一、概述
1、为什么使用多线程
在我们开发系统过程中,经常会处理一些好费时间的任务(如:向数据库中插入上百万数据,将会导致系统等待),这个时候就会自然想到使用多线程。
2、为什么使用Spring来实现多线程
- 使用Spring比使用JDK原生的并发API更简单。(@Async就能解决)。
- 一般的开发环境都会集成Spring框架,Bean也都交给Spring来管理,因此,Spring实现多线程更简单。
3、为什么需要使用异步
传统的调用方式:调用一个服务,需要等待服务调用完成后,才能执行后面的代码,因此,需要等待时间。
使用异步的方式:调用一个服务的同时,继续执行后面的代码,几乎是不需要多少的等待时间。
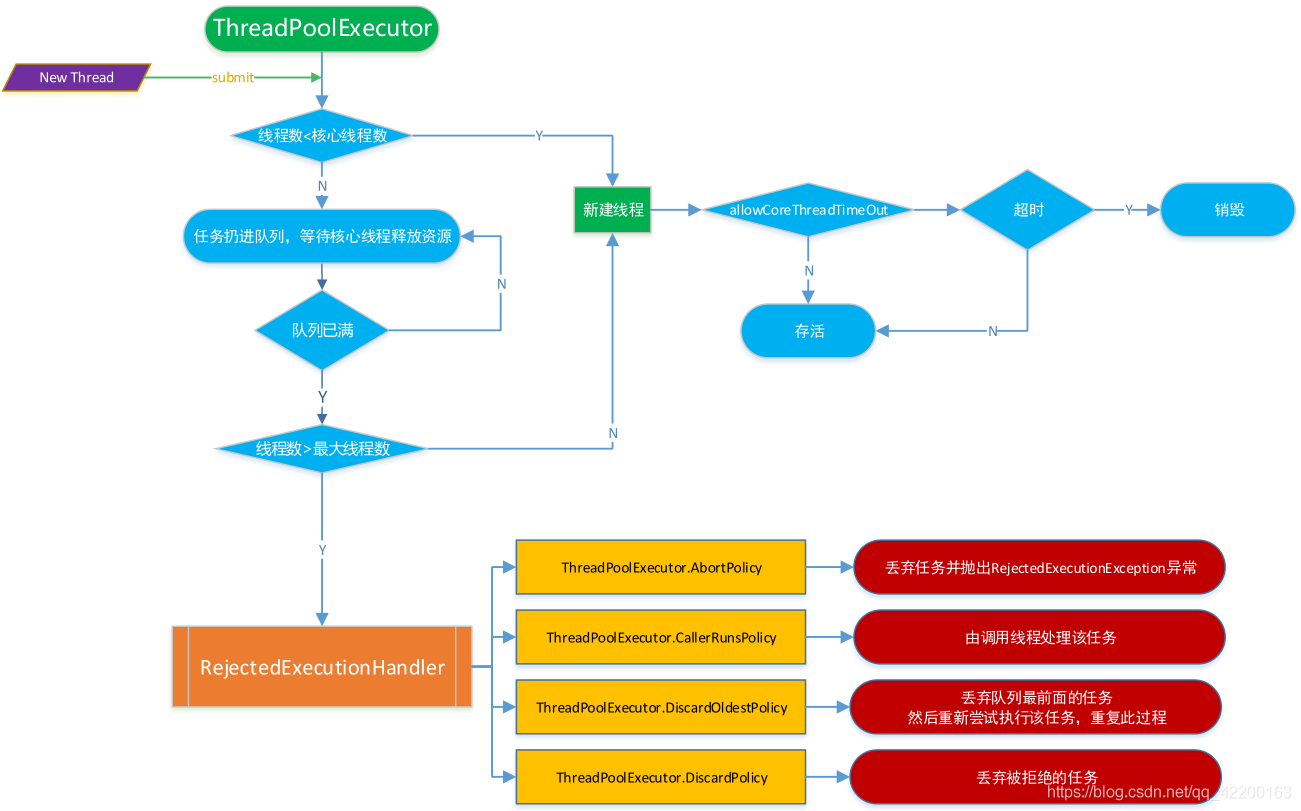
4、线程池ThreadPoolExecutor执行规则如下
二、SpringBoot使用多线程
1、如何使用
在 SpringBoot 中对其进行了简化处理,只需要配置一个类型为 java.util.concurrent.TaskExecutor
或其子类的 bean,并在配置类或直接在程序入口类上声明注解 @EnableAsync。
调用也简单,在由Spring管理的对象的方法上标注注解 @Async,显式调用即可生效。 一般使用 Spring 提供的
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor 类。
2、新增一个配置类,默认情况下使用 SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor
@Configuration
@EnableAsync //启用异步任务
public class ThreadConfig {
@Bean
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor(){
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
//配置核心线程数
executor.setCorePoolSize(15);
//配置最大线程数
executor.setMaxPoolSize(30);
//配置队列大小
executor.setQueueCapacity(1000);
//线程的名称前缀
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("Executor-");
//线程活跃时间(秒)
//executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(60);
//等待所有任务结束后再关闭线程池
executor.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(true);
//设置拒绝策略
//executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
//执行初始化
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
}
3、使用线程池
//-----------------------接口类--------------------------
public interface UserService{
/**
* 执行异步任务
*/
void writeText();
}
//-----------------------接口实现类----------------------
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implement UserService{
private static Logger logger = LogManager.getLogger(AsyncServiceImpl.class.getName());
@Async("asyncServiceExecutor")
@Over
public void writeTxt(String fileName){
logger.info("线程-" + Thread.currentThread().getId() + "在执行写入");
try {
File file = new File(fileName);
List<String> lines = FileUtils.readLines(file);
File copyFile = new File(fileName + "_copy.txt");
lines.stream().forEach(string->{
try {
FileUtils.writeStringToFile(copyFile,string,"utf8",true);
FileUtils.writeStringToFile(copyFile,"\r\n","utf8",true);
} catch (IOException e) {
logger.info(e.getMessage());
}
});
}catch (Exception e) {
logger.info(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
//-----------------------测试----------------------------
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class BootApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private AsyncService asyncService;
@Test
public void write() {
File file = new File("F://ac_code_1//test.txt");
try {
FileUtils.writeStringToFile(file, "ceshi", "utf8");
FileUtils.writeStringToFile(file, "\r\n", "utf8");
FileUtils.writeStringToFile(file, "ceshi2", "utf8");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
三、SpringBoot使用多线程批量插入数据
1、新建配置类
@Configuration
public class ThreadConfig {
@Bean
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor(){
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
//配置核心线程数
executor.setCorePoolSize(15);
//配置最大线程数
executor.setMaxPoolSize(30);
//配置队列大小
executor.setQueueCapacity(1000);
//线程的名称前缀
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("Executor-");
//等待所有任务结束后再关闭线程池
executor.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(true);
//执行初始化
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
}
2、service接口类
public interface ExchangeCouponInfoService extends IService<ExchangeCodeInfo> {
/**
* 批量新增兑换码
* @param info
* @return
*/
boolean addBatchExchangeCode(List<ExchangeCodeInfo> info);
}
3、接口实现类
@Service
public class ExchangeCodeInfoServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<ExchangeCodeInfoMapper, ExchangeCodeInfo> implements ExchangeCouponInfoService{
@Override
public boolean addBatchExchangeCode(List<ExchangeCodeInfo> info) {
return saveBatch(info);
}
}
4、controller类
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/exchangecoupon")
public class ExchangeCouponController {
@Autowired
private ExchangeCouponInfoService exchangeCouponInfoService;
@Autowired
private ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor;
@PostMapping("/saveExchangeCoupon")
@BizDigestLog(bizType = "兑换券新增")
public Results saveExchangeCoupon(@RequestBody ExchangeCouponModelAddReqDto model){
log.info("兑换券新增入口 -> [{}]",model);
//线程异步导入数据库,会异步开始执行新增方法,同时原线程不会等待,继续执行。实现了异步操作。
executor.execute(() -> exchangeCouponInfoService.addBatchExchangeCode(model));
Results results = Results.success(response);
log.info("兑换券新增出口 -> [{}]",JSON.toJSONString(response));
return results;
}
}
转载:小幸运安然 - SpringBoot使用多线程