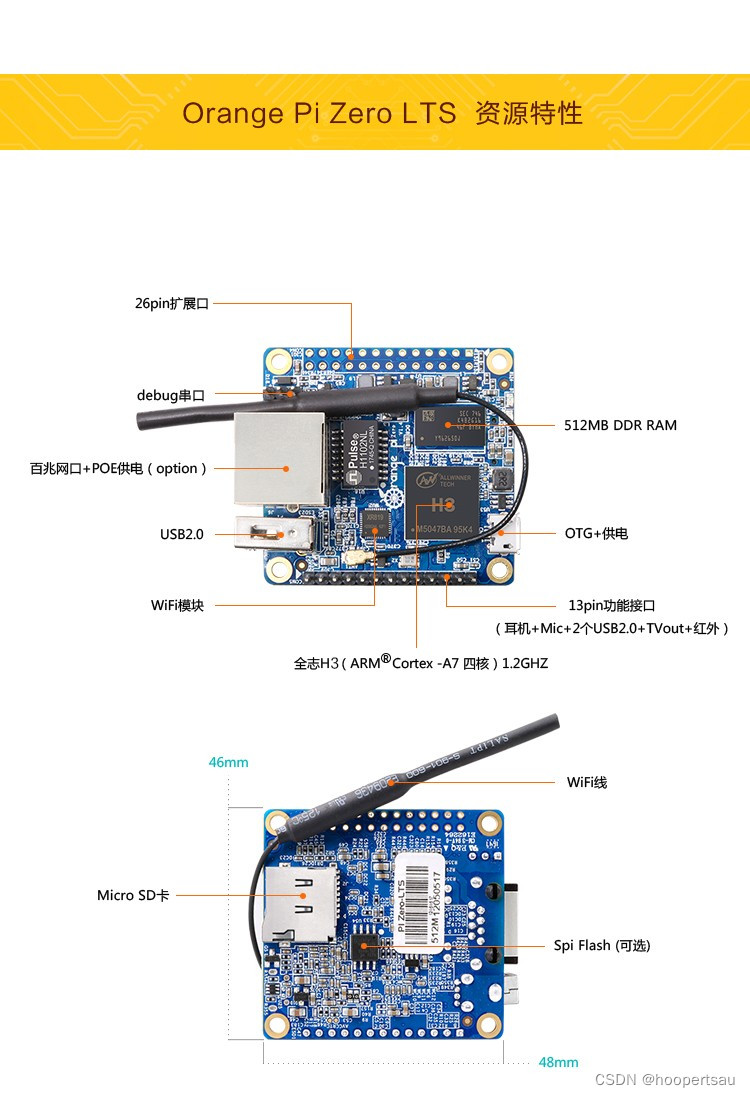
1、OrangePi Zero
全志的H3处理器,只要大概120块钱。但是没有CSI接口的摄像头,需要外接使用USB摄像头。
2、OrangePi i96
RDA8810PL处理器,非常便宜,开发板只要39块钱!摄像头32块。当然,性能不是太好,而且CPU也很老了,也很难找到技术支持,而且坑也比较多。但是架不住它便宜啊,哈哈。

3、Banana pi-M2 Zero
使用的也是全志H3处理器,价格140左右,但是摄像头贵了,要60块钱。

本文内容由网友自发贡献,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有涉嫌抄袭侵权的内容,请联系:hwhale#tublm.com(使用前将#替换为@)