GitHub - jzplp/aoapc-UVA-Answer: 算法竞赛入门经典 例题和习题答案 刘汝佳 第二版
以三个点的当前位置作为状态,广度优先遍历,找到终点即为最短次数。
注意:
一次可以移动多个点,但是每个点只能移动一步。在同一次中,B可以移动到A离开前的位置上,即如果A走了,B可以去A之前的位置。因此,这三个点的移动和判断是有先后顺序的。对每个状态遍历时,情况实际上有 3的全排列(值为6),以及每个点移动的可能四种位置: 3! * 4^3。当然因为墙的存在,因此并没有这么多。
由于最高只有3,因此我的全排列写的不怎么优雅,直接嵌套循环完成了。注意每个点可以动,也可以不动,因此我们要考虑只有一个点动,两个点动的情况。写全排列时。如果第一个点动了大现已经遍历过,这时候不能放入队列(因为在其他点不动的情况下,这个状态已经遍历过了)。但是如果后面的点还继续动,那么这并不是一个完整的状态,因此不应该终止全排列。
按照上面的方法做的话,耗时很久,我扣了点细节,最后终于压线AC。(时间限制12000ms)
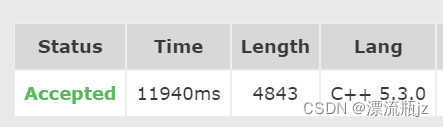
1. 根据题目描述,很多节点周围都是墙,因此用邻接表效率更高一些。
2. 一个点的坐标位置为1-16, x和y很容易放到一个数字中存储的。相对于每次计算x1 == x2 && y1 == y2, 一个数字的计算次数更少。其实三个结点的xy位置应该可以整合为一个数字的,这样效率会更高。
3. 我的答案中用到了struct,一些辅助的判断函数,使用引用而不是直接将整个对象值作为参数,性能会提高一些。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int graph[20][20];
vector<int> graphVec[300];
int w, h, n;
struct Point {
char ch;
int pos;
};
Point initPoints[3];
Point suppPoints[3];
struct Status {
int pos[3];
int step;
};
Status origin, terminal;
bool access[300][300][300];
int steps[4][2] = { {1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1} };
bool sameLetter(char small, char big) {
return small == big - 'A' + 'a';
}
bool statusEqual(Status &s1, Status &s2) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
if (s1.pos[i] != s2.pos[i]) return false;
}
return true;
}
int xy2Num(int x, int y) {
return x * 17 + y;
}
void num2XY(int num, int *x, int *y) {
*x = num / 17;
*y = num % 17;
}
bool judgeAcc(Status &s) {
if (n == 1) return access[s.pos[0]][0][0];
if (n == 2) return access[s.pos[0]][s.pos[1]][0];
if (n == 3) return access[s.pos[0]][s.pos[1]][s.pos[2]];
}
void setAcc(Status &s) {
if (n == 1) access[s.pos[0]][0][0] = true;
if (n == 2) access[s.pos[0]][s.pos[1]][0] = true;
if (n == 3) access[s.pos[0]][s.pos[1]][s.pos[2]] = true;
}
void printStatus(Status &s) {
int x, y;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
num2XY(s.pos[i], &x, &y);
printf("[%d %d] ", x, y);
}
printf(" %d\n", s.step);
}
void printGraphVec() {
int i, j, x, y;
for(i = 0; i < 300; ++i) {
if(graphVec[i].size()) {
num2XY(i, &x, &y);
printf("%d %d - ", x, y);
for(j = 0; j < graphVec[i].size(); ++j) {
num2XY(graphVec[i][j], &x, &y);
printf("[%d %d] ", x, y);
}
putchar('\n');
}
}
putchar('\n');
}
void init() {
int i, j, k, initLen = 0, suppLen = 0;
int x, y;
memset(access, 0, sizeof(access));
for(i = 0; i < 300; ++i) {
graphVec[i].clear();
}
for (i = 1; i <= h; ++i) {
while (getchar() != '\n') ;
for (j = 1; j <= w; ++j) {
graph[i][j] = getchar();
if (graph[i][j] >= 'a' && graph[i][j] <= 'z')
initPoints[initLen++] = {char(graph[i][j]), xy2Num(i, j)};
if (graph[i][j] >= 'A' && graph[i][j] <= 'Z')
suppPoints[suppLen++] = {char(graph[i][j]), xy2Num(i, j)};
}
}
for(i = 2; i < h; ++i) {
for (j = 2; j < w; ++j) {
if(graph[i][j] == '#') continue;
for(k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
x = i + steps[k][0];
y = j + steps[k][1];
if(graph[x][y] == '#') continue;
graphVec[xy2Num(i, j)].push_back(xy2Num(x, y));
}
}
}
// printGraphVec();
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
origin.pos[i] = initPoints[i].pos;
for (j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (sameLetter(initPoints[i].ch, suppPoints[j].ch)) {
terminal.pos[i] = suppPoints[j].pos;
break;
}
}
}
origin.step = 0;
terminal.step = 0;
setAcc(origin);
// printStatus(origin);
// printStatus(terminal);
}
bool judgePos(Status &s) {
int i, j;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (i == j) continue;
if (s.pos[i] == s.pos[j]) return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int compute() {
int i, j, k, a1, a2, a3;
int num1, num2, num3, len1, len2, len3;
queue<Status> qu;
Status s0, s1, s2, s3;
qu.push(origin);
while (!qu.empty()) {
s0 = qu.front();
qu.pop();
// putchar('\n');
// printStatus(s0);
s0.step++;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
num1 = s0.pos[i]; len1 = graphVec[num1].size();
for (a1 = 0; a1 < len1; ++a1) {
s1 = s0;
s1.pos[i] = graphVec[num1][a1];
if (!judgePos(s1)) continue;
if (!judgeAcc(s1)) {
// printStatus(s1);
setAcc(s1); qu.push(s1);
}
if (statusEqual(s1, terminal)) return s1.step;
for (j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
if (i == j) continue;
num2 = s1.pos[j]; len2 = graphVec[num2].size();
for (a2 = 0; a2 < len2; ++a2) {
s2 = s1;
s2.pos[j] = graphVec[num2][a2];
if (!judgePos(s2)) continue;
if (!judgeAcc(s2)) {
// printStatus(s2);
setAcc(s2); qu.push(s2);
}
if (statusEqual(s2, terminal)) return s2.step;
for (k = 0; k < n; ++k) {
if (k == i || k == j) continue;
num3 = s2.pos[k]; len3 = graphVec[num3].size();
for (a3 = 0; a3 < len3; ++a3) {
s3 = s2;
s3.pos[k] = graphVec[num3][a3];
if (!judgePos(s3)) continue;
if (!judgeAcc(s3)) {
// printStatus(s3);
setAcc(s3); qu.push(s3);
}
if (statusEqual(s3, terminal)) return s3.step;
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
int main() {
while (scanf("%d %d %d", &w, &h, &n) == 3 && w != 0) {
init();
printf("%d\n", compute());
}
return 0;
}