Python可以玩的方向有很多,比如爬虫、预测分析、GUI、自动化、图像处理、可视化等等,可能只需要十几行代码就能实现酷炫的功能。
因为Python是动态脚本语言,所以代码逻辑比Java要简要很多,实现同样的功能少写很多代码。而且Python生态有众多的第三方工具库,把功能都封装在包里,只需要你调用接口,就能使用复杂的功能。
下面举几个简单好玩的脚本例子,初学者可以照着代码写写,能快速掌握python语法。
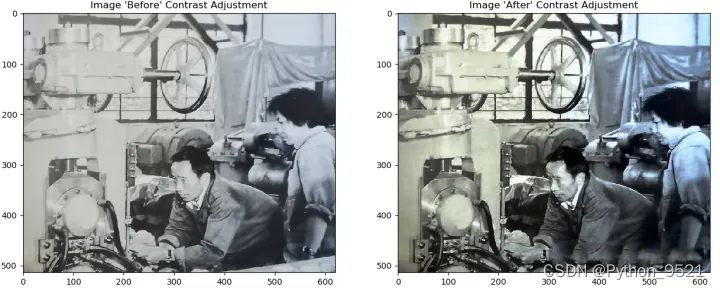
1、使用PIL、Matplotlib、Numpy对模糊老照片进行修复
# encoding=utf-8
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image
import os.path
# 读取图片
img_path = "E:\\test.jpg"
img = Image.open(img_path)
# 图像转化为numpy数组
img = np.asarray(img)
flat = img.flatten()
# 创建函数
def get_histogram(image, bins):
# array with size of bins, set to zeros
histogram = np.zeros(bins)
# loop through pixels and sum up counts of pixels
for pixel in image:
histogram[pixel] += 1
# return our final result
return histogram
# execute our histogram function
hist = get_histogram(flat, 256)
# execute the fn
cs = np.cumsum(hist)
# numerator & denomenator
nj = (cs - cs.min()) * 255 N = cs.max() - cs.min()
# re-normalize the cumsum
cs = nj / N
# cast it back to uint8 since we can't use floating point values in images
cs = cs.astype('uint8')
# get the value from cumulative sum for every index in flat, and set that as img_new
img_new = cs[flat]
# put array back into original shape since we flattened it
img_new = np.reshape(img_new, img.shape)
# set up side-by-side image display
fig = plt.figure()
fig.set_figheight(15)
fig.set_figwidth(15)
# display the real image
fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.imshow(img, cmap='gray')
plt.title("Image 'Before' Contrast Adjustment")
# display the new image
fig.add_subplot(1, 2, 2)
plt.imshow(img_new, cmap='gray')
plt.title("Image 'After' Contrast Adjustment")
filename = os.path.basename(img_path)
# plt.savefig("E:\\" + filename)
plt.show()
2、将文件批量压缩,使用zipfile库
import os import zipfile from random import randrange def zip_dir(path, zip_handler): for root, dirs, files in os.walk(path): for file in files: zip_handler.write(os.path.join(root, file)) if __name__ == '__main__': to_zip = input(""" Enter the name of the folder you want to zip (N.B.: The folder name should not contain blank spaces) > """) to_zip = to_zip.strip() + "/" zip_file_name = f'zip{randrange(0,10000)}.zip' zip_file = zipfile.ZipFile(zip_file_name, 'w', zipfile.ZIP_DEFLATED) zip_dir(to_zip, zip_file) zip_file.close() print(f'File Saved as {zip_file_name}')
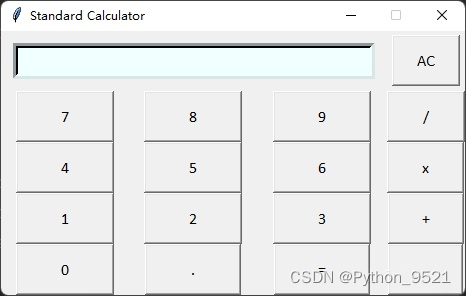
3、使用tkinter制作计算器GUI
tkinter是python自带的GUI库,适合初学者练手创建小软件
import tkinter as tk
root = tk.Tk() # Main box window
root.title("Standard Calculator") # Title shown at the title bar
root.resizable(0, 0) # disabling the resizeing of the window
# Creating an entry field:
e = tk.Entry(root,
width=35,
bg='#f0ffff',
fg='black',
borderwidth=5,
justify='right',
font='Calibri 15')
e.grid(row=0, column=0, columnspan=3, padx=12, pady=12)
def buttonClick(num):
# function for clicking
temp = e.get(
)# temporary varibale to store the current input in the screen
e.delete(0, tk.END) # clearing the screen from index 0 to END
e.insert(0, temp + num)
# inserting the incoming number input
def buttonClear(): # function for clearing
e.delete(0, tk.END)
# 代码过长,部分略
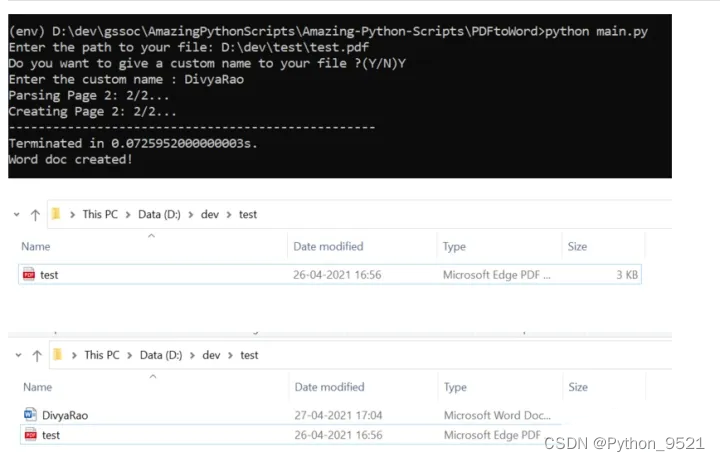
4、PDF转换为Word文件
使用pdf2docx库,可以将PDF文件转为Word格式
from pdf2docx
import Converter
import os
import sys
# Take PDF's path as input
pdf = input("Enter the path to your file: ")
assert os.path.exists(pdf), "File not found at, "+str(pdf)
f = open(pdf,'r+')
#Ask for custom name for the word doc
doc_name_choice = input("Do you want to give a custom name to your file ?(Y/N)")
if(doc_name_choice == 'Y' or doc_name_choice == 'y'):
# User input
doc_name = input("Enter the custom name : ")+".docx"
else:
# Use the same name as pdf
# Get the file name from the path provided by the user
pdf_name = os.path.basename(pdf)
# Get the name without the extension .pdf
doc_name = os.path.splitext(pdf_name)[0] + ".docx"
# Convert PDF to Word
cv = Converter(pdf)
#Path to the directory
path = os.path.dirname(pdf)
cv.convert(os.path.join(path, "", doc_name) , start=0, end=None)
print("Word doc created!") cv.close()
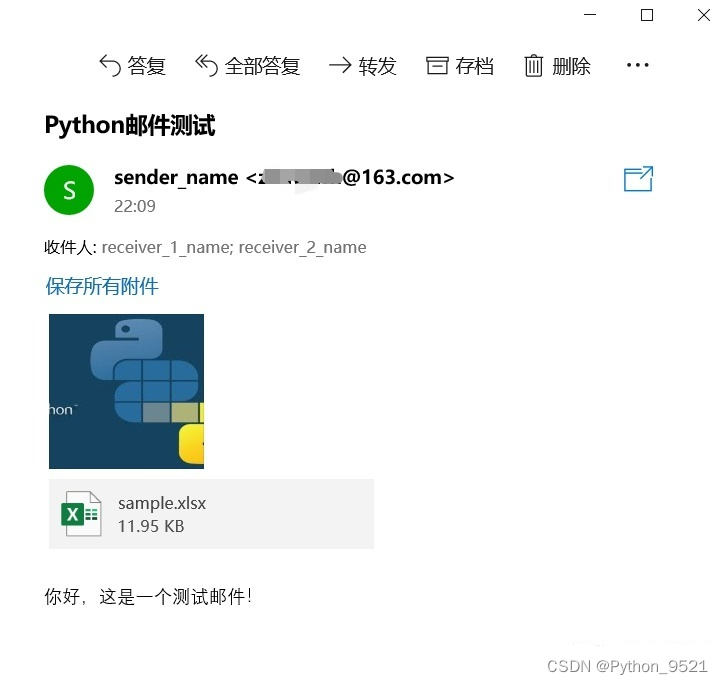
5、Python自动发送邮件
使用smtplib和email库可以实现脚本发送邮件
import smtplib
import email
# 负责构造文本
from email.mime.text import MIMEText
# 负责构造图片
from email.mime.image import MIMEImage
# 负责将多个对象集合起来
from email.mime.multipart import MIMEMultipart
from email.header import Header
# SMTP服务器,这里使用163邮箱
mail_host = "smtp.163.com"
# 发件人邮箱
mail_sender = "******@163.com"
# 邮箱授权码,注意这里不是邮箱密码,如何获取邮箱授权码,请看本文最后教程
mail_license = "********"
# 收件人邮箱,可以为多个收件人
mail_receivers = ["******@qq.com","******@outlook.com"]
mm = MIMEMultipart('related')
# 邮件主题 subject_content = """Python邮件测试"""
# 设置发送者,注意严格遵守格式,里面邮箱为发件人邮箱
mm["From"] = "sender_name<******@163.com>"
# 设置接受者,注意严格遵守格式,里面邮箱为接受者邮箱
mm["To"] = "receiver_1_name<******@qq.com>,receiver_2_name<******@outlook.com>"
# 设置邮件主题
mm["Subject"] = Header(subject_content,'utf-8')
# 邮件正文内容
body_content = """你好,这是一个测试邮件!"""
# 构造文本,参数1:正文内容,参数2:文本格式,参数3:编码方式
message_text = MIMEText(body_content,"plain","utf-8")
# 向MIMEMultipart对象中添加文本对象
mm.attach(message_text)
# 二进制读取图片
image_data = open('a.jpg','rb')
# 设置读取获取的二进制数据
message_image = MIMEImage(image_data.read())
# 关闭刚才打开的文件
image_data.close()
# 添加图片文件到邮件信息当中去
mm.attach(message_image)
# 构造附件
atta = MIMEText(open('sample.xlsx', 'rb').read(), 'base64', 'utf-8')
# 设置附件信息
atta["Content-Disposition"] = 'attachment; filename="sample.xlsx"'
# 添加附件到邮件信息当中去
mm.attach(atta)
# 创建SMTP对象
stp = smtplib.SMTP()
# 设置发件人邮箱的域名和端口,端口地址为25
stp.connect(mail_host, 25)
# set_debuglevel(1)可以打印出和SMTP服务器交互的所有信息
stp.set_debuglevel(1)
# 登录邮箱,传递参数1:邮箱地址,参数2:邮箱授权码
stp.login(mail_sender,mail_license)
# 发送邮件,传递参数1:发件人邮箱地址,参数2:收件人邮箱地址,参数3:把邮件内容格式改为str
stp.sendmail(mail_sender, mail_receivers, mm.as_string())
print("邮件发送成功")
# 关闭SMTP对象
stp.quit()