Spring cache
简单使用
实体类(缓存的对象)
@Data
public class User {
private String name;
private String age;
}
模拟获取缓存的方法
@Component
public class UserServier {
//开启缓存 对应配置文件
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "default")
public User getUser(String name)
{
User user = new User();
user.setName(name);
user.setAge("15");
return user;
}
}
需要配置文件,配置缓存
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:cache="http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache/spring-cache.xsd">
<!--开启缓存-->
<cache:annotation-driven/>
<context:component-scan base-package="cache"/>
<!--配置缓存的信息-->
<bean id="cacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.support.SimpleCacheManager">
<property name="caches">
<bean class="org.springframework.cache.concurrent.ConcurrentMapCacheFactoryBean" p:name="default"/>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
使用缓存
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ApplicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
UserServier userServier = ApplicationContext.getBean("userServier", UserServier.class);
User dpz = userServier.getUser("dpz");
User dpz1 = userServier.getUser("dpz");
System.out.println(dpz == dpz1);//true
}
}
- 第二次调用,如果发现缓存里有,不会调用业务代码,而是直接返回
注解缓存
@Cacheable

都相等
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "default")
@Cacheable("default")
@Cacheable(value = "default")
键生成器
缓存的本质就是键值对(放在map中),如果没有指定key,Spring会用KeyGenerator的实现SimpleKeyGenerator来生成key,也可以自己实现这个接口并配置key逻辑
public class SimpleKeyGenerator implements KeyGenerator {
@Override
public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) {
return generateKey(params);
}
public static Object generateKey(Object... params) {
if (params.length == 0) {
return SimpleKey.EMPTY;
}
if (params.length == 1) {
Object param = params[0];
if (param != null && !param.getClass().isArray()) {
return param;
}
}
return new SimpleKey(params);
}
}
- 如果没有参数,使用SimpleKey.EMPTY (两个方法都没有入参,缓存会有问题)
- 一个参数使用该入参作为key
- 多个入参返回一个包含所有入参生成的一个SimpleKey对象
也可以使用spel表达式来设置key值
@Cacheable(value = "default",key = "#user.name")
自定义的键生成器
@Component
public class MyKeyGenerator implements KeyGenerator {
@Override
public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) {
//params为被注解方法的参数
return 6;
}
}
@Cacheable(value = "default",keyGenerator = "myKeyGenerator")
带条件的缓存
缓存参数中age大于15的返回值
@Cacheable(value = "default",key = "#user.name",condition = "#user.age>15")
unless和condition效果相反
@Cacheable(value = "default",key = "#user.name",unless= "#user.age>15")
@CachePut
@Cacheable如果在判断为有缓存时,不会执行内部方法,而直接返回缓存。@CachePut会强制执行方法后跟新缓存(所以CachePut适合做跟新操作,Cacheable做查询操作)
例子
@CachePut(value = "default",key = "#user.name")
//对比如果
//@Cacheable(value = "default",key = "#user.name")
public User getUser(User user)
{
User user1 = new User();
user1.setName(user.getName());
user1.setAge(user.getAge());
return user1;
}
执行代码
User user = new User();
user.setName("ck");
user.setAge(10);
User dpz = userServier.getUser(user);
user.setAge(15);
User dpz1 = userServier.getUser(user);
- 如果是Cacheable注解 dpz = dpz1 age=10
- 如果是CachePut注解 dpz ≠ dpz1 age = 15
@CacheEvict
根据参数或者key删除缓存,执行方法。适用于删除操作。
@CacheEvict(value = "default",key = "#user.name")
public Boolean delUser(User user)
{
Boolean b = sevice.del(user);
return b;
}
多两个属性
- allEntries 默认为false,修改为true表示忽略key删除所有缓存
- beforeInvocation 默认为false,修改为true表示在方法执行之前就删除缓存。false表示在方法之后才删除,避免方法异常。
@Caching
类似组合注解,可以组合@Cacheable,@CachePut,@CacheEvict,根据不同条件加到不同的缓存策略中
@Component
public class UserServier {
public static final HashMap<Integer, User> map = new HashMap<>();
static {
map.put(1,new Dpz("dpz",1));
map.put(2,new Person("person",2));
}
@Caching(
cacheable = {
@Cacheable(value = "default",condition = "#user instanceof T(cache.Dpz)"),
@Cacheable(value = "cache1",condition = "#user instanceof T(cache.Person)")
}
)
public User getUser(User user)
{
return map.get(user.getAge());
}
}
@CacheConfig
可以注解在类上,统一配置其中方法的缓存策略
@Component
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "default")
public class UserServier {
public static final HashMap<Integer, User> map = new HashMap<>();
static {
map.put(1,new Dpz("dpz",1));
map.put(2,new Person("person",2));
}
@Cacheable
public User getUserA(Integer id)
{
return map.get(id);
}
@Cacheable
public User getUserB(Integer id)
{
return map.get(id);
}
}
使用Spel表达式
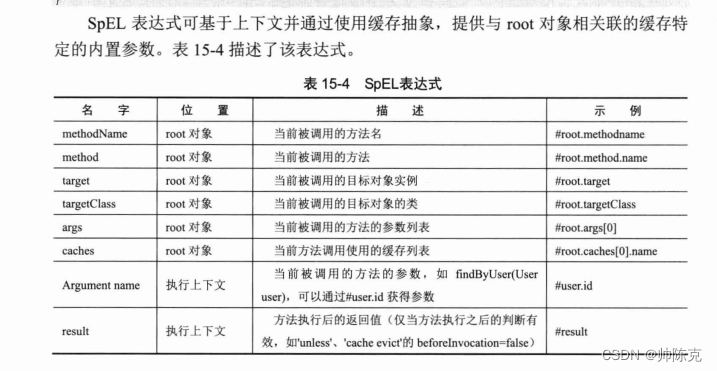
方法名为getUserA才进行缓存
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "default",condition = "#root.methodName == 'getUserA'")
public User getUserA(Integer id)
{
return map.get(id);
}
使用xml配置缓存
适合没有源码,无法添加注解的情况·
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:cache="http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache" xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache/spring-cache.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<cache:annotation-driven/>
<context:component-scan base-package="cache"/>
<bean id="cacheManager" class="org.springframework.cache.support.SimpleCacheManager">
<property name="caches">
<set>
<bean class="org.springframework.cache.concurrent.ConcurrentMapCacheFactoryBean" p:name="default"/>
<bean class="org.springframework.cache.concurrent.ConcurrentMapCacheFactoryBean" p:name="cache1"/>
</set>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="userServier" class="cache.UserServier"/>
<!--配置-->
<cache:advice id="cacheAdvice" cache-manager="cacheManager">
<cache:caching cache="default">
<cache:cacheable method="getUserA" key="#id"/>
</cache:caching>
</cache:advice>
<aop:config proxy-target-class="true">
<aop:advisor advice-ref="cacheAdvice" pointcut="execution(* cache.cache.*(..))"/>
</aop:config>
</beans>
以编程的方式初始缓存
某些缓存在系统启动时就可以预先加载
config
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"cache"})
public class cacheConfig {
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager()
{
SimpleCacheManager simpleCacheManager = new SimpleCacheManager();
simpleCacheManager.setCaches(Arrays.asList(new ConcurrentMapCache("users")));
return simpleCacheManager;
}
}
缓存初始化
@Component
public class UserServier{
public static final HashMap<Integer, User> map = new HashMap<>();
@Autowired
private CacheManager cacheManager;
static {
map.put(1,new Dpz("dpz",1));
map.put(2,new Person("person",2));
}
//项目启动时自动初始化
@PostConstruct
public void setup()
{
Cache users = cacheManager.getCache("users");
for (Integer integer : map.keySet()) {
users.put(integer,map.get(integer));
}
}
@Cacheable("users")
public User getUser(Integer id)
{
return new User("CK",66666);
}
}
使用
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(cacheConfig.class);
UserServier bean = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean(UserServier.class);
User user = bean.getUser(1);
System.out.println(user);
在getUser的时候会发现返回的是User(name=dpz, age=1)而不是User(“CK”,66666),说明走了缓存
自定义缓存注解
