| import random from operator import itemgetter class Gene: """ This is a class to represent individual(Gene) in GA algorithom each object of this class have two attribute: data, size """ def __init__(self, **data): self.__dict__.update(data) self.size = len(data['data']) # length of gene class GA: """ This is a class of GA algorithm. """ def __init__(self, parameter): """ Initialize the pop of GA algorithom and evaluate the pop by computing its' fitness value. The data structure of pop is composed of several individuals which has the form like that: {'Gene':a object of class Gene, 'fitness': 1.02(for example)} Representation of Gene is a list: [b s0 u0 sita0 s1 u1 sita1 s2 u2 sita2] """ # parameter = [CXPB, MUTPB, NGEN, popsize, low, up] self.parameter = parameter low = self.parameter[4] up = self.parameter[5] self.bound = [] self.bound.append(low) self.bound.append(up) pop = [] for i in range(self.parameter[3]): geneinfo = [] for pos in range(len(low)): geneinfo.append(random.randint(self.bound[0][pos], self.bound[1][pos])) # initialise popluation fitness = self.evaluate(geneinfo) # evaluate each chromosome pop.append({'Gene': Gene(data=geneinfo), 'fitness': fitness}) # store the chromosome and its fitness self.pop = pop self.bestindividual = self.selectBest(self.pop) # store the best chromosome in the population def evaluate(self, geneinfo): """ fitness function """ x1 = geneinfo[0] x2 = geneinfo[1] x3 = geneinfo[2] x4 = geneinfo[3] y = x1**2 + x2**2 + x3**3 + x4**4 return y def selectBest(self, pop): """ select the best individual from pop """ s_inds = sorted(pop, key=itemgetter("fitness"), reverse=True) # from large to small, return a pop return s_inds[0] def selection(self, individuals, k): """ select some good individuals from pop, note that good individuals have greater probability to be choosen for example: a fitness list like that:[5, 4, 3, 2, 1], sum is 15, [-----|----|---|--|-] 012345|6789|101112|1314|15 we randomly choose a value in [0, 15], it belongs to first scale with greatest probability """ s_inds = sorted(individuals, key=itemgetter("fitness"), reverse=True) # sort the pop by the reference of fitness sum_fits = sum(ind['fitness'] for ind in individuals) # sum up the fitness of the whole pop chosen = [] for i in range(k): u = random.random() * sum_fits # randomly produce a num in the range of [0, sum_fits], as threshold sum_ = 0 for ind in s_inds: sum_ += ind['fitness'] # sum up the fitness if sum_ >= u: # when the sum of fitness is bigger than u, choose the one, which means u is in the range of # [sum(1,2,...,n-1),sum(1,2,...,n)] and is time to choose the one ,namely n-th individual in the pop chosen.append(ind) break # from small to large, due to list.pop() method get the last element chosen = sorted(chosen, key=itemgetter("fitness"), reverse=False) return chosen def crossoperate(self, offspring): """ cross operation here we use two points crossoperate for example: gene1: [5, 2, 4, 7], gene2: [3, 6, 9, 2], if pos1=1, pos2=2 5 | 2 | 4 7 3 | 6 | 9 2 = 3 | 2 | 9 2 5 | 6 | 4 7 """ dim = len(offspring[0]['Gene'].data) geninfo1 = offspring[0]['Gene'].data # Gene's data of first offspring chosen from the selected pop geninfo2 = offspring[1]['Gene'].data # Gene's data of second offspring chosen from the selected pop if dim == 1: pos1 = 1 pos2 = 1 else: pos1 = random.randrange(1, dim) # select a position in the range from 0 to dim-1, pos2 = random.randrange(1, dim) newoff1 = Gene(data=[]) # offspring1 produced by cross operation newoff2 = Gene(data=[]) # offspring2 produced by cross operation temp1 = [] temp2 = [] for i in range(dim): if min(pos1, pos2) <= i < max(pos1, pos2): temp2.append(geninfo2[i]) temp1.append(geninfo1[i]) else: temp2.append(geninfo1[i]) temp1.append(geninfo2[i]) newoff1.data = temp1 newoff2.data = temp2 return newoff1, newoff2 def mutation(self, crossoff, bound): """ mutation operation """ dim = len(crossoff.data) if dim == 1: pos = 0 else: pos = random.randrange(0, dim) # chose a position in crossoff to perform mutation. crossoff.data[pos] = random.randint(bound[0][pos], bound[1][pos]) return crossoff def GA_main(self): """ main frame work of GA """ popsize = self.parameter[3] print("Start of evolution") # Begin the evolution for g in range(NGEN): print("############### Generation {} ###############".format(g)) # Apply selection based on their converted fitness selectpop = self.selection(self.pop, popsize) nextoff = [] while len(nextoff) != popsize: # Apply crossover and mutation on the offspring # Select two individuals offspring = [selectpop.pop() for _ in range(2)] if random.random() < CXPB: # cross two individuals with probability CXPB crossoff1, crossoff2 = self.crossoperate(offspring) if random.random() < MUTPB: # mutate an individual with probability MUTPB muteoff1 = self.mutation(crossoff1, self.bound) muteoff2 = self.mutation(crossoff2, self.bound) fit_muteoff1 = self.evaluate(muteoff1.data) # Evaluate the individuals fit_muteoff2 = self.evaluate(muteoff2.data) # Evaluate the individua
| nextoff.append({'Gene': muteoff1, 'fitness': fit_muteoff1}) nextoff.append({'Gene': muteoff2, 'fitness': fit_muteoff2}) else: fit_crossoff1 = self.evaluate(crossoff1.data) # Evaluate the individuals fit_crossoff2 = self.evaluate(crossoff2.data) nextoff.append({'Gene': crossoff1, 'fitness': fit_crossoff1}) nextoff.append({'Gene': crossoff2, 'fitness': fit_crossoff2}) else: nextoff.extend(offspring) # The population is entirely replaced by the offspring self.pop = nextoff # Gather all the fitnesses in one list and print the stats fits = [ind['fitness'] for ind in self.pop] best_ind = self.selectBest(self.pop) if best_ind['fitness'] > self.bestindividual['fitness']: self.bestindividual = best_ind print("Best individual found is {}, {}".format(self.bestindividual['Gene'].data, self.bestindividual['fitness'])) print(" Max fitness of current pop: {}".format(max(fits))) 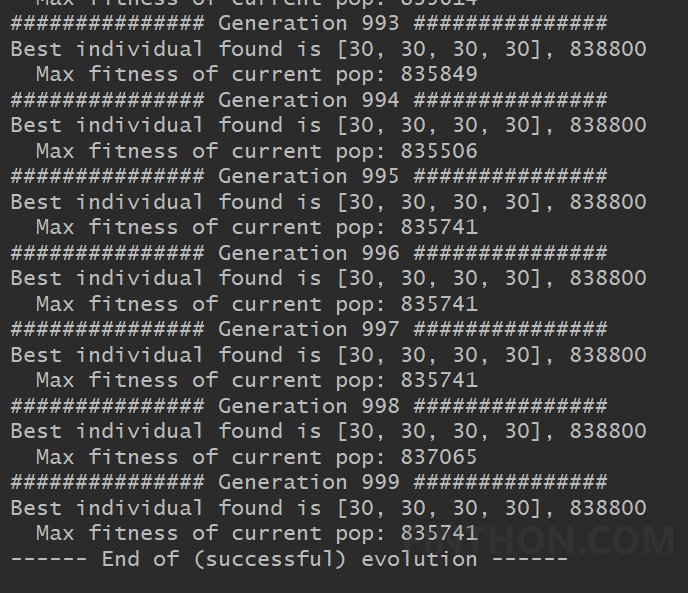
print("------ End of (successful) evolution ------") if __name__ == "__main__": CXPB, MUTPB, NGEN, popsize = 0.8, 0.1, 1000, 100 # popsize must be even number up = [30, 30, 30, 30] # upper range for variables low = [1, 1, 1, 1] # lower range for variables parameter = [CXPB, MUTPB, NGEN, popsize, low, up] run = GA(parameter) run.GA_main() |
在if __name__ == "__main__":语句后面,我们设定所有的参数。在这里交叉概率CXPB为0.8,变异概率MUTPB为0.1,总共跑NGEN=1000代,每代的种群大小为100。 得到结果如下: 事实上按照目前的参数,在第342代的时候已经找到最优解。如果使用枚举法需要30*30*30*30=810000次才能寻找到最优解,通过遗传算法只计算了34200次,大大缩短最优解的搜索空间。 参考:Python手把手构建遗传算法(GA)实现最优化搜索 - FINTHON |