在SpringBoot项目中,应用在启动时会扫描项目中的@Controller和@RequestMapping注解,并将其解析为RequestMapping Bean类型的对象供DispatcherServlet调用。本文主要分析这个解析的过程。
在SpringBoot项目的启动类中@ComponentScan用于扫描value配置的包路径下的组件。
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableSwagger2
@ComponentScans(value={@ComponentScan(value="com.changshin")})
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
在API类中
@RestController
public class UserApi {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(UserApi.class);
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@PostMapping(value = "user/queryUserName")
public UserInfoResponse queryUserNameById(@RequestBody UserInfoRequest request){
log.info("查询用户姓名请求参数",request);
UserInfoResponse response = userService.selectUserNameById(request);
log.info("查询用户姓名返回参数",request);
return response;
}
}
点开RestController在点开RestController里声明的Controller发现其被@Component声明,会解析为被Spring上下文管理的Bean。
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Controller
@ResponseBody
public @interface RestController {
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Controller {
而在@RequestMapping注解中不存在@Component声明,所以不会解析为Spring上下文管理的Bean
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Mapping
public @interface RequestMapping {
在SpringBoot源码中存在DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration
这个类,观察这个类
@Configuration
public class DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
发现该类是被@Configuration注解在Spring启动过程中引入到Spring容器管理。在该类继承了
WebMvcConfigurationSupport类。在该类中发现了一个被@Bean注解标注的方法。
@Bean
public RequestMappingHandlerMapping requestMappingHandlerMapping() {//。。。。省略}
而WebMvcAutoConfiguration这个配置类中也可以看到@Configuration注解。
//配置类声明
@Configuration
//当Spring为Servlet类型的web服务时,才使注解的类生效
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
//类加载器中存在Servlet, DispatcherServlet, WebMvcConfigurer三个类时
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class })
//Spring容器中不存在WebMvcConfigurationSupport这种类型的实例时
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class)
//用于确定配置加载的优先级顺序,Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE加载的优先级最高
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10)
//用在自动配置类上面,表示该自动配置类需要在另外指定的自动配置类配置完之后。即
//DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration、ValidationAutoConfiguration配置完后开始配置
@AutoConfigureAfter({ DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class,
ValidationAutoConfiguration.class })
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {
在该类中同样存在被@Bean声明的RequestMappingHandlerMapping类型的方法。
@Bean
@Primary
@Override
public RequestMappingHandlerMapping requestMappingHandlerMapping() {
// Must be @Primary for MvcUriComponentsBuilder to work
//实际调用的是WebMvcConfigurationSupport类中的requestMappingHandlerMapping方法
return super.requestMappingHandlerMapping();
}
但是WebMvcAutoConfiguration中存在@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10)注解,所以WebMvcAutoConfiguration比WebMvcConfigurationSupport中requestMappingHandlerMapping方法加载的优先级高。
Spring中@Bean注解用于告诉被声明的方法,产生一个Bean对象,然后这个Bean对象交给Spring容器管理。产生这个Bean对象的方法Spring只会调用一次,随后将会将这个Bean对象放入Spring的IOC容器中。
那么这个项目会返回一个类型为RequestMappingHandlerMapping,beanName为requestMappingHandlerMapping的Bean对象。该类的主要作用是将请求的url与对应方法之间的映射关系保存下来。
@Bean
public RequestMappingHandlerMapping requestMappingHandlerMapping() {
//初始化一个RequestMappingHandlerMapping类型的对象.
RequestMappingHandlerMapping mapping = createRequestMappingHandlerMapping();
mapping.setOrder(0);
//设置拦截器
mapping.setInterceptors(getInterceptors());
mapping.setContentNegotiationManager(mvcContentNegotiationManager());
mapping.setCorsConfigurations(getCorsConfigurations());
PathMatchConfigurer configurer = getPathMatchConfigurer();
Boolean useSuffixPatternMatch = configurer.isUseSuffixPatternMatch();
if (useSuffixPatternMatch != null) {
mapping.setUseSuffixPatternMatch(useSuffixPatternMatch);
}
Boolean useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch = configurer.isUseRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch();
if (useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch != null) {
mapping.setUseRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch(useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch);
}
Boolean useTrailingSlashMatch = configurer.isUseTrailingSlashMatch();
if (useTrailingSlashMatch != null) {
mapping.setUseTrailingSlashMatch(useTrailingSlashMatch);
}
UrlPathHelper pathHelper = configurer.getUrlPathHelper();
if (pathHelper != null) {
mapping.setUrlPathHelper(pathHelper);
}
PathMatcher pathMatcher = configurer.getPathMatcher();
if (pathMatcher != null) {
mapping.setPathMatcher(pathMatcher);
}
return mapping;
}
同RequestMappingHandlerMapping的注入优先级在WebMvcAutoConfiguration同时也注入了一个适配器RequestMappingHandlerAdapter
@Bean
@Override
public RequestMappingHandlerAdapter requestMappingHandlerAdapter() {
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter adapter = super.requestMappingHandlerAdapter();
adapter.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.mvcProperties == null
|| this.mvcProperties.isIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect());
return adapter;
}
@Bean
public RequestMappingHandlerAdapter requestMappingHandlerAdapter() {
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter adapter = createRequestMappingHandlerAdapter();
adapter.setContentNegotiationManager(mvcContentNegotiationManager());
adapter.setMessageConverters(getMessageConverters());
adapter.setWebBindingInitializer(getConfigurableWebBindingInitializer());
adapter.setCustomArgumentResolvers(getArgumentResolvers());
adapter.setCustomReturnValueHandlers(getReturnValueHandlers());
if (jackson2Present) {
adapter.setRequestBodyAdvice(Collections.singletonList(new JsonViewRequestBodyAdvice()));
adapter.setResponseBodyAdvice(Collections.singletonList(new JsonViewResponseBodyAdvice()));
}
AsyncSupportConfigurer configurer = new AsyncSupportConfigurer();
configureAsyncSupport(configurer);
if (configurer.getTaskExecutor() != null) {
adapter.setTaskExecutor(configurer.getTaskExecutor());
}
if (configurer.getTimeout() != null) {
adapter.setAsyncRequestTimeout(configurer.getTimeout());
}
adapter.setCallableInterceptors(configurer.getCallableInterceptors());
adapter.setDeferredResultInterceptors(configurer.getDeferredResultInterceptors());
return adapter;
}
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter类实现了InitializingBean接口,所以在初始化bean的时候会调用
类内部的afterPropertiesSet方法。在方法中调用了initControllerAdviceCache方法,
实现逻辑来看,它将容器中所有使用了注解@ControllerAdvice的bean或者其方法都分门别类做了统计,记录到了RequestMappingHandlerAdapter实例的三个属性中 :
-
requestResponseBodyAdvice
-
用于记录所有@ControllerAdvice + RequestBodyAdvice/ResponseBodyAdvice bean组件
-
modelAttributeAdviceCache
-
用于记录所有 @ControllerAdvice bean组件中的 @ModuleAttribute 方法
-
initBinderAdviceCache
-
用于记录所有@ControllerAdvice bean组件中的 @InitBinder 方法
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
// Do this first, it may add ResponseBody advice beans
initControllerAdviceCache();
if (this.argumentResolvers == null) {
List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> resolvers = getDefaultArgumentResolvers();
this.argumentResolvers = new HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite().addResolvers(resolvers);
}
if (this.initBinderArgumentResolvers == null) {
List<HandlerMethodArgumentResolver> resolvers = getDefaultInitBinderArgumentResolvers();
this.initBinderArgumentResolvers = new HandlerMethodArgumentResolverComposite().addResolvers(resolvers);
}
if (this.returnValueHandlers == null) {
List<HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler> handlers = getDefaultReturnValueHandlers();
this.returnValueHandlers = new HandlerMethodReturnValueHandlerComposite().addHandlers(handlers);
}
}
分析RequestMappingHandlerMapping的继承实现关系,其实现了InitializingBean接口,该接口中有一个待实现的方法afterPropertiesSet。当一个类实现这个接口并且该类是一个被Spring容器管理的Bean,Spring启动后,初始化Bean时,若该Bean实现InitialzingBean接口,会自动调用该Bean重写的afterPropertiesSet()方法。
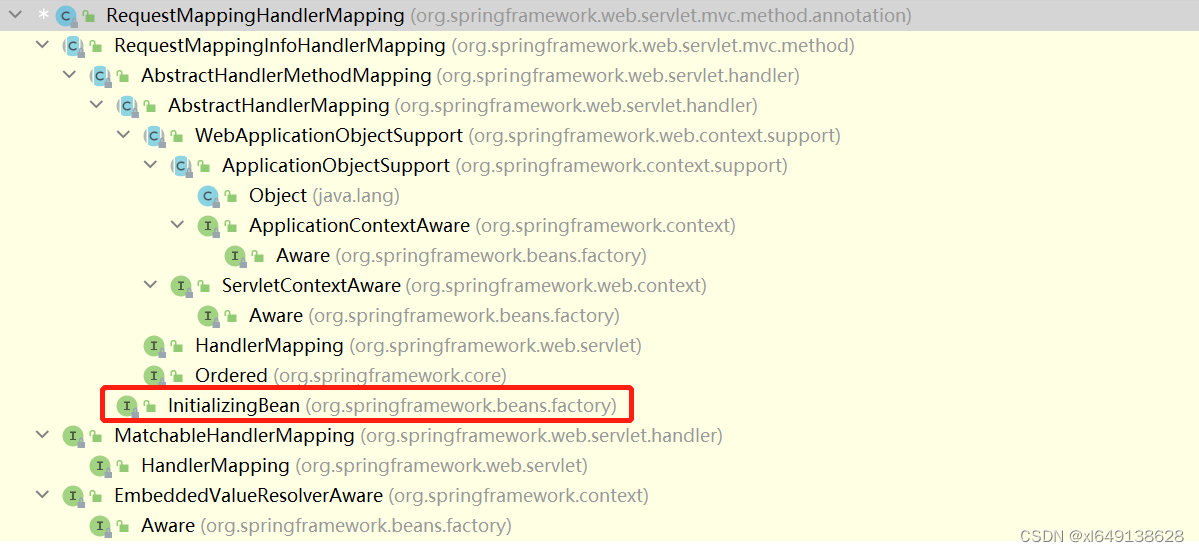
在RequestMappingHandlerMapping中重写的afterPropertiesSet方法如下:
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
//配置属性
this.config = new RequestMappingInfo.BuilderConfiguration();
this.config.setUrlPathHelper(getUrlPathHelper());
this.config.setPathMatcher(getPathMatcher());
this.config.setSuffixPatternMatch(this.useSuffixPatternMatch);
this.config.setTrailingSlashMatch(this.useTrailingSlashMatch);
this.config.setRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch(this.useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch);
this.config.setContentNegotiationManager(getContentNegotiationManager());
//调用父类AbstractHandlerMethodMapping中的afterPropertiesSet方法
super.afterPropertiesSet();
}
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping中的afterPropertiesSet方法如下
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
initHandlerMethods();
}
initHandlerMethods方法的具体实现如下:
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking for request mappings in application context: " + getApplicationContext());
}
//获取applicationContext上下文中中所有类型是Object的beanName
String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ?
BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(obtainApplicationContext(), Object.class) :
obtainApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class));
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
Class<?> beanType = null;
try {
beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not resolve target class for bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
//beanType不为空,并且beanType是 Controller或RequestMapping类型的
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
}
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
在上面的源码中我们分别分析重点关注以下几行代码
1.isHandler(beanType)//判断bean是否可以解析为符合条件的处理器
2.detectHandlerMethods(beanName)//查明处理方法
3.getHandlerMethods()//获取处理方法
分别分析这四个方法
方法一:isHandler(beanType)
方法作用:判断是否是Controller或者RequestMapping类型的,因为是判断Bean类型,被@Controller或者@RequestMapping声明的类只有,@Controller会被解析为Bean,所以此处过滤的是@Controller声明的类。
注:RestController注解被@Controller声明所以也可以判断是Controller类型的
protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) {
return (AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) ||
AnnotatedElementUtils.hasAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class));
}
方法二:detectHandlerMethods(beanName)
方法作用:查明处理方法
protected void detectHandlerMethods(final Object handler) {
//获取处理器的类类型
Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
if (handlerType != null) {
//如果是CGLIB增强的类,返回其被增强的类
final Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
Map<Method, T> methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T>) method -> {
try {
//返回RequestMappingInfo对象
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +
userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);
}
});
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(methods.size() + " request handler methods found on " + userType + ": " + methods);
}
methods.forEach((method, mapping) -> {
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(method, userType);
//将处理器注入到Map容器中
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
});
}
}
Introspector 是一个专门处理bean的工具类.用来获取Bean体系里的 propertiesDescriptor(属性描述符),methodDescriptor(方法描述符).
利用反射获取Method信息,是反射的上层.
性能优化: 只进行一次反射解析. 通过WeakReference静态类级别缓存Method, 在jvm不够时会被回收.
public static <T> Map<Method, T> selectMethods(Class<?> targetType, MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup<T> metadataLookup) {
Map<Method, T> methodMap = new LinkedHashMap();
Set<Class<?>> handlerTypes = new LinkedHashSet();
Class<?> specificHandlerType = null;
//非JDK动态代理类
if (!Proxy.isProxyClass(targetType)) {
//获取CGLIiB代理类被代理的类即代理类的父类
//(注意CGLIB实际上生成了一个继承被代理类的子类)
specificHandlerType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(targetType);
handlerTypes.add(specificHandlerType);
}
//获取targetType的所有接口包括接口的父接口
handlerTypes.addAll(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetType));
Iterator var5 = handlerTypes.iterator();
while(var5.hasNext()) {
Class<?> currentHandlerType = (Class)var5.next();
Class<?> targetClass = specificHandlerType != null ? specificHandlerType : currentHandlerType;
//获取currentHandlerType所有父类所有接口里的方法
ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(currentHandlerType, (method) -> {
//根据方法对象获取targetClass里具体的方法
Method specificMethod = ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, targetClass);
//result返回的是getMappingForMethod(method, userType)返回的
//RequestMappingInfo对象
T result = metadataLookup.inspect(specificMethod);
if (result != null) {
//获取过桥方法
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(specificMethod);
if (bridgedMethod == specificMethod || metadataLookup.inspect(bridgedMethod) == null) {
methodMap.put(specificMethod, result);
}
}
}, ReflectionUtils.USER_DECLARED_METHODS);
}
//返回Method类为key,value为RequestMappingInfo对象
return methodMap;
}
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) {
//获取方法上的RequestMapping注解
//(注意@PostMapping,@GetMapping都是RequestMapping声明的注解)
RequestMappingInfo info = createRequestMappingInfo(method);
if (info != null) {
//获取类@RequestMapping注解封装的RequestMappingInfo对象
RequestMappingInfo typeInfo = createRequestMappingInfo(handlerType);
if (typeInfo != null) {
//合并两个RequstMappingInfo 包括路径还有声明条件的合并等
//比如合并请求路径@RequestMapping("/home")
// @PostMapping("/hello")路径合并成/home/hello
info = typeInfo.combine(info);
}
}
return info;
}
获取使用@RequestMapping注解的RequestMapping对象并通过createRequestMappingInfo方法
封装成RequestMappingInfo对象
private RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(AnnotatedElement element) {
RequestMapping requestMapping = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(element, RequestMapping.class);
//返回null
RequestCondition<?> condition = (element instanceof Class ?
getCustomTypeCondition((Class<?>) element) : getCustomMethodCondition((Method) element));
return (requestMapping != null ? createRequestMappingInfo(requestMapping, condition) : null);
}
将Method对象生成的RequestMapping对象转换成RequestMappingInfo对象
protected RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(
RequestMapping requestMapping, @Nullable RequestCondition<?> customCondition) {
RequestMappingInfo.Builder builder = RequestMappingInfo
.paths(resolveEmbeddedValuesInPatterns(requestMapping.path()))
.methods(requestMapping.method())
.params(requestMapping.params())
.headers(requestMapping.headers())
.consumes(requestMapping.consumes())
.produces(requestMapping.produces())
.mappingName(requestMapping.name());
if (customCondition != null) {
builder.customCondition(customCondition);
}
return builder.options(this.config).build();
}
将HandlerMethod注册到AbstractHandlerMethodMapping类的mappingRegistry属性中
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) {
this.mappingRegistry.register(mapping, handler, method);
}
public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
//1.获取处理方法对象
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
//2.判断handlerMethod在mappingLookup容器中是否唯一,不唯一抛错
assertUniqueMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Mapped \"" + mapping + "\" onto " + handlerMethod);
}
this.mappingLookup.put(mapping, handlerMethod);
//访问url添加到集合中
List<String> directUrls = getDirectUrls(mapping);
for (String url : directUrls) {
this.urlLookup.add(url, mapping);
}
String name = null;
if (getNamingStrategy() != null) {
name = getNamingStrategy().getName(handlerMethod, mapping);
addMappingName(name, handlerMethod);
}
CorsConfiguration corsConfig = initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping);
if (corsConfig != null) {
this.corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig);
}
this.registry.put(mapping, new MappingRegistration<>(mapping, handlerMethod, directUrls, name));
}
finally {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
register方法 AbstractHandlerMethodMapping类中的
mappingLookup 类型是LinkedHashMap
urlLookup 类型为MultiValueMap
corsLookup 类型是ConcurrentHashMap类型
registry 类型是HashMap
四个属性进行赋值
protected HandlerMethod createHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method) {
//HandlerMethod对象是对handler和method的包装
HandlerMethod handlerMethod;
if (handler instanceof String) {
String beanName = (String) handler;
handlerMethod = new HandlerMethod(beanName,
obtainApplicationContext().getAutowireCapableBeanFactory(), method);
}
else {
//初始化并对bean和method属性赋值
handlerMethod = new HandlerMethod(handler, method);
}
return handlerMethod;
}
方法三:getHandlerMethods
描述:返回一个不可修改的包含HandlerMethod元素的Map集合。
总结:
本文主要的讲述了Spring容器对@Controller及@RequestMapping的解析过程。并在解析过程中将Spring容器里被@Controller及@RequestMapping声明类生成的bean对象封装成RequestMappingInfo对象。