1)首先在导言区加入语句:
\usepackage{algorithm}
\usepackage{algorithmic}
2)例1
\begin{algorithm}
\caption{A}
\label{alg:A}
\begin{algorithmic}
\STATE {set $r(t)=x(t)$}
\REPEAT
\STATE set $h(t)=r(t)$
\REPEAT
\STATE set $h(t)=r(t)$
\UNTIL{B}
\UNTIL{B}
\end{algorithmic}
\end{algorithm}
排版结果如下:

3)例2
\begin{algorithm}
\caption{Calculate $y = x^n$}
\label{alg1}
\begin{algorithmic}
\REQUIRE $n \geq 0 \vee x \neq 0$
\ENSURE $y = x^n$
\STATE $y \Leftarrow 1$
\IF{$n < 0$}
\STATE $X \Leftarrow 1 / x$
\STATE $N \Leftarrow -n$
\ELSE
\STATE $X \Leftarrow x$
\STATE $N \Leftarrow n$
\ENDIF
\WHILE{$N \neq 0$}
\IF{$N$ is even}
\STATE $X \Leftarrow X \times X$
\STATE $N \Leftarrow N / 2$
\ELSE[$N$ is odd]
\STATE $y \Leftarrow y \times X$
\STATE $N \Leftarrow N - 1$
\ENDIF
\ENDWHILE
\end{algorithmic}
\end{algorithm}
排版结果如下:

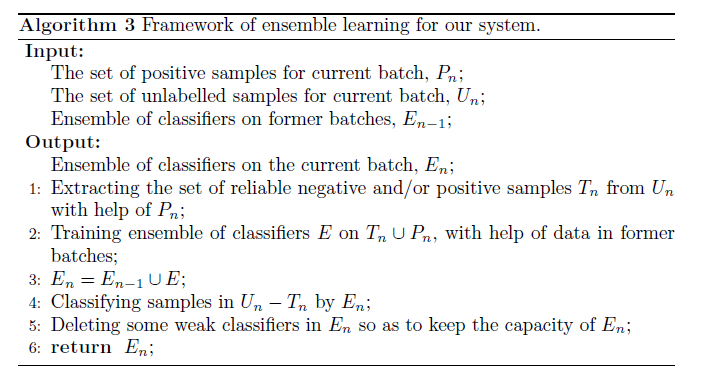
4)\renewcommand 改变现有命令的定义。在导言区加入如下语句:
\renewcommand{\algorithmicrequire}{ \textbf{Input:}} %Use Input in the format of Algorithm
\renewcommand{\algorithmicensure}{ \textbf{Output:}} %UseOutput in the format of Algorithm
使得原来软件包中定义的命令\REQUIRE和\ENSURE显示为Input:和Output:
一个例子如下:
\begin{algorithm}[htb]
\caption{ Framework of ensemble learning for our system.}
\label{alg:Framwork}
\begin{algorithmic}[1] %这个1 表示每一行都显示数字
\REQUIRE ~~\\ %算法的输入参数:Input
The set of positive samples for current batch, $P_n$;\\
The set of unlabelled samples for current batch, $U_n$;\\
Ensemble of classifiers on former batches, $E_{n-1}$;
\ENSURE ~~\\ %算法的输出:Output
Ensemble of classifiers on the current batch, $E_n$;
\STATE Extracting the set of reliable negative and/or positive samples $T_n$ from $U_n$ with help of $P_n$;
\label{ code:fram:extract }%对此行的标记,方便在文中引用算法的某个步骤
\STATE Training ensemble of classifiers $E$ on $T_n \cup P_n$, with help of data in former batches;
\label{code:fram:trainbase}
\STATE $E_n=E_{n-1}\cup E$;
\label{code:fram:add}
\STATE Classifying samples in $U_n-T_n$ by $E_n$;
\label{code:fram:classify}
\STATE Deleting some weak classifiers in $E_n$ so as to keep the capacity of $E_n$;
\label{code:fram:select}
\RETURN $E_n$; %算法的返回值
\end{algorithmic}
\end{algorithm}
排版结果如下:
5)一个例子
\begin{algorithm}[h]
\caption{An example for format For \& While Loop in Algorithm}
\begin{algorithmic}[1]
\FOR{each $i \in [1,9]$}
\STATE initialize a tree $T_{i}$ with only a leaf (the root);\
\STATE $T=T \cup T_{i};$\
\ENDFOR
\FORALL {$c$ such that $c \in RecentMBatch(E_{n-1})$}
\label{code:TrainBase:getc}
\STATE $T=T \cup PosSample(c)$;
\label{code:TrainBase:pos}
\ENDFOR
\FOR{$i=1$; $i<n$; $i++$ }
\STATE $//$ Your source here;
\ENDFOR
\FOR{$i=1$ to $n$}
\STATE $//$ Your source here;
\ENDFOR
\STATE $//$ Reusing recent base classifiers.
\label{code:recentStart}
\WHILE {$(|E_n| \leq L_1 )and( D \neq \phi)$}
\STATE Selecting the most recent classifier $c_i$ from $D$;
\STATE $D=D-c_i$;
\STATE $E_n=E_n+c_i$;
\ENDWHILE
\label{code:recentEnd}
\end{algorithmic}
\end{algorithm}
排版结果如下:

6)开始中头部加入
\makeatletter
\newenvironment{breakablealgorithm}
{% \begin{breakablealgorithm}
\begin{center}
\refstepcounter{algorithm}% New algorithm
\hrule height.8pt depth0pt \kern2pt% \@fs@pre for \@fs@ruled
\renewcommand{\caption}[2][\relax]{% Make a new \caption
{
\raggedright\textbf{\ALG@name~\thealgorithm} ##2\par}%
\ifx\relax##1\relax % #1 is \relax
\addcontentsline{loa}{algorithm}{\protect\numberline{\thealgorithm}##2}%
\else % #1 is not \relax
\addcontentsline{loa}{algorithm}{\protect\numberline{\thealgorithm}##1}%
\fi
\kern2pt\hrule\kern2pt
}
}{% \end{breakablealgorithm}
\kern2pt\hrule\relax% \@fs@post for \@fs@ruled
\end{center}
}
\makeatother
算法中使用:
\begin{breakablealgorithm}
\caption{Multi task balanced scheduling algorithm}
\label{alg1}
\begin{algorithmic}[1]
%%%REQUIRE 输入
\REQUIRE ~~\\
$G$ = 250;
Size = 30;
CodeL = 10;
\FOR{$i = 1:3$}
\STATE Min $X(i)$ = 0.1 * ones(1);
\STATE Max $X(i)$ = 3 * ones(1);
\ENDFOR
\FOR{$i = 4:1:9$}
\STATE Min $X(i)$ = -3 * ones(1);
\STATE Max $X(i)$ = 3 * ones(1);
\ENDFOR
\FOR{$i = 10:1:12$}
\STATE Min $X(i)$ = -ones(1);
\STATE Max $X(i)$ = ones(1);
\ENDFOR
\STATE $E$ = round(rand(Size,12*CodeL));
\STATE BsJ = 0;
\FOR{$kg = 1:1:G$}
\STATE time(kg) = kg
\FOR{$s$ = 1:1:Size}
\STATE $m = E(s,:)$;
\FOR{$j = 1:1:12$}
\STATE $y(j) = 0;$
\STATE $mj = m((j-1)$ * CodeL + $1:1:j$ * CodeL);
\FOR{$i = 1:1:$CodeL}
\STATE $y(j) = y(j) + mj(i) * 2^(i - 1);$
\ENDFOR
\STATE $f(s,j) =$ (Max $X(j)$ - Min $X(j)$) * $y(j)/1023$ + Min $X(j)$;
\ENDFOR
\STATE $p = f(s,:);$
\STATE [p,BsJ] = fitness(p,BsJ);
\STATE BsJi(s) = BsJ;
\ENDFOR
\STATE [OderJi,IndexJi] = sort(BsJi);
\STATE BestJ(kg) = OderJi(1);
\STATE BJ = BestJ(kg);
\STATE Ji = BsJi + 1e-10;
\STATE fi = 1./Ji;
\STATE [Oderfi,Indexfi] = sort(fi);
\STATE Bestfi = Oderfi(Size);
\STATE BestS = E(Indexfi(Size),:);
\STATE kg
\STATE p
\STATE BJ
\STATE fi\_sum = sum(fi);
\STATE fi\_Size = (Oderfi/fi\_sum) * Size;
\STATE fi\_S = floor(fi\_Size);
\ENDFOR
%%%%%注意下句 ensure 输出
\ENSURE
\STATE kk = 1;
\FOR{$i = 1:1:$Size}
\FOR{$j = 1:1:$fi\_S(i)}
\STATE TempE(kk,:) = E(Indexfi(i),:);
\STATE kk = kk + 1;
\ENDFOR
\ENDFOR
\end{algorithmic}
\end{breakablealgorithm}
样式:


7)例子7
\begin{algorithm}[!htb]
\caption{Low latency video coding rate control algorithm}
\label{alg1}
\begin{algorithmic}[1]
\FOR{$n=1$ to $N$}
\STATE $G n=S B S_{n}$;
\ENDFOR
\STATE $G=\left\{G_{1}, G_{2}, \ldots G_{N}\right\}$
\STATE $N=\{G, G, \ldots, G\}$
\WHILE{The minimum value of $L$ is less than $K$}
\STATE Find out the subscripts of the two groups corresponding to the minimum value of $n^{*}, m^{*}$;
\STATE $G_{m^{*}}$ and $G_{n^{*}}$ were removed from $G$;
\STATE Merge $\left\{G_{n^{*}}, G_{m^{*}}\right\}$ into $G$;
\STATE Reset $L$ to null;
\FOR{$G_{n} \subset G$ and $n>0$}
\FOR{$G_{m} \subset G$ and $m>n$}
\STATE $L^{\prime} \leftarrow L\left(G_{n}, G_{m}\right)$; $m$\hspace{2pt}-\hspace{-2pt} -; $n$\hspace{2pt}-\hspace{-2pt} -
\ENDFOR
\ENDFOR
\ENDWHILE
\ENSURE group set $G$;
\end{algorithmic}
\end{algorithm}
样式:
