大数加法
思路:
从后往前算(即由低位向高位运算),计算的结果依次添加到结果中去,最后将结果字符串反转。
输入的时候两个数都是以字符串的形式输入的,测出每个字符串的长度(也就是该数的位数),因为字符串不能直接进行运算,所以测出长度之后将字符串形的数反向转化为整形数组的形式(例如输入两个数为86369和22123,转化为整形数组形式储存为96368和32122,让低位在前,是运算更方便),然后进行运算。
要用到两个字符型数组来先保存输入的数,再定义3个整形数组,要将这三个数组中的元素开始的时候全部清零,其中两个来储存将字符型数转化过的整型数,再有一个就是来保存运算结果的数组。
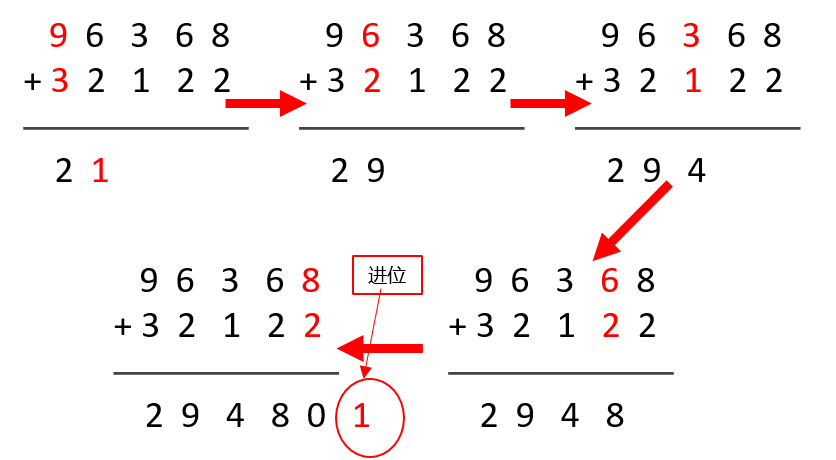
最后逆序输出结果108492
核心代码
for(i=lena-1;i>=0;i--)
c[lena-1-i]=a[i]-'0';
for(i=lenb-1;i>=0;i--)
d[lenb-1-i]=b[i]-'0';
k=0;
for(i=0;i<lenb||i<lena;i++)
{
h=c[i]+d[i]+k;
f[i]=h%10;
k=h/10;//进位
}
if(k)
f[i++]=k;
例题:HDU - 1002
A + B Problem II
Problem Description
I have a very simple problem for you. Given two integers A and B, your job is to calculate the Sum of A + B.
Input
The first line of the input contains an integer T(1<=T<=20) which means the number of test cases. Then T lines follow, each line consists of two positive integers, A and B. Notice that the integers are very large, that means you should not process them by using 32-bit integer. You may assume the length of each integer will not exceed 1000.
Output
For each test case, you should output two lines. The first line is “Case #:”, # means the number of the test case. The second line is the an equation “A + B = Sum”, Sum means the result of A + B. Note there are some spaces int the equation. Output a blank line between two test cases.
Sample Input
2
1 2
112233445566778899 998877665544332211
Sample Output
Case 1:
1 + 2 = 3
Case 2:
112233445566778899 + 998877665544332211 = 1111111111111111110
思路:使用数组模拟加法
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
char a[10000],b[10000];
char c[1000001];
int main()
{
int n=0,i=0;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%s %s",a,b);
printf("Case %d:\n%s + %s = ",i,a,b);
int len1,len2,j=0,k=0;
len1=strlen(a)-1; len2=strlen(b)-1;
for(j=0;len1>=0||len2>=0;j++,len1--,len2--)
{
if(len1>=0&&len2>=0)
c[j]=a[len1]+b[len2]-'0'+k;
if(len1>=0&&len2<0)
c[j]=a[len1]+k;
if(len1<0&&len2>=0)
c[j]=b[len2]+k;
k=0;
if(c[j]>'9')
{
c[j]=c[j]-10;
k=1;
}
}
if(k)
printf("1");
while(j--)
{
printf("%c",c[j]);
}
if(i<n)
printf("\n\n");
else
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
高精度加法
HDU - 1753
Problem Description
话说,经过了漫长的一个多月,小明已经成长了许多,所以他改了一个名字叫“大明”。
这时他已经不是那个只会做100以内加法的那个“小明”了,现在他甚至会任意长度的正小数的加法。
现在,给你两个正的小数A和B,你的任务是代表大明计算出A+B的值。
Input
本题目包含多组测试数据,请处理到文件结束。
每一组测试数据在一行里面包含两个长度不大于400的正小数A和B。
Output
请在一行里面输出输出A+B的值,请输出最简形式。详细要求请见Sample Output。
Sample Input
1.1 2.9
1.1111111111 2.3444323343
1 1.1
Sample Output
4
3.4555434454
2.1
思路:
找到小数点把整数部分和小数部分分开
先计算小数部分再计算整数部分(防止小数部分进位)
使用数组存储数,再逆序模拟加法
计算过程和大数加法一样(小数部分位数小的注意补0)
输出的时候注意判断小数点是否存在
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
char s1[500],s2[500];
int a[500],b[500],c[500],d[500];
int main(){
int i,j,k,len1,len2,s,t,kk1,kk2;
while(scanf("%s %s",s1,s2)!=EOF)
{
//别忘了初始化
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
memset(b,0,sizeof(b));
memset(c,0,sizeof(c));
memset(d,0,sizeof(d));
len1=strlen(s1);
len2=strlen(s2);
s=len1;
t=len2;
//找到小数点位置
for(i=0;i<len1;i++)
if(s1[i]=='.')
{
s=i;
break;
}
for(i=0;i<len2;i++)
if(s2[i]=='.')
{
t=i;break;
}
//小数部分 //先算小数部分防止有进位
k=1;
if(s+1<len1)
for(j=s+1;j<=len1-1;j++)
c[k++]=s1[j]-'0';
k=1;
if(t+1<len2)
for(j=t+1;j<=len2-1;j++)
d[k++]=s2[j]-'0';
kk1=len1-s;
if(len2-t>kk1)
kk1=len2-t;
for(i=kk1;i>=1;i--)
{
c[i]+=d[i];
if(c[i]>=10)
{
c[i]-=10;
c[i-1]++;
}
}
//整数部分
k=0;
for(j=s-1;j>=0;j--)
a[k++]=s1[j]-'0';
k=0;
for(j=t-1;j>=0;j--)
b[k++]=s2[j]-'0';
kk2=s-1;
if(t-1>kk2)
kk2=t-1;
a[0]+=c[0];//小数进位
for(i=0;i<=kk2;i++){
a[i]+=b[i];
if(a[i]>=10)
{
a[i]-=10;
a[i+1]++;
}
}
//输出整数部分
if(a[kk2+1])
printf("%d",a[kk2+1]);
for(i=kk2;i>=0;i--)
printf("%d",a[i]);
//输出小数部分
for(i=kk1;i>=1;i--)
if(c[i])
break;
if(i)//判断是否有小数
{
printf(".");
for(j=1;j<=i;j++)
printf("%d",c[j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
大数减法
基本思路和加法类似,进位变为借位,在运算之前需要判断正负,将大的数放在被减数上,因此,在需要的时候将被减数和减数调换一下位置。
首先,要判断减数和被减数哪一个位数长,减数位数长是正常减;被减数位数长,则被减数减减数,最后还要加上负号;两数位数长度相等时,最好比较一下哪一个数字大,否则负号处理会很繁琐,用大的减去小的,最后加上负号;
其次,处理每一项时要,如果前一位相减有借位,就先减去上一位的借位,无则不减;再去判断是否能够减开被减数,如果减不开,就要借位后再去减,同时置借位为1,否则置借位为0。
结果可能会出现前面是一堆0的情况,要处理好,如当减数为112,而被减数为111时,会出现001 ,这时,需要将前面的0删除。

输出时将0删除,并加上负号,即-9896
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int x[11000]={0},y[11000]={0},z[11050]={0};//将数组元素全部初始化为0
void sub(int x[],int y[],int len)
{
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<len;i++)
{
if(x[i]>=y[i])//如果x[i]>=y[i],不用向前一位借1,可直接减
z[i]=x[i]-y[i];
else //如果x[i]<y[i],向前一位借1,同时前一位应减1
{
z[i]=x[i]+10-y[i];
x[i+1]=x[i+1]-1;
}
}
for(i=len-1;i>0;i--)//删除前缀0
{
if(z[i])
break;
}
for(;i>=0;i--) //倒序输出数组
printf("%d",z[i]);
// printf("\n");
}
int main()
{
char a[100],b[100];//通过字符串对大数进行输入并储存
int len1,len2;
while(~scanf("%s %s",a,b))
{
memset(x,0,sizeof(x));
memset(y,0,sizeof(y));
memset(z,0,sizeof(z));
int i,j=0,k=0;
len1=strlen(a);
len2=strlen(b);
for(i=len1-1,j=0;i>=0;i--)//将两个字符串中的字符转化为数字,并倒序储存到数组中,即字符串为123456,则数组为654321
x[j++]=a[i]-'0';
for(i=len2-1,k=0;i>=0;i--)
y[k++]=b[i]-'0';
if(len1>len2) //若减数长度 > 被减数,正常减
sub(x,y,len1);
else
if(len1<len2) //若减数长度 < 被减数,被减数 减 减数
{
printf("-");
sub(y,x,len2);
}
else //若减数长度 == 被减数,判断两个数的大小
{ k=0;
for(i=len1-1;i>=0;i--)//判断每一位两个数的大小
{
if(x[i]==y[i])
{
k++;
continue;
}
if(x[i]>y[i])//即减数大
{
sub(x,y,len1);
break;
}
if(x[i]<y[i])//即被减数大
{
printf("-");
sub(y,x,len1);
break;
}
}
if(k==len1)
{
printf("0");
}
}
}
return 0;
}
大整数减法 OpenJ_Bailian - 2736
题目描述
求两个大的正整数相减的差。
Input
共2行,第1行是被减数a,第2行是减数b(a > b)。每个大整数不超过200位,不会有多余的前导零。
Output
一行,即所求的差。
Sample Input
9999999999999999999999999999999999999
9999999999999
Sample Output
9999999999999999999999990000000000000
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
char a[10001];
char b[10001];
int a1[10001];
int b1[10001];
int c[10001];
int main()
{
scanf("%s",&a);
scanf("%s",&b);
int la=strlen(a);
int lb=strlen(b);
if(lb>la||(la==lb&&strcmp(a,b)<0))
{
swap(a,b);
printf("-");
}
la=strlen(a);
lb=strlen(b);
for(int i=0;i<la;i++)
{
a1[i]=a[la-i-1]-'0';
}
for(int i=0;i<lb;i++)
{
b1[i]=b[lb-i-1]-'0';
}
int i=0;//当前位数
while(i<la)
{
if(a1[i]-b1[i]<0)
{
a1[i]=a1[i]+10;
a1[i+1]--;
}
c[i]=a1[i]-b1[i];
i++;
}
while(1)
{
if(c[i]==0&&i>=1)
i--;
else break;
}
for(int j=i;j>=0;j--)
printf("%d",c[j]);
return 0;
}
大数乘法
第一个数据的第i位与第二个数据的第j位相乘存放在结果的第[i+j]个元素中,因为结果的每一位不是顺序得出,所以不方便用字符串存储,转而用数组存储。另一方面,第一步不考虑进位的问题,先将相乘的结果保存在数组中,然后对数组中的元素需要进位的按进位规则处理。
即一个数的第i 位和另一个数的第j 位相乘所得的数,一定是要累加到结果的第i+j 位上。这里i, j 都是从右往左,从0 开始数。
c[i+j] = a[i]*b[j];
注意进位时要处理,当前的值加上进位的值再看本位数字是否又有进位;前导清零
例:22123*83
逆序输出得到结果1836209
POJ - 2389
Description
Bulls are so much better at math than the cows. They can multiply huge integers together and get perfectly precise answers … or so they say. Farmer John wonders if their answers are correct. Help him check the bulls’ answers. Read in two positive integers (no more than 40 digits each) and compute their product. Output it as a normal number (with no extra leading zeros).
FJ asks that you do this yourself; don’t use a special library function for the multiplication.
Input
11111111111111
1111111111
Sample Output
12345679011110987654321
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<string.h>
int main()
{
char a[1000],b[1000],i,j,k;
int c[10000],x[1000],y[1000];
memset(c,0,sizeof(c));
scanf("%s %s",a,b);
int len1=strlen(a);//a位数
int len2=strlen(b);//b位数
for(i=len1-1,j=0;i>=0;i--)//将字符串中各个元素倒序储存在数组中
{
x[j++]=a[i]-'0';
}
for(i=len2-1,k=0;i>=0;i--)
{
y[k++]=b[i]-'0';
}
for(i=0;i<len2;i++)
{
k=i;
for(j=0;j<len1;j++)
{
if(c[k]!=0)
{
c[k]+=y[i]*x[j];
}
else
c[k]=y[i]*x[j];
k++;
}
}
for(i=0;i<=k;i++)
{
if(c[i]>=10)
{
c[i+1]+=c[i]/10;
c[i]=c[i]%10;
}
}
for(i=k;i>=0;i--)
{
if(c[i])
break;
}
for(;i>=0;i--)
printf("%d",c[i]);
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
大数乘法(幂运算)
POJ - 3199
Description
Dear Uncle Jack is willing to give away some of his collectable CDs to his nephews. Among the titles you can find very rare albums of Hard Rock, Classical Music, Reggae and much more; each title is considered to be unique. Last week he was listening to one of his favorite songs, Nobody’s fool, and realized that it would be prudent to be aware of the many ways he can give away the CDs among some of his nephews.
So far he has not made up his mind about the total amount of CDs and the number of nephews. Indeed, a given nephew may receive no CDs at all.
Please help dear Uncle Jack, given the total number of CDs and the number of nephews, to calculate the number of different ways to distribute the CDs among the nephews.
Input
The input consists of several test cases. Each test case is given in a single line of the input by, space separated, integers N (1 ≤ N ≤ 10) and D (0 ≤ D ≤ 25), corresponding to the number of nephews and the number of CDs respectively. The end of the test cases is indicated with N = D = 0.
Output
The output consists of several lines, one per test case, following the order given by the input. Each line has the number of all possible ways to distribute D CDs among N nephews.
Sample Input
1 20
3 10
0 0
Sample Output
1
59049
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
#include<string.h>
int main()
{
int n,m,i,j;
int f[3000];
while(scanf("%d %d",&n,&m),n||m)
{
memset(f,0,sizeof(f));
int k=m+2;
if(n==1)
{
printf("1\n");
continue;
}
if(n==10)
{
printf("1");
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
printf("0");
printf("\n");
continue;
}
int sum;
f[0]=1;
for(i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
int c=0;
for(j=0;j<k;j++)
{
sum=f[j]*n+c;
f[j]=sum%10;
c=sum/10;
}
}
for(j=k-1;j>=0;j--)
if(f[j])
break;
for(i=j;i>=0;i--)
{
printf("%d",f[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
大数乘法(高精度幂运算)
以下两个例题都是高精度幂运算(使用模板都可以AC)
POJ - 1001
Description
Problems involving the computation of exact values of very large magnitude and precision are common. For example, the computation of the national debt is a taxing experience for many computer systems.
This problem requires that you write a program to compute the exact value of Rn where R is a real number ( 0.0 < R < 99.999 ) and n is an integer such that 0 < n <= 25.
Input
The input will consist of a set of pairs of values for R and n. The R value will occupy columns 1 through 6, and the n value will be in columns 8 and 9.
Output
The output will consist of one line for each line of input giving the exact value of R^n. Leading zeros should be suppressed in the output. Insignificant trailing zeros must not be printed. Don’t print the decimal point if the result is an integer.
Sample Input
95.123 12
0.4321 20
5.1234 15
6.7592 9
98.999 10
1.0100 12
Sample Output
548815620517731830194541.899025343415715973535967221869852721
.00000005148554641076956121994511276767154838481760200726351203835429763013462401
43992025569.928573701266488041146654993318703707511666295476720493953024
29448126.764121021618164430206909037173276672
90429072743629540498.107596019456651774561044010001
1.126825030131969720661201
浮点数求高精度幂 OpenJ_Bailian - 2951
有一个实数 R ( 0.0 < R < 99.999 ) ,要求写程序精确计算 R 的 n 次方。n 是整数并且 0 < n <= 25。
Input
T输入包括多组 R 和 n。 R 的值占第 1 到 第 6 列, n 的值占第 8 和第 9 列。
Output
对于每组输入,要求输出一行,该行包含精确的 R 的 n 次方。输出需要去掉前导的 0 后后面不不要的 0 。如果输出是整数,不要输出小数点。
Sample Input
95.123 12
0.4321 20
5.1234 15
6.7592 9
98.999 10
1.0100 12
Sample Output
548815620517731830194541.899025343415715973535967221869852721
.00000005148554641076956121994511276767154838481760200726351203835429763013462401
43992025569.928573701266488041146654993318703707511666295476720493953024
29448126.764121021618164430206909037173276672
90429072743629540498.107596019456651774561044010001
1.126825030131969720661201
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
char c[1000];
void kk(char a[],char b[])
{
int i,j,num,k1;
int k[1000];
memset(k,0,sizeof(k));
int len=strlen(a);
int len1=strlen(b);
for(i=len-1; i>=0; i--)
{
for(j=len1-1,k1=len-1-i;j>=0; j--,k1++)
{
num=(a[i]-'0')*(b[j]-'0')+k[k1];
k[k1]=num%10;
k[k1+1]+=num/10;
}
}
for(i=k1;i>=0; i--)
{
if(k[i])
break;
}
for(j=0;i>=0; i--)
c[j++]=k[i]+'0';
}
int main()
{
char a[51];
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
int n,i,k,num,flag;
while(scanf("%s%d",a,&n)!=EOF)
{
int kkn=n;
int k1=0;
int numk=0;
int len=strlen(a);
memset(c,0,sizeof(c));
int sum=0;
int fort=0;
for(i=0,num=0; i<len; i++)
{
if(a[i]=='.')
{
k=len-1-i;
for(;i<len;i++)
a[i]=a[i+1];
num=k*n;
numk=num;
break;
}
else
{
fort=1;
k1=i;
}
}
if(fort)
{
for(;a[k1]=='0';k1--)
sum++;
}
for(i=0; i<len; i++)
if(a[i]!='0')
break;
for(k=0; i<=len; i++)
a[k++]=a[i];
strcpy(c,a);
n--;
while(n--)
{
kk(c,a);
}
int len1=strlen(c);
if(num<=len1)
{
for(i=len1-1; i>=0; i--)
if(c[i]!='0'&&c[i]!='.')
{
flag=i;
break;
}
for(i=0; i<len1; i++)
{
printf("%c",c[i]);
if(i==len1-num-1)
{
if(i==flag)
break;
printf(".");fort=0;
}
if(flag==i)
break;
}
num++;
}
else
{
for(i=len1-1; i>=0; i--)
if(c[i]!='0')
{
c[i+1]='\0';
break;
}
printf(".");fort=0;
for(i=len1; i<num; i++)
{
printf("0");
}
printf("%s",c);
}
if(fort)
{
int sum1=sum*kkn;
while(sum1--)
printf("0");
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
大数除法
基本思想是反复做除法,看从被除数里面最多能减去多少个除数,商就是多少。逐个减显然太慢,要判断一次最多能减少多少个整数(除数)的10的n次方。
以7546除以23为例:
先用7546减去23的100倍,即减去2300,可以减3次,余下646,此时商就是300 (300=100*3);
然后646减去23的10倍,即减去230,可以减2次,余下186,此时商就是320 (320=300+10*2);
然后186减去23,可以减8次,余下2,此时商就是328 (328=320+1*8);
因为2除以23的结果小于1,而我们又不用计算小数点位,所以不必再继续算下去了。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
char a[100],b[100];//用两个字符串用来输入两个大数
int x[100],y[100],z[100],m[100];//被除数 除数 商 余数
int digit;//大数的位数
void sub(int x[],int y[],int len1,int len2)//大数减法
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<len1;i++)
{
if(x[i]<y[i])
{
x[i]=x[i]+10-y[i];
x[i+1]--;
}
else
x[i]=x[i]-y[i];
}
for(i=len1-1;i>=0;i--)//判断减法结束之后,被除数的位数
{
if(x[i])
{
digit=i+1;
break;
}
}
}
int judge(int x[],int y[],int len1,int len2)
{
int i;
if(len1<len2)
return -1;
if(len1==len2)//若两个数位数相等
{
for(i=len1-1;i>=0;i--)
{
if(x[i]==y[i])//对应位的数相等
continue;
if(x[i]>y[i])//被除数 大于 除数,返回值为1
return 1;
if(x[i]<y[i])//被除数 小于 除数,返回值为-1
return -1;
}
return 0;//被除数 等于 除数,返回值为0
}
}
int main()
{
int i,j=0,k=0,temp;
int len1,len2,len;//len两个大数位数的差值
while(~scanf("%s %s",a,b))
{
len1=strlen(a);//被除数位数
len2=strlen(b);//除数位数
for(i=len1-1,j=0;i>=0;i--)//将字符串中各个元素倒序储存在数组中
x[j++]=a[i]-'0';
for(i=len2-1,k=0;i>=0;i--)
y[k++]=b[i]-'0';
if(len1<len2)//当被除数位数 小于 除数位数时
{
printf("商是:0\n");
printf("余数是:");
puts(a);
}
else //当被除数位数 大于或者 除数位数时
{
len=len1-len2;//两个大数位数的差值
for(i=len1-1;i>=0;i--)//将除数后补零,使得两个大数位数相同。被除数:4541543329 除数:98745,加零后:9874500000
{
if(i>=len)
y[i]=y[i-len];
else
y[i]=0;
}
len2=len1;//将两个大数数位相同
digit=len1; //将原被除数位数赋值给digit
for(j=0;j<=len;j++)
{
z[len-j]=0;
while(((temp=judge(x,y,len1,len2))>=0)&&digit>=k)//判断两个数之间的关系以及位数与除数原位数的关系
{
sub(x,y,len1,len2); //大数减法函数
z[len-j]++;//储存商的每一位
len1=digit;//重新修改被除数的长度
if(len1<len2&&y[len2-1]==0)
len2=len1;//将len1长度赋给len2;
}
if(temp<0)//若被除数 小于 除数,除数减小一位。例如:被除数:4541543329 除数:(原)98745,(加零后)9874500000,后退一位后:0987450000
{
for(i=1;i<len2;i++)
y[i-1]=y[i];
y[i-1]=0;
if(len1<len2)
len2--;
}
}
printf("商是:");
for(i=len;i>0;i--)//去掉前缀0
{
if(z[i])
break;
}
for(;i>=0;i--)
printf("%d",z[i]);
printf("\n");
printf("余数是:");
for(i=len1;i>0;i--)
{
if(x[i])
break;
}
for(;i>=0;i--)
printf("%d",x[i]);
printf("\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
大整数除法 OpenJ_Bailian - 2737
求两个大的正整数相除的商。
Input
第1行是被除数,第2行是除数。每个数均不超过100位。
Output
一行,相应的商的整数部分
Sample Input
2376
24
Sample Output
99
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int dividend[100],divisor[100],quotient[100],len1,len2;
char line1[101],line2[101];
/***************************************************
长度为lenn1的大整数p1减去长度为lenn2的大整数p2
减得结果放在p1里返回值代表结果的长度,不够减返回-1,正好剪完返回0
****************************************************/
int substract(int* p1,int* p2,int lenn1,int lenn2)
{
int i;
if(lenn1 < lenn2) return -1;
if(lenn1 == lenn2)
for(i = lenn1-1;i>=0;i--)
{
if(p1[i] > p2[i])
break;
else if(p1[i] < p2[i]) return -1;
else continue;
}
for(i = 0;i < lenn1;i++)
{
p1[i] -= p2[i];
if(p1[i] < 0)
{
p1[i] += 10;
p1[i+1]--;
}
}
for(i = lenn1-1;i >= 0;i--)
if(p1[i]) break;
return i+1;
}
int main()
{
int i,j;
gets(line1);
gets(line2);
len1 = strlen(line1);
len2 = strlen(line2);
for(i = len1-1,j = 0;i >= 0;i--,j++)
dividend[j] = line1[i] - '0';
for(i = len2-1,j = 0;i >= 0;i--,j++)
divisor[j] = line2[i] - '0';
len1 = substract(dividend,divisor,len1,len2);
if(len1 == -1)
{
printf("0");
return 0;
}
if(len1 == 0)
{
printf("1");
return 0;
}
quotient[0]++;
int times = len1 - len2;
for(i = len1-1;i >= 0;i--)
{
if(i >= times)
divisor[i] = divisor[i - times];
else
divisor[i] = 0;
}
len2 = len1;
for(j = 0;j <= times;j++)
{
int tmp;
while((tmp = substract(dividend,divisor+j,len1,len2-j)) >= 0)
{
len1 = tmp;
quotient[times-j]++;
}
}
for(i = 0;i < 99;i++)
if(quotient[i] >= 10)
{
quotient[i+1] += quotient[i]/10;
quotient[i] %= 10;
}
i = 99;
while(!quotient[i] && i >=0) i--;
if(i == -1)
printf("0");
else
while(i >= 0)
printf("%d",quotient[i--]);
return 0;
}