这篇文章是基于我四年前的一篇文章进行更正和深入探究。背景是,2019年4月份我在找工作,看到一个问题,问this,getBaseContext()、getApplication()、getApplicationContext()的区别。当时我写了简单的demo验证,得出了跟网上答案一致的结论。但就在昨天,我发现,这个问题或许还有其他的答案。
这是四年前那篇文章:getBaseContext()、getApplication()、getApplicationContext()的区别_heart荼毒的博客-CSDN博客
目录
一、回顾之前的demo
二、一个偶然的发现
三、Context的继承关系
四、getBaseContext
1、Activity的attachBaseContext
2、AppCompactActivity的attachBaseContext
一、回顾之前的demo
首先,这是我当时测试用到的demo,很简单,就默认创建的项目,MainActivity继承Activity。我直接实现了如下代码:
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Log.d("TTTT", "this:" + this);
Log.d("TTTT", "getBaseContext():" + getBaseContext().toString());
Log.d("TTTT", "getApplication():" + getApplication().toString());
Log.d("TTTT", "getApplicationContext():" + getApplicationContext().toString());
}
}
运行后,打印的Log如下:

于是,我基于demo和打印的log信息得出了这样的结论:
- this获取到的是当前Activity的对象;
- getApplication和getApplicationContext获取到的均为同一个Application对象。
- getBaseContext()获取到的是ContextImpl。
到这里,在2019年那次验证中,就结束了,可以说是浅尝辄止。其实基于这三条结论,可能会有同学跟现在的我一样,存在诸多疑惑。比如说:getBaseContext获取到的ContextImpl是什么?
二、一个偶然的发现
我有一个习惯,我会时不时的review自己之前写过的一些文章,以防止因为当时的认知问题得出一些错误的结论。或者随着技术的更新迭代,一些结论有失偏颇。我会及时的去完善和更新之前的一些文章。也正是在看到那篇文章时,我突然发现一个问题,我当时的demo继承的是Activity,而不是时下流行的androidx中的AppCompactActivity。
于是,接下来,我把MainActivity改成继承自AppCompactActivity:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompactActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Log.d("TTTT", "this:" + this.toString());
Log.d("TTTT", "getBaseContext():" + this.getBaseContext().toString());
Log.d("TTTT", "getApplication():" + this.getApplication().toString());
Log.d("TTTT", "getApplicationContext():" + this.getApplicationContext().toString());
}
}
运行后,打印的log如下:
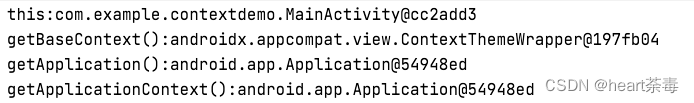
可以看到,前两个结论站得住脚。而getBaseContext()获取的结果变了,由之前的ContextImpl变成了ContextThemeWrapper。那么,带着前面的问题以及新发现的问题,我们一起去揭开Context的神秘面纱。
三、Context的继承关系
Context是一个抽象类,它有多个直接或间接的子类。首先,我们看下Context的继承关系:
Context
├── ContextImpl
├── ContextWrapper
│ ├── Application
│ ├── Service
│ ├── ContextThemeWrapper
│ │ ├── Activity
│ │ │ ├── ComponentActivity
│ │ │ └── ... └── FragmentActivity
│ │ └── ... └── AppCompatActivity
│ └── ...
└── ...
(1)ContextImpl
上面我们也提到,Context是一个抽象类,那么他需要有个实现类。ContextImpl是Context的实现类,真正实现了Context中的所有方法。我们调用的各种Context类的方法,其实现均来自于该类。(注:Android系统源码的很多设计,都遵循这样的规则:抽象类X一定对应一个XImpl的实现类)
(2)ContextWrapper
ContextWrapper是Context的包装类,可以包装另一个Context对象,并在其基础上添加新的功能。
(3)ContextThemeWrapper
ContextThemeWrapper是一个特殊的包装类,可以为应用程序的UI组件添加theme样式。从继承关系层级也可以看出来,Application和Service不需要UI样式。而Activity需要Theme,Activity就是直接继承自ContextThemeWrapper。
四、getBaseContext
首先,我们看下getBaseContext方法。上面我们也提到过,ContextWrapper是Context的包装类,因此点击该方法后,直接进入到ContextWrapper中的getBaseContext的实现中。

看下mBase在哪里被赋值的。

接下来,分别看下Activity和AppCompactActivity对attachBaseContext是如何重写的。
1、Activity的attachBaseContext
首先是Activity的attachBaseContext:
protected void attachBaseContext(Context newBase) {
super.attachBaseContext(newBase);
if (newBase != null) {
newBase.setAutofillClient(getAutofillClient());
newBase.setContentCaptureOptions(getContentCaptureOptions());
}
}
Activity的attachBaseContext的调用,是在Activity的attach方法调用的:
final void attach(Context context, ActivityThread aThread,
Instrumentation instr, IBinder token, int ident,
Application application, Intent intent, ActivityInfo info,
CharSequence title, Activity parent, String id,
NonConfigurationInstances lastNonConfigurationInstances,
Configuration config, String referrer, IVoiceInteractor voiceInteractor,
Window window, ActivityConfigCallback activityConfigCallback, IBinder assistToken,
IBinder shareableActivityToken) {
attachBaseContext(context);
......................
}
那Activity的attach方法是在哪里调用的?这就得从Activity的启动来说起,我们不在此去详细说,点击感兴趣可以自行百度。我直接抛出答案:在ActivityThread的performLaunchActivity方法去启动Activity。这个方法很长,感兴趣的自己看源码,我只截取关键代码:
/** Core implementation of activity launch. */
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
..............
ContextImpl appContext = createBaseContextForActivity(r);
Activity activity = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = appContext.getClassLoader();
activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(
cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
................
} catch (Exception e) {
......
}
try {
.................
activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token,
r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent,
r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config,
r.referrer, r.voiceInteractor, window, r.activityConfigCallback,
r.assistToken, r.shareableActivityToken);
.................
} catch (SuperNotCalledException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
......
}
return activity;
}
通过上面的代码可以清晰地看到,attach方法传给Activity的Context就是ContextImpl。
2、AppCompactActivity的attachBaseContext
接下来,一起看下AppCompactActivity的attachBaseContext方法:
protected void attachBaseContext(Context newBase) {
super.attachBaseContext(getDelegate().attachBaseContext2(newBase));
}
可以看到,调用了getDategate(),进而调用了AppCompactDelegate的attachBaseContext2方法,看下这个方法:
/**
* Should be called from {@link Activity#attachBaseContext(Context)}.
*/
@NonNull
@CallSuper
public Context attachBaseContext2(@NonNull Context context) {
attachBaseContext(context);
return context;
}
调用了自身的attachBaseContext方法,看下:
/**
* @deprecated use {@link #attachBaseContext2(Context)} instead.
*/
@Deprecated
public void attachBaseContext(Context context) {
}
可以看到,是一个@deprecated的空方法。其实AppCompatDelegate也是一个抽象类,按照Android的通常设计原则,必然有一个AppCompactImpl的实现类。我们直接看下实现类AppCompatDelegateImpl的attachBaseContext2方法,也是一个非常长的方法,仍然只保留关键代码:
@NonNull
@Override
@CallSuper
public Context attachBaseContext2(@NonNull final Context baseContext) {
....................
// If the base context is a ContextThemeWrapper (thus not an Application context)
// and nobody's touched its Resources yet, we can shortcut and directly apply our
// override configuration.
if (sCanApplyOverrideConfiguration
&& baseContext instanceof android.view.ContextThemeWrapper) {
final Configuration config = createOverrideAppConfiguration(
baseContext, modeToApply, localesToApply, null, false);
if (DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, String.format("Attempting to apply config to base context: %s",
config.toString()));
}
try {
AppCompatDelegateImpl.ContextThemeWrapperCompatApi17Impl.applyOverrideConfiguration(
(android.view.ContextThemeWrapper) baseContext, config);
return baseContext;
} catch (IllegalStateException e) {
if (DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, "Failed to apply configuration to base context", e);
}
}
}
// Again, but using the AppCompat version of ContextThemeWrapper.
if (baseContext instanceof ContextThemeWrapper) {
final Configuration config = createOverrideAppConfiguration(
baseContext, modeToApply, localesToApply, null, false);
if (DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, String.format("Attempting to apply config to base context: %s",
config.toString()));
}
try {
((ContextThemeWrapper) baseContext).applyOverrideConfiguration(config);
return baseContext;
} catch (IllegalStateException e) {
if (DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, "Failed to apply configuration to base context", e);
}
}
}
// We can't apply the configuration directly to the existing base context, so we need to
// wrap it. We can't create a new configuration context since the app may rely on method
// overrides or a specific theme -- neither of which are preserved when creating a
// configuration context. Instead, we'll make a best-effort at wrapping the context and
// rebasing the original theme.
if (!sCanReturnDifferentContext) {
return super.attachBaseContext2(baseContext);
}
...........
// Next, we'll wrap the base context to ensure any method overrides or themes are left
// intact. Since ThemeOverlay.AppCompat theme is empty, we'll get the base context's theme.
final ContextThemeWrapper wrappedContext = new ContextThemeWrapper(baseContext,
R.style.Theme_AppCompat_Empty);
.........
return super.attachBaseContext2(wrappedContext);
}
可以看到,有两段类似的代码分别instanceof不同版本的ContextThemeWrapper(android.view包和androidx包),最后的话,是把这个wrappedContext丢到了AppCompactDelegate的attachBaseContext2方法里。
最后,简单总结下。这篇文章是为了更正自己4年前的一篇文章所写,通过从Context的继承关系以及继承不同的Activity去实现demo,回答开篇提到的this,getBaseContext()、getApplication()、getApplicationContext()等的区别。尤其是对getBaseContext()在Activity和AppCompactActivity里返回的Context对象不同进行了深究。在最后的最后,也抛出一个小问题:那么FragmentActivity的getBaseContext是什么呢?