RGB、YUV和YCbCr
自己复现的网络跑出来的模型进行预测的时候,不知道为啥算出来的结果比论文中要低好多。不论scale factor为多少,我算出来的结果均普遍低于论文中给出的,PSNR大概低个1-2,其他指标正常,后来细读论文,查阅资料,看了一下别人写的网络,发现论文中这个指标是计算的YCbCr彩色空间下的PSNR,所以计算出的结果会有差异。

RGB
RGB(红绿蓝)是依据人眼识别的颜色定义出的空间,可表示大部分颜色。但在科学研究一般不采用RGB颜色空间,因为它的细节难以进行数字化的调整。它将色调,亮度,饱和度三个量放在一起表示,很难分开。它是最通用的面向硬件的彩色模型。该模型用于彩色监视器和一大类彩色视频摄像。还可能见到BGR,它就是把颜色通道换了个位置。
YUV
YUV是北美NTSC系统和欧洲PAL系统中模拟电视信号编码的基础。YUV,电视机的神,哈哈。
在 YUV 空间中,每一个颜色有一个亮度信号 Y,和两个色度信号 U 和 V。亮度信号是强度的感觉,它和色度信号断开,这样的话强度就可以在不影响颜色的情况下改变。YUV 使用RGB的信息,但它从全彩色图像中产生一个黑白图像,然后提取出三个主要的颜色变成两个额外的信号来描述颜色。把这三个信号组合回来就可以产生一个全彩色图像。Y 通道描述 Luma 信号,它与亮度信号有一点点不同,值的范围介于亮和暗之间。 Luma 是黑白电视可以看到的信号。U (Cb) 和 V (Cr) 通道从红 (U) 和蓝 (V) 中提取亮度值来减少颜色信息量。这些值可以从新组合来决定红,绿和蓝的混合信号。
YCbCr
YCbCr 颜色空间是YUV的国际标准化变种,在数字电视和图像压缩(比如JPEG)方面都有应用。YCbCr 是在世界数字组织视频标准研制过程中作为ITU - R BT1601 建议的一部分, 其实是YUV经过缩放和偏移的翻版。其中Y与YUV 中的Y含义一致, Cb , Cr 同样都指色彩, 只是在表示方法上不同而已。在YUV 家族中, YCbCr 是在计算机系统中应用最多的成员, 其应用领域很广泛,JPEG、MPEG均采用此格式。一般人们所讲的YUV大多是指YCbCr。
如何转换
一件非常幸运的事情,OpenCV提供了它们之间互相转换的函数,举个例子:
先读取图片:
t1 = cv2.imread('data/Set5/baby.png')
如果图片是RGB的,想要转为YCbCr,就通过以下方式:
t1 = cv2.cvtColor(t1, cv2.COLOR_RGB2YCrCb)
除此之外,它们之间可以任意进行转换,甚至还有BGR这种,COLOR_BGR2YCrCb就是BGR转YCbCr,也有COLOR_YUV2BGR是YUV转BGR,COLOR_YCrCb2RGB是YCbCr转RGB,可以根据自己需求进行转换。
也可以用公式进行转换,如RGB与YCbCr互转:
def convert_rgb_to_ycbcr(img, dim_order='hwc'):
if dim_order == 'hwc':
y = 16. + (64.738 * img[..., 0] + 129.057 * img[..., 1] + 25.064 * img[..., 2]) / 256.
cb = 128. + (-37.945 * img[..., 0] - 74.494 * img[..., 1] + 112.439 * img[..., 2]) / 256.
cr = 128. + (112.439 * img[..., 0] - 94.154 * img[..., 1] - 18.285 * img[..., 2]) / 256.
else:
y = 16. + (64.738 * img[0] + 129.057 * img[1] + 25.064 * img[2]) / 256.
cb = 128. + (-37.945 * img[0] - 74.494 * img[1] + 112.439 * img[2]) / 256.
cr = 128. + (112.439 * img[0] - 94.154 * img[1] - 18.285 * img[2]) / 256.
return np.array([y, cb, cr]).transpose([1, 2, 0])
def convert_ycbcr_to_rgb(img, dim_order='hwc'):
if dim_order == 'hwc':
r = 298.082 * img[..., 0] / 256. + 408.583 * img[..., 2] / 256. - 222.921
g = 298.082 * img[..., 0] / 256. - 100.291 * img[..., 1] / 256. - 208.120 * img[..., 2] / 256. + 135.576
b = 298.082 * img[..., 0] / 256. + 516.412 * img[..., 1] / 256. - 276.836
else:
r = 298.082 * img[0] / 256. + 408.583 * img[2] / 256. - 222.921
g = 298.082 * img[0] / 256. - 100.291 * img[1] / 256. - 208.120 * img[2] / 256. + 135.576
b = 298.082 * img[0] / 256. + 516.412 * img[1] / 256. - 276.836
return np.array([r, g, b]).transpose([1, 2, 0])
PSNR与SSIM计算
公式原理等等可以参考图像质量评价指标之 PSNR 和 SSIM - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
PSNR

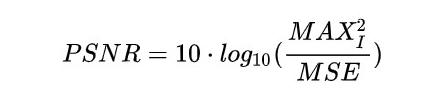
SSIM

公式法
PSNR
def psnr1(img1, img2):
mse = np.mean((img1/1.0 - img2/1.0) ** 2)
if mse < 1.0e-10:
return 100
return 10 * math.log10(255.0 ** 2 / mse)
def psnr2(img1, img2):
mse = np.mean((img1 / 255. - img2 / 255.) ** 2)
if mse < 1.0e-10:
return 100
PIXEL_MAX = 1
return 20 * math.log10(PIXEL_MAX / math.sqrt(mse))
使用 :
t1 = cv2.imread('data/Set5/baby.png')
t2 = cv2.imread('data/Set5/baby_fsrcnn_x4.png')
print(psnr1(t1,t2))
print(psnr2(t1,t2))
在Pytorch中也可以用公式来计算
def calc_psnr(img1, img2):
return 10. * torch.log10(1. / torch.mean((img1 - img2) ** 2))
SSIM这玩意用公式计算太麻烦了,我放弃。
TensorFlow计算
TensorFlow计算PSNR
tf.image.psnr(img1, img2, max_val=255)
TensorFlow计算SSIM
tf.image.ssim(img1, img2, max_val=255)
skimage法
skimage也提供了计算psnr和ssim的函数,如果要安装,就
pip install scikit-image
skimage计算PSNR
skimage.measure.compare_psnr(img1, img2, data_range=255)
skimage计算SSIM
skimage.measure.compare_ssim(img1, img2, data_range=255)
有警告就这么写:
skimage.measure.compare_ssim(t1, t2, data_range=255, multichannel=True)
综合写法
用于循环遍历SR与HR文件路径下的所有图片,计算平均,最大,最小的PSNR,SSIM
将main.py和utils.py放在同级目录下,也可以随便放,改一下main.py的导包路径就行
main.py
import math
from utils import utils_image as util
import os
import cv2
# HR_path = '/home/wanbo/E1_MSRN/src/SSIM/HR/'
# SR_path = '/home/wanbo/E1_MSRN/src/SSIM/SR/'
# HR_path = '/home/wanbo/E1_MSRN/src/SSIM/Set5/'
# SR_path = '/home/wanbo/E1_MSRN/src/SSIM/Set55/'
HR_path = '/home/wanbo/E1_MSRN/src/SSIM/urban/'
SR_path = '/home/wanbo/E1_MSRN/src/SSIM/UrbanS/'
n_channels = 3
def evulate_diff_name():
hr_paths = util.get_image_paths(HR_path)
sr_paths = util.get_image_paths(SR_path)
numbers = len(hr_paths)
sum_psnr = 0
max_psnr = 0
min_psnr = 100
sum_ssim = 0
max_ssim = 0
min_ssim = 1
for hr_path, sr_path in zip(hr_paths, sr_paths):
# name, ext = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(hr_path))
# img_name = os.path.basename(hr_path)
# print(img_name)
# temp = str(name) + '_x4_SR.png'
# # print(temp)
# sr_path = os.path.join(SR_path, temp)
# print(sr_path)
print(hr_path)
img_Hr = util.imread_uint(hr_path, n_channels=n_channels) # HR image, int8
img_Sr = util.imread_uint(sr_path, n_channels=n_channels) # HR image, int8
# img_Hr = cv2.imread(hr_path)
# img_Sr = cv2.imread(sr_path)
psnr = util.calculate_psnr(img_Sr, img_Hr,)
# psnr2 = calc_psnr(img_Sr, img_Hr, 4, 255)
print(psnr)
# print(psnr2)
sum_psnr += psnr
max_psnr = max(max_psnr,psnr)
min_psnr = min(min_psnr, psnr)
ssim = util.calculate_ssim(img_Sr, img_Hr,)
# print(ssim)
sum_ssim += ssim
max_ssim = max(max_ssim,ssim)
min_ssim = min(min_ssim, ssim)
print('Average psnr = ', sum_psnr / numbers)
print('min_psnr = ', min_psnr)
print('Max_psnr = ', max_psnr)
print('Average ssim = ', sum_ssim / numbers)
print('min_ssim = ', min_ssim)
print('Max_ssim = ', max_ssim)
if __name__ == '__main__':
print('-------------------------compute psnr and ssim for evulate sr model---------------------------------')
evulate_diff_name()
utils.py
import os
import math
import random
import numpy as np
import torch
import cv2
from torchvision.utils import make_grid
from datetime import datetime
# import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
'''
modified by Kai Zhang (github: https://github.com/cszn)
03/03/2019
https://github.com/twhui/SRGAN-pyTorch
https://github.com/xinntao/BasicSR
'''
IMG_EXTENSIONS = ['.jpg', '.JPG', '.jpeg', '.JPEG', '.png', '.PNG', '.ppm', '.PPM', '.bmp', '.BMP']
def is_image_file(filename):
return any(filename.endswith(extension) for extension in IMG_EXTENSIONS)
def get_timestamp():
return datetime.now().strftime('%y%m%d-%H%M%S')
def imshow(x, title=None, cbar=False, figsize=None):
plt.figure(figsize=figsize)
plt.imshow(np.squeeze(x), interpolation='nearest', cmap='gray')
if title:
plt.title(title)
if cbar:
plt.colorbar()
plt.show()
def surf(Z):
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
fig = plt.figure()
ax = Axes3D(fig)
X = np.arange(0, 25, 1)
Y = np.arange(0, 25, 1)
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap='rainbow')
# ax3.contour(X, Y, Z, zdim='z', offset=-2, cmap='rainbow)
# ax.view_init(elev=45, azim=45)
# ax.set_xlabel("x")
# plt.title(" ")
plt.tight_layout(0.9)
plt.show()
'''
# =======================================
# get image pathes of files
# =======================================
'''
def get_image_paths(dataroot):
paths = None # return None if dataroot is None
if dataroot is not None:
paths = sorted(_get_paths_from_images(dataroot))
return paths
def _get_paths_from_images(path):
assert os.path.isdir(path), '{:s} is not a valid directory'.format(path)
images = []
for dirpath, _, fnames in sorted(os.walk(path)):
for fname in sorted(fnames):
if is_image_file(fname):
img_path = os.path.join(dirpath, fname)
images.append(img_path)
assert images, '{:s} has no valid image file'.format(path)
return images
'''
# =======================================
# makedir
# =======================================
'''
def mkdir(path):
if not os.path.exists(path):
os.makedirs(path)
def mkdirs(paths):
if isinstance(paths, str):
mkdir(paths)
else:
for path in paths:
mkdir(path)
def mkdir_and_rename(path):
if os.path.exists(path):
new_name = path + '_archived_' + get_timestamp()
print('Path already exists. Rename it to [{:s}]'.format(new_name))
os.rename(path, new_name)
os.makedirs(path)
'''
# =======================================
# read image from path
# Note: opencv is fast
# but read BGR numpy image
# =======================================
'''
# ----------------------------------------
# get single image of size HxWxn_channles (BGR)
# ----------------------------------------
def read_img(path):
# read image by cv2
# return: Numpy float32, HWC, BGR, [0,1]
img = cv2.imread(path, cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED) # cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE
img = img.astype(np.float32) / 255.
if img.ndim == 2:
img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=2)
# some images have 4 channels
if img.shape[2] > 3:
img = img[:, :, :3]
return img
# ----------------------------------------
# get uint8 image of size HxWxn_channles (RGB)
# ----------------------------------------
def imread_uint(path, n_channels=3):
# input: path
# output: HxWx3(RGB or GGG), or HxWx1 (G)
if n_channels == 1:
img = cv2.imread(path, 0) # cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE
img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=2) # HxWx1
elif n_channels == 3:
img = cv2.imread(path, cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED) # BGR or G
if img.ndim == 2:
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2RGB) # GGG
else:
# img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # RGB
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2YCrCb) # ycbcr
return img
def imsave(img, img_path):
if img.ndim == 3:
img = img[:, :, [2, 1, 0]]
cv2.imwrite(img_path, img)
'''
# =======================================
# numpy(single) <---> numpy(unit)
# numpy(single) <---> tensor
# numpy(unit) <---> tensor
# =======================================
'''
# --------------------------------
# numpy(single) <---> numpy(unit)
# --------------------------------
def uint2single(img):
return np.float32(img / 255.)
def unit2single(img):
return np.float32(img / 255.)
def single2uint(img):
return np.uint8((img.clip(0, 1) * 255.).round())
def unit162single(img):
return np.float32(img / 65535.)
def single2uint16(img):
return np.uint8((img.clip(0, 1) * 65535.).round())
# --------------------------------
# numpy(unit) <---> tensor
# uint (HxWxn_channels (RGB) or G)
# --------------------------------
# convert uint (HxWxn_channels) to 4-dimensional torch tensor
def uint2tensor4(img):
if img.ndim == 2:
img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=2)
return torch.from_numpy(np.ascontiguousarray(img)).permute(2, 0, 1).float().div(255.).unsqueeze(0)
# convert uint (HxWxn_channels) to 3-dimensional torch tensor
def uint2tensor3(img):
if img.ndim == 2:
img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=2)
return torch.from_numpy(np.ascontiguousarray(img)).permute(2, 0, 1).float().div(255.)
# convert torch tensor to uint
def tensor2uint(img):
img = img.data.squeeze().float().clamp_(0, 1).cpu().numpy()
if img.ndim == 3:
img = np.transpose(img, (1, 2, 0))
return np.uint8((img * 255.0).round())
# --------------------------------
# numpy(single) <---> tensor
# single (HxWxn_channels (RGB) or G)
# --------------------------------
# convert single (HxWxn_channels) to 4-dimensional torch tensor
def single2tensor4(img):
return torch.from_numpy(np.ascontiguousarray(img)).permute(2, 0, 1).float().unsqueeze(0)
def single2tensor5(img):
return torch.from_numpy(np.ascontiguousarray(img)).permute(2, 0, 1, 3).float().unsqueeze(0)
def single42tensor4(img):
return torch.from_numpy(np.ascontiguousarray(img)).permute(2, 0, 1, 3).float()
# convert single (HxWxn_channels) to 3-dimensional torch tensor
def single2tensor3(img):
return torch.from_numpy(np.ascontiguousarray(img)).permute(2, 0, 1).float()
# convert torch tensor to single
def tensor2single(img):
img = img.data.squeeze().float().clamp_(0, 1).cpu().numpy()
if img.ndim == 3:
img = np.transpose(img, (1, 2, 0))
return img
def tensor2single3(img):
img = img.data.squeeze().float().clamp_(0, 1).cpu().numpy()
if img.ndim == 3:
img = np.transpose(img, (1, 2, 0))
elif img.ndim == 2:
img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=2)
return img
# from skimage.io import imread, imsave
def tensor2img(tensor, out_type=np.uint8, min_max=(0, 1)):
'''
Converts a torch Tensor into an image Numpy array of BGR channel order
Input: 4D(B,(3/1),H,W), 3D(C,H,W), or 2D(H,W), any range, RGB channel order
Output: 3D(H,W,C) or 2D(H,W), [0,255], np.uint8 (default)
'''
tensor = tensor.squeeze().float().cpu().clamp_(*min_max) # squeeze first, then clamp
tensor = (tensor - min_max[0]) / (min_max[1] - min_max[0]) # to range [0,1]
n_dim = tensor.dim()
if n_dim == 4:
n_img = len(tensor)
img_np = make_grid(tensor, nrow=int(math.sqrt(n_img)), normalize=False).numpy()
img_np = np.transpose(img_np[[2, 1, 0], :, :], (1, 2, 0)) # HWC, BGR
elif n_dim == 3:
img_np = tensor.numpy()
img_np = np.transpose(img_np[[2, 1, 0], :, :], (1, 2, 0)) # HWC, BGR
elif n_dim == 2:
img_np = tensor.numpy()
else:
raise TypeError(
'Only support 4D, 3D and 2D tensor. But received with dimension: {:d}'.format(n_dim))
if out_type == np.uint8:
img_np = (img_np * 255.0).round()
# Important. Unlike matlab, numpy.unit8() WILL NOT round by default.
return img_np.astype(out_type)
'''
# =======================================
# image processing process on numpy image
# augment(img_list, hflip=True, rot=True):
# =======================================
'''
def augment_img(img, mode=0):
if mode == 0:
return img
elif mode == 1:
return np.flipud(np.rot90(img))
elif mode == 2:
return np.flipud(img)
elif mode == 3:
return np.rot90(img, k=3)
elif mode == 4:
return np.flipud(np.rot90(img, k=2))
elif mode == 5:
return np.rot90(img)
elif mode == 6:
return np.rot90(img, k=2)
elif mode == 7:
return np.flipud(np.rot90(img, k=3))
def augment_img_np3(img, mode=0):
if mode == 0:
return img
elif mode == 1:
return img.transpose(1, 0, 2)
elif mode == 2:
return img[::-1, :, :]
elif mode == 3:
img = img[::-1, :, :]
img = img.transpose(1, 0, 2)
return img
elif mode == 4:
return img[:, ::-1, :]
elif mode == 5:
img = img[:, ::-1, :]
img = img.transpose(1, 0, 2)
return img
elif mode == 6:
img = img[:, ::-1, :]
img = img[::-1, :, :]
return img
elif mode == 7:
img = img[:, ::-1, :]
img = img[::-1, :, :]
img = img.transpose(1, 0, 2)
return img
def augment_img_tensor(img, mode=0):
img_size = img.size()
img_np = img.data.cpu().numpy()
if len(img_size) == 3:
img_np = np.transpose(img_np, (1, 2, 0))
elif len(img_size) == 4:
img_np = np.transpose(img_np, (2, 3, 1, 0))
img_np = augment_img(img_np, mode=mode)
img_tensor = torch.from_numpy(np.ascontiguousarray(img_np))
if len(img_size) == 3:
img_tensor = img_tensor.permute(2, 0, 1)
elif len(img_size) == 4:
img_tensor = img_tensor.permute(3, 2, 0, 1)
return img_tensor.type_as(img)
def augment_imgs(img_list, hflip=True, rot=True):
# horizontal flip OR rotate
hflip = hflip and random.random() < 0.5
vflip = rot and random.random() < 0.5
rot90 = rot and random.random() < 0.5
def _augment(img):
if hflip:
img = img[:, ::-1, :]
if vflip:
img = img[::-1, :, :]
if rot90:
img = img.transpose(1, 0, 2)
return img
return [_augment(img) for img in img_list]
'''
# =======================================
# image processing process on numpy image
# channel_convert(in_c, tar_type, img_list):
# rgb2ycbcr(img, only_y=True):
# bgr2ycbcr(img, only_y=True):
# ycbcr2rgb(img):
# modcrop(img_in, scale):
# =======================================
'''
def rgb2ycbcr(img, only_y=True):
'''same as matlab rgb2ycbcr
only_y: only return Y channel
Input:
uint8, [0, 255]
float, [0, 1]
'''
in_img_type = img.dtype
img.astype(np.float32)
if in_img_type != np.uint8:
img *= 255.
# convert
if only_y:
rlt = np.dot(img, [65.481, 128.553, 24.966]) / 255.0 + 16.0
else:
rlt = np.matmul(img, [[65.481, -37.797, 112.0], [128.553, -74.203, -93.786],
[24.966, 112.0, -18.214]]) / 255.0 + [16, 128, 128]
if in_img_type == np.uint8:
rlt = rlt.round()
else:
rlt /= 255.
return rlt.astype(in_img_type)
def ycbcr2rgb(img):
'''same as matlab ycbcr2rgb
Input:
uint8, [0, 255]
float, [0, 1]
'''
in_img_type = img.dtype
img.astype(np.float32)
if in_img_type != np.uint8:
img *= 255.
# convert
rlt = np.matmul(img, [[0.00456621, 0.00456621, 0.00456621], [0, -0.00153632, 0.00791071],
[0.00625893, -0.00318811, 0]]) * 255.0 + [-222.921, 135.576, -276.836]
if in_img_type == np.uint8:
rlt = rlt.round()
else:
rlt /= 255.
return rlt.astype(in_img_type)
def bgr2ycbcr(img, only_y=True):
'''bgr version of rgb2ycbcr
only_y: only return Y channel
Input:
uint8, [0, 255]
float, [0, 1]
'''
in_img_type = img.dtype
img.astype(np.float32)
if in_img_type != np.uint8:
img *= 255.
# convert
if only_y:
rlt = np.dot(img, [24.966, 128.553, 65.481]) / 255.0 + 16.0
else:
rlt = np.matmul(img, [[24.966, 112.0, -18.214], [128.553, -74.203, -93.786],
[65.481, -37.797, 112.0]]) / 255.0 + [16, 128, 128]
if in_img_type == np.uint8:
rlt = rlt.round()
else:
rlt /= 255.
return rlt.astype(in_img_type)
def modcrop(img_in, scale):
# img_in: Numpy, HWC or HW
img = np.copy(img_in)
if img.ndim == 2:
H, W = img.shape
H_r, W_r = H % scale, W % scale
img = img[:H - H_r, :W - W_r]
elif img.ndim == 3:
H, W, C = img.shape
H_r, W_r = H % scale, W % scale
img = img[:H - H_r, :W - W_r, :]
else:
raise ValueError('Wrong img ndim: [{:d}].'.format(img.ndim))
return img
def shave(img_in, border=0):
# img_in: Numpy, HWC or HW
img = np.copy(img_in)
h, w = img.shape[:2]
img = img[border:h - border, border:w - border]
return img
def channel_convert(in_c, tar_type, img_list):
# conversion among BGR, gray and y
if in_c == 3 and tar_type == 'gray': # BGR to gray
gray_list = [cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) for img in img_list]
return [np.expand_dims(img, axis=2) for img in gray_list]
elif in_c == 3 and tar_type == 'y': # BGR to y
y_list = [bgr2ycbcr(img, only_y=True) for img in img_list]
return [np.expand_dims(img, axis=2) for img in y_list]
elif in_c == 1 and tar_type == 'RGB': # gray/y to BGR
return [cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR) for img in img_list]
else:
return img_list
'''
# =======================================
# metric, PSNR and SSIM
# =======================================
'''
# ----------
# PSNR
# ----------
def calculate_psnr(img1, img2, border=0):
# img1 and img2 have range [0, 255]
if not img1.shape == img2.shape:
raise ValueError('Input images must have the same dimensions.')
h, w = img1.shape[:2]
img1 = img1[border:h - border, border:w - border]
img2 = img2[border:h - border, border:w - border]
img1 = img1.astype(np.float64)
img2 = img2.astype(np.float64)
mse = np.mean((img1 - img2) ** 2)
if mse == 0:
return float('inf')
return 20 * math.log10(255.0 / math.sqrt(mse))
# ----------
# SSIM
# ----------
def calculate_ssim(img1, img2, border=0):
'''calculate SSIM
the same outputs as MATLAB's
img1, img2: [0, 255]
'''
if not img1.shape == img2.shape:
raise ValueError('Input images must have the same dimensions.')
h, w = img1.shape[:2]
img1 = img1[border:h - border, border:w - border]
img2 = img2[border:h - border, border:w - border]
if img1.ndim == 2:
return ssim(img1, img2)
elif img1.ndim == 3:
if img1.shape[2] == 3:
ssims = []
for i in range(3):
ssims.append(ssim(img1, img2))
return np.array(ssims).mean()
elif img1.shape[2] == 1:
return ssim(np.squeeze(img1), np.squeeze(img2))
else:
raise ValueError('Wrong input image dimensions.')
def ssim(img1, img2):
C1 = (0.01 * 255) ** 2
C2 = (0.03 * 255) ** 2
img1 = img1.astype(np.float64)
img2 = img2.astype(np.float64)
kernel = cv2.getGaussianKernel(11, 1.5)
window = np.outer(kernel, kernel.transpose())
mu1 = cv2.filter2D(img1, -1, window)[5:-5, 5:-5] # valid
mu2 = cv2.filter2D(img2, -1, window)[5:-5, 5:-5]
mu1_sq = mu1 ** 2
mu2_sq = mu2 ** 2
mu1_mu2 = mu1 * mu2
sigma1_sq = cv2.filter2D(img1 ** 2, -1, window)[5:-5, 5:-5] - mu1_sq
sigma2_sq = cv2.filter2D(img2 ** 2, -1, window)[5:-5, 5:-5] - mu2_sq
sigma12 = cv2.filter2D(img1 * img2, -1, window)[5:-5, 5:-5] - mu1_mu2
ssim_map = ((2 * mu1_mu2 + C1) * (2 * sigma12 + C2)) / ((mu1_sq + mu2_sq + C1) *
(sigma1_sq + sigma2_sq + C2))
return ssim_map.mean()
'''
# =======================================
# pytorch version of matlab imresize
# =======================================
'''
# matlab 'imresize' function, now only support 'bicubic'
def cubic(x):
absx = torch.abs(x)
absx2 = absx ** 2
absx3 = absx ** 3
return (1.5 * absx3 - 2.5 * absx2 + 1) * ((absx <= 1).type_as(absx)) + \
(-0.5 * absx3 + 2.5 * absx2 - 4 * absx + 2) * (((absx > 1) * (absx <= 2)).type_as(absx))
def calculate_weights_indices(in_length, out_length, scale, kernel, kernel_width, antialiasing):
if (scale < 1) and (antialiasing):
# Use a modified kernel to simultaneously interpolate and antialias- larger kernel width
kernel_width = kernel_width / scale
# Output-space coordinates
x = torch.linspace(1, out_length, out_length)
# Input-space coordinates. Calculate the inverse mapping such that 0.5
# in output space maps to 0.5 in input space, and 0.5+scale in output
# space maps to 1.5 in input space.
u = x / scale + 0.5 * (1 - 1 / scale)
# What is the left-most pixel that can be involved in the computation?
left = torch.floor(u - kernel_width / 2)
# What is the maximum number of pixels that can be involved in the
# computation? Note: it's OK to use an extra pixel here; if the
# corresponding weights are all zero, it will be eliminated at the end
# of this function.
P = math.ceil(kernel_width) + 2
# The indices of the input pixels involved in computing the k-th output
# pixel are in row k of the indices matrix.
indices = left.view(out_length, 1).expand(out_length, P) + torch.linspace(0, P - 1, P).view(
1, P).expand(out_length, P)
# The weights used to compute the k-th output pixel are in row k of the
# weights matrix.
distance_to_center = u.view(out_length, 1).expand(out_length, P) - indices
# apply cubic kernel
if (scale < 1) and (antialiasing):
weights = scale * cubic(distance_to_center * scale)
else:
weights = cubic(distance_to_center)
# Normalize the weights matrix so that each row sums to 1.
weights_sum = torch.sum(weights, 1).view(out_length, 1)
weights = weights / weights_sum.expand(out_length, P)
# If a column in weights is all zero, get rid of it. only consider the first and last column.
weights_zero_tmp = torch.sum((weights == 0), 0)
if not math.isclose(weights_zero_tmp[0], 0, rel_tol=1e-6):
indices = indices.narrow(1, 1, P - 2)
weights = weights.narrow(1, 1, P - 2)
if not math.isclose(weights_zero_tmp[-1], 0, rel_tol=1e-6):
indices = indices.narrow(1, 0, P - 2)
weights = weights.narrow(1, 0, P - 2)
weights = weights.contiguous()
indices = indices.contiguous()
sym_len_s = -indices.min() + 1
sym_len_e = indices.max() - in_length
indices = indices + sym_len_s - 1
return weights, indices, int(sym_len_s), int(sym_len_e)
# --------------------------------
# imresize for tensor image
# --------------------------------
def imresize(img, scale, antialiasing=True):
# Now the scale should be the same for H and W
# input: img: pytorch tensor, CHW or HW [0,1]
# output: CHW or HW [0,1] w/o round
need_squeeze = True if img.dim() == 2 else False
if need_squeeze:
img.unsqueeze_(0)
in_C, in_H, in_W = img.size()
out_C, out_H, out_W = in_C, math.ceil(in_H * scale), math.ceil(in_W * scale)
kernel_width = 4
kernel = 'cubic'
# Return the desired dimension order for performing the resize. The
# strategy is to perform the resize first along the dimension with the
# smallest scale factor.
# Now we do not support this.
# get weights and indices
weights_H, indices_H, sym_len_Hs, sym_len_He = calculate_weights_indices(
in_H, out_H, scale, kernel, kernel_width, antialiasing)
weights_W, indices_W, sym_len_Ws, sym_len_We = calculate_weights_indices(
in_W, out_W, scale, kernel, kernel_width, antialiasing)
# process H dimension
# symmetric copying
img_aug = torch.FloatTensor(in_C, in_H + sym_len_Hs + sym_len_He, in_W)
img_aug.narrow(1, sym_len_Hs, in_H).copy_(img)
sym_patch = img[:, :sym_len_Hs, :]
inv_idx = torch.arange(sym_patch.size(1) - 1, -1, -1).long()
sym_patch_inv = sym_patch.index_select(1, inv_idx)
img_aug.narrow(1, 0, sym_len_Hs).copy_(sym_patch_inv)
sym_patch = img[:, -sym_len_He:, :]
inv_idx = torch.arange(sym_patch.size(1) - 1, -1, -1).long()
sym_patch_inv = sym_patch.index_select(1, inv_idx)
img_aug.narrow(1, sym_len_Hs + in_H, sym_len_He).copy_(sym_patch_inv)
out_1 = torch.FloatTensor(in_C, out_H, in_W)
kernel_width = weights_H.size(1)
for i in range(out_H):
idx = int(indices_H[i][0])
for j in range(out_C):
out_1[j, i, :] = img_aug[j, idx:idx + kernel_width, :].transpose(0, 1).mv(weights_H[i])
# process W dimension
# symmetric copying
out_1_aug = torch.FloatTensor(in_C, out_H, in_W + sym_len_Ws + sym_len_We)
out_1_aug.narrow(2, sym_len_Ws, in_W).copy_(out_1)
sym_patch = out_1[:, :, :sym_len_Ws]
inv_idx = torch.arange(sym_patch.size(2) - 1, -1, -1).long()
sym_patch_inv = sym_patch.index_select(2, inv_idx)
out_1_aug.narrow(2, 0, sym_len_Ws).copy_(sym_patch_inv)
sym_patch = out_1[:, :, -sym_len_We:]
inv_idx = torch.arange(sym_patch.size(2) - 1, -1, -1).long()
sym_patch_inv = sym_patch.index_select(2, inv_idx)
out_1_aug.narrow(2, sym_len_Ws + in_W, sym_len_We).copy_(sym_patch_inv)
out_2 = torch.FloatTensor(in_C, out_H, out_W)
kernel_width = weights_W.size(1)
for i in range(out_W):
idx = int(indices_W[i][0])
for j in range(out_C):
out_2[j, :, i] = out_1_aug[j, :, idx:idx + kernel_width].mv(weights_W[i])
if need_squeeze:
out_2.squeeze_()
return out_2
# --------------------------------
# imresize for numpy image
# --------------------------------
def imresize_np(img, scale, antialiasing=True):
# Now the scale should be the same for H and W
# input: img: Numpy, HWC or HW [0,1]
# output: HWC or HW [0,1] w/o round
img = torch.from_numpy(img)
need_squeeze = True if img.dim() == 2 else False
if need_squeeze:
img.unsqueeze_(2)
in_H, in_W, in_C = img.size()
out_C, out_H, out_W = in_C, math.ceil(in_H * scale), math.ceil(in_W * scale)
kernel_width = 4
kernel = 'cubic'
# Return the desired dimension order for performing the resize. The
# strategy is to perform the resize first along the dimension with the
# smallest scale factor.
# Now we do not support this.
# get weights and indices
weights_H, indices_H, sym_len_Hs, sym_len_He = calculate_weights_indices(
in_H, out_H, scale, kernel, kernel_width, antialiasing)
weights_W, indices_W, sym_len_Ws, sym_len_We = calculate_weights_indices(
in_W, out_W, scale, kernel, kernel_width, antialiasing)
# process H dimension
# symmetric copying
img_aug = torch.FloatTensor(in_H + sym_len_Hs + sym_len_He, in_W, in_C)
img_aug.narrow(0, sym_len_Hs, in_H).copy_(img)
sym_patch = img[:sym_len_Hs, :, :]
inv_idx = torch.arange(sym_patch.size(0) - 1, -1, -1).long()
sym_patch_inv = sym_patch.index_select(0, inv_idx)
img_aug.narrow(0, 0, sym_len_Hs).copy_(sym_patch_inv)
sym_patch = img[-sym_len_He:, :, :]
inv_idx = torch.arange(sym_patch.size(0) - 1, -1, -1).long()
sym_patch_inv = sym_patch.index_select(0, inv_idx)
img_aug.narrow(0, sym_len_Hs + in_H, sym_len_He).copy_(sym_patch_inv)
out_1 = torch.FloatTensor(out_H, in_W, in_C)
kernel_width = weights_H.size(1)
for i in range(out_H):
idx = int(indices_H[i][0])
for j in range(out_C):
out_1[i, :, j] = img_aug[idx:idx + kernel_width, :, j].transpose(0, 1).mv(weights_H[i])
# process W dimension
# symmetric copying
out_1_aug = torch.FloatTensor(out_H, in_W + sym_len_Ws + sym_len_We, in_C)
out_1_aug.narrow(1, sym_len_Ws, in_W).copy_(out_1)
sym_patch = out_1[:, :sym_len_Ws, :]
inv_idx = torch.arange(sym_patch.size(1) - 1, -1, -1).long()
sym_patch_inv = sym_patch.index_select(1, inv_idx)
out_1_aug.narrow(1, 0, sym_len_Ws).copy_(sym_patch_inv)
sym_patch = out_1[:, -sym_len_We:, :]
inv_idx = torch.arange(sym_patch.size(1) - 1, -1, -1).long()
sym_patch_inv = sym_patch.index_select(1, inv_idx)
out_1_aug.narrow(1, sym_len_Ws + in_W, sym_len_We).copy_(sym_patch_inv)
out_2 = torch.FloatTensor(out_H, out_W, in_C)
kernel_width = weights_W.size(1)
for i in range(out_W):
idx = int(indices_W[i][0])
for j in range(out_C):
out_2[:, i, j] = out_1_aug[:, idx:idx + kernel_width, j].mv(weights_W[i])
if need_squeeze:
out_2.squeeze_()
return out_2.numpy()
if __name__ == '__main__':
img = imread_uint('../1.png', 3)
PS:utils中我设置计算的PSNR是YCbCr的,如果要计算RGB类型的,就把imread_uint的else下面那个换成RGB的,如果是BGR或者别的什么,可以自己调用函数改就行。
def imread_uint(path, n_channels=3):
# input: path
# output: HxWx3(RGB or GGG), or HxWx1 (G)
if n_channels == 1:
img = cv2.imread(path, 0) # cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE
img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=2) # HxWx1
elif n_channels == 3:
img = cv2.imread(path, cv2.IMREAD_UNCHANGED) # BGR or G
if img.ndim == 2:
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2RGB) # GGG
else:
# img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB) # RGB
img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2YCrCb) # ycbcr
return img
Matlab法
推荐使用matlab进行计算,也是我最常用的
来源:Yulun Zhang, Kunpeng Li, Kai Li, Lichen Wang, Bineng Zhong, and Yun Fu, "Image Super-Resolution Using Very Deep Residual Channel Attention Networks", ECCV 2018, [arXiv]
function Evaluate_PSNR_SSIM()
clear all; close all; clc
%% set path
degradation = 'BI'; % BI, BD
methods = {'RCAN', 'RCANplus'};
dataset = {'Set5'};
ext = {'*.jpg', '*.png', '*.bmp'};
num_method = length(methods);
num_set = length(dataset);
record_results_txt = ['PSNR_SSIM_Results_', degradation,'_model.txt'];
results = fopen(fullfile(record_results_txt), 'wt');
if strcmp(degradation, 'BI')
scale_all = [2, 3, 4, 8];
else
scale_all = 3;
end
for idx_method = 1:num_method
for idx_set = 1:num_set
fprintf(results, '**********************\n');
fprintf(results, 'Method_%d: %s; Set: %s\n', idx_method, methods{idx_method}, dataset{idx_set});
fprintf('**********************\n');
fprintf('Method_%d: %s; Set: %s\n', idx_method, methods{idx_method}, dataset{idx_set});
for scale = scale_all
filepaths = [];
for idx_ext = 1:length(ext)
filepaths = cat(1, filepaths, dir(fullfile('./HR', dataset{idx_set}, ['x', num2str(scale)], ext{idx_ext})));
end
PSNR_all = zeros(1, length(filepaths));
SSIM_all = zeros(1, length(filepaths));
for idx_im = 1:length(filepaths)
name_HR = filepaths(idx_im).name;
name_SR = strrep(name_HR, 'HR', methods{idx_method});
im_HR = imread(fullfile('./HR', dataset{idx_set}, ['x', num2str(scale)], name_HR));
im_SR = imread(fullfile('./SR', degradation, [methods{idx_method}], dataset{idx_set}, ['x', num2str(scale)], name_SR));
% change channel for evaluation
if 3 == size(im_HR, 3)
im_HR_YCbCr = single(rgb2ycbcr(im2double(im_HR)));
im_HR_Y = im_HR_YCbCr(:,:,1);
im_SR_YCbCr = single(rgb2ycbcr(im2double(im_SR)));
im_SR_Y = im_SR_YCbCr(:,:,1);
else
im_HR_Y = single(im2double(im_HR));
im_SR_Y = single(im2double(im_SR));
end
% calculate PSNR, SSIM
[PSNR_all(idx_im), SSIM_all(idx_im)] = Cal_Y_PSNRSSIM(im_HR_Y*255, im_SR_Y*255, scale, scale);
fprintf(results, 'x%d %d %s: PSNR= %f SSIM= %f\n', scale, idx_im, name_SR, PSNR_all(idx_im), SSIM_all(idx_im));
fprintf('x%d %d %s: PSNR= %f SSIM= %f\n', scale, idx_im, name_SR, PSNR_all(idx_im), SSIM_all(idx_im));
end
fprintf(results, '--------Mean--------\n');
fprintf('--------Mean--------\n');
fprintf(results, 'x%d: PSNR= %f SSIM= %f\n', scale, mean(PSNR_all), mean(SSIM_all));
fprintf('x%d: PSNR= %f SSIM= %f\n', scale, mean(PSNR_all), mean(SSIM_all));
end
end
end
fclose(results);
end
function [psnr_cur, ssim_cur] = Cal_Y_PSNRSSIM(A,B,row,col)
% shave border if needed
if nargin > 2
[n,m,~]=size(A);
A = A(row+1:n-row,col+1:m-col,:);
B = B(row+1:n-row,col+1:m-col,:);
end
% RGB --> YCbCr
if 3 == size(A, 3)
A = rgb2ycbcr(A);
A = A(:,:,1);
end
if 3 == size(B, 3)
B = rgb2ycbcr(B);
B = B(:,:,1);
end
% calculate PSNR
A=double(A); % Ground-truth
B=double(B); %
e=A(:)-B(:);
mse=mean(e.^2);
psnr_cur=10*log10(255^2/mse);
% calculate SSIM
[ssim_cur, ~] = ssim_index(A, B);
end
function [mssim, ssim_map] = ssim_index(img1, img2, K, window, L)
%========================================================================
%SSIM Index, Version 1.0
%Copyright(c) 2003 Zhou Wang
%All Rights Reserved.
%
%The author is with Howard Hughes Medical Institute, and Laboratory
%for Computational Vision at Center for Neural Science and Courant
%Institute of Mathematical Sciences, New York University.
%
%----------------------------------------------------------------------
%Permission to use, copy, or modify this software and its documentation
%for educational and research purposes only and without fee is hereby
%granted, provided that this copyright notice and the original authors'
%names appear on all copies and supporting documentation. This program
%shall not be used, rewritten, or adapted as the basis of a commercial
%software or hardware product without first obtaining permission of the
%authors. The authors make no representations about the suitability of
%this software for any purpose. It is provided "as is" without express
%or implied warranty.
%----------------------------------------------------------------------
%
%This is an implementation of the algorithm for calculating the
%Structural SIMilarity (SSIM) index between two images. Please refer
%to the following paper:
%
%Z. Wang, A. C. Bovik, H. R. Sheikh, and E. P. Simoncelli, "Image
%quality assessment: From error measurement to structural similarity"
%IEEE Transactios on Image Processing, vol. 13, no. 1, Jan. 2004.
%
%Kindly report any suggestions or corrections to zhouwang@ieee.org
%
%----------------------------------------------------------------------
%
%Input : (1) img1: the first image being compared
% (2) img2: the second image being compared
% (3) K: constants in the SSIM index formula (see the above
% reference). defualt value: K = [0.01 0.03]
% (4) window: local window for statistics (see the above
% reference). default widnow is Gaussian given by
% window = fspecial('gaussian', 11, 1.5);
% (5) L: dynamic range of the images. default: L = 255
%
%Output: (1) mssim: the mean SSIM index value between 2 images.
% If one of the images being compared is regarded as
% perfect quality, then mssim can be considered as the
% quality measure of the other image.
% If img1 = img2, then mssim = 1.
% (2) ssim_map: the SSIM index map of the test image. The map
% has a smaller size than the input images. The actual size:
% size(img1) - size(window) + 1.
%
%Default Usage:
% Given 2 test images img1 and img2, whose dynamic range is 0-255
%
% [mssim ssim_map] = ssim_index(img1, img2);
%
%Advanced Usage:
% User defined parameters. For example
%
% K = [0.05 0.05];
% window = ones(8);
% L = 100;
% [mssim ssim_map] = ssim_index(img1, img2, K, window, L);
%
%See the results:
%
% mssim %Gives the mssim value
% imshow(max(0, ssim_map).^4) %Shows the SSIM index map
%
%========================================================================
if (nargin < 2 || nargin > 5)
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
if (size(img1) ~= size(img2))
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
[M N] = size(img1);
if (nargin == 2)
if ((M < 11) || (N < 11))
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return
end
window = fspecial('gaussian', 11, 1.5); %
K(1) = 0.01; % default settings
K(2) = 0.03; %
L = 255; %
end
if (nargin == 3)
if ((M < 11) || (N < 11))
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return
end
window = fspecial('gaussian', 11, 1.5);
L = 255;
if (length(K) == 2)
if (K(1) < 0 || K(2) < 0)
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
else
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
end
if (nargin == 4)
[H W] = size(window);
if ((H*W) < 4 || (H > M) || (W > N))
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return
end
L = 255;
if (length(K) == 2)
if (K(1) < 0 || K(2) < 0)
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
else
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
end
if (nargin == 5)
[H W] = size(window);
if ((H*W) < 4 || (H > M) || (W > N))
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return
end
if (length(K) == 2)
if (K(1) < 0 || K(2) < 0)
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
else
ssim_index = -Inf;
ssim_map = -Inf;
return;
end
end
C1 = (K(1)*L)^2;
C2 = (K(2)*L)^2;
window = window/sum(sum(window));
img1 = double(img1);
img2 = double(img2);
mu1 = filter2(window, img1, 'valid');
mu2 = filter2(window, img2, 'valid');
mu1_sq = mu1.*mu1;
mu2_sq = mu2.*mu2;
mu1_mu2 = mu1.*mu2;
sigma1_sq = filter2(window, img1.*img1, 'valid') - mu1_sq;
sigma2_sq = filter2(window, img2.*img2, 'valid') - mu2_sq;
sigma12 = filter2(window, img1.*img2, 'valid') - mu1_mu2;
if (C1 > 0 & C2 > 0)
ssim_map = ((2*mu1_mu2 + C1).*(2*sigma12 + C2))./((mu1_sq + mu2_sq + C1).*(sigma1_sq + sigma2_sq + C2));
else
numerator1 = 2*mu1_mu2 + C1;
numerator2 = 2*sigma12 + C2;
denominator1 = mu1_sq + mu2_sq + C1;
denominator2 = sigma1_sq + sigma2_sq + C2;
ssim_map = ones(size(mu1));
index = (denominator1.*denominator2 > 0);
ssim_map(index) = (numerator1(index).*numerator2(index))./(denominator1(index).*denominator2(index));
index = (denominator1 ~= 0) & (denominator2 == 0);
ssim_map(index) = numerator1(index)./denominator1(index);
end
mssim = mean2(ssim_map);
end
本文内容由网友自发贡献,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有涉嫌抄袭侵权的内容,请联系:hwhale#tublm.com(使用前将#替换为@)