本篇介绍C语言函数大全-- u 开头的函数
1. ultoa
1.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 |
函数功能 |
char *ultoa(unsigned long value, char *str, int base); |
用于将无符号长整型数转换成指定基数下的字符串表示 |
参数:
-
value : 要转换的无符号长整型数
-
str : 用于存储转换后的字符串
-
base : 要使用的进制数,可以为 2、8、10 或 16
函数 ultoa() 将参数 value 转换为以 base 进制表示的形式,并将结果存储在缓冲区 str 中。如果转换成功,则返回指向 str 的指针。
注意: 函数 ultoa() 不会检查缓冲区是否足够大,因此调用者需要确保缓冲区足够大以避免发生缓冲区溢出。
1.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
unsigned long num = 0xDEADBEEF;
char str[20];
_ultoa(num, str, 16);
printf("The hexadecimal representation of %lu is %s\n", num, str);
return 0;
}
1.3 运行结果
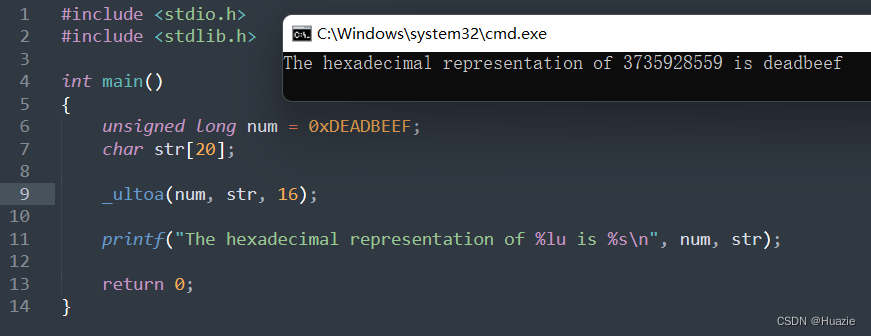
2. ungetc
2.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 |
函数功能 |
int ungetc(int c, FILE *stream); |
用于将字符推回输入流中 |
参数:
-
c : 要推回的字符
-
stream : 要推回字符的文件指针
2.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
//int ungetc(int c, FILE *stream);
int main()
{
int c;
FILE *fp = fopen("test.txt", "r");
if (fp == NULL)
{
printf("Failed to open file\n");
return 1;
}
// 读取一个字符
c = fgetc(fp);
if (c == EOF)
{
printf("Failed to read character\n");
return 1;
}
printf("Read character: %c\n", c);
// 推回字符到输入流中
if (ungetc(c, fp) == EOF)
{
printf("Failed to unget character\n");
return 1;
}
// 再次读取字符
c = fgetc(fp);
if (c == EOF)
{
printf("Failed to read character\n");
return 1;
}
printf("Read character again: %c\n", c);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
在上面的示例代码中,
- 我们首先打开了一个名为
test.txt 的文本文件;
- 接着,使用
fgetc() 函数从中读取一个字符;
- 然后,我们使用
ungetc() 函数将该字符推回输入流中;
- 再接着使用
fgetc() 函数从输入流中读取字符;
- 最后,我们使用
printf() 函数将两次读取的字符打印到标准输出流中。
注意: 在使用 ungetc() 函数推回字符之前,必须先读取一个字符并检查其是否成功读取。否则,ungetc() 函数将无法确定将字符推回哪个位置。
2.3 运行结果
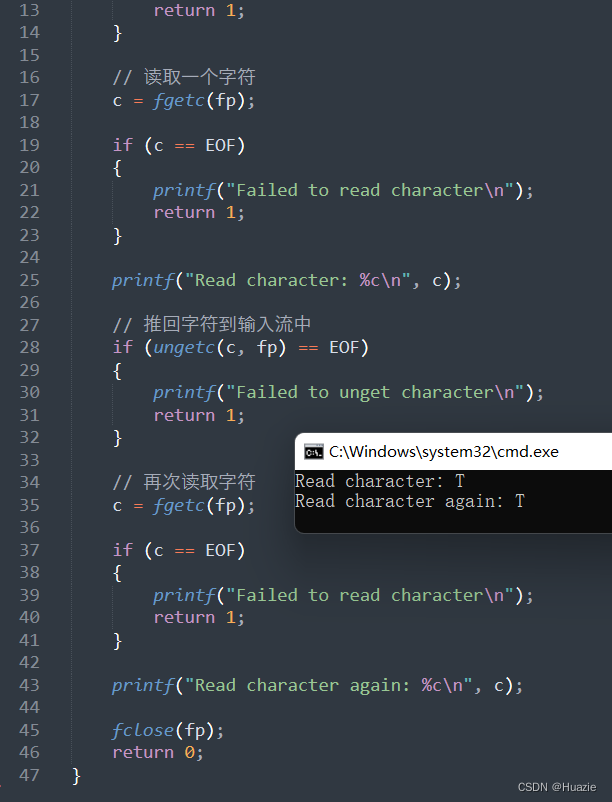
3. ungetch
3.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 |
函数功能 |
int ungetch(int c); |
用于将字符推回输入流中 |
参数:
3.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <conio.h>
int main()
{
int i=0;
char ch;
puts("Input an integer followed by a char:");
while((ch = getche()) != EOF && isdigit(ch))
i = 10 * i + ch - 48;
if (ch != EOF)
ungetch(ch);
printf("\n\ni = %d, next char in buffer = %c\n", i, getch());
return 0;
}
在上述的示例代码中,
- 我们首先输出一条提示信息
"Input an integer followed by a char:"
- 接着,通过循环调用
getche() 函数从输入流中逐个读取字符,并检查它是否是数字字符。如果是数字字符,则将其转换为整数并存储在变量 i 中。
- 然后,在读取到非数字字符时,使用
ungetch() 函数将该字符推回输入流中,以保留它供后续使用。
- 最后,使用
getch() 函数从输入流中读取一个字符,并打印出读取到的下一个字符和此时 i 的值。
注意: getch() 和 ungetch() 函数通常只在 Windows 平台上可用,因此这段代码可能不可移植到其他操作系统或编译器中。
3.3 运行结果
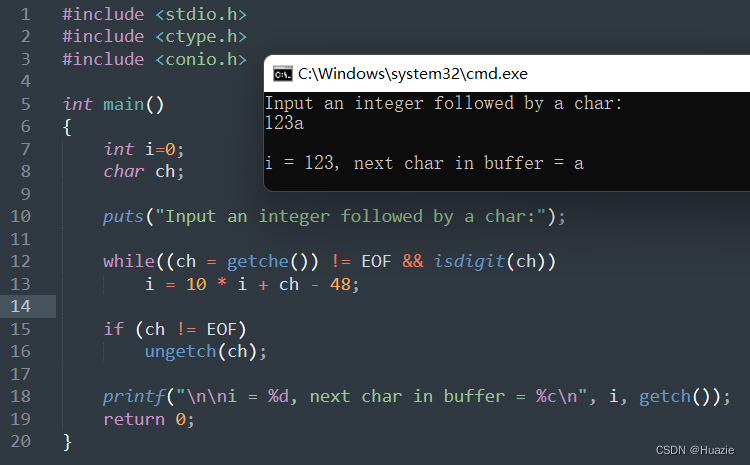
4. unix2dos
4.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 |
函数功能 |
int unix2dos(const char *src_file, const char *dst_file); |
用于将文本文件的行末标志符从 Unix 风格的 \n 转换为 Windows/DOS 风格的 \r\n
|
int dos2unix(const char *src_file, const char *dst_file); |
用于将将文本文件的行末标志符从 Windows/DOS 风格的 \r\n 转换为 Unix 风格的 \n
|
参数:
-
src_file : 要转换的源文件名
-
dst_file : 转换后保存到的目标文件名
返回值:
- 如果转换成功,则返回
0;
- 否则返回一个 非零值, 表示错误代码。
4.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int unix2dos(const char *src_file, const char *dst_file);
int dos2unix(const char *src_file, const char *dst_file);
int main()
{
int status;
// 将 Unix 格式的文件转换为 DOS 格式
status = unix2dos("input_unix.txt", "output_dos.txt");
if (status != 0)
{
printf("Failed to convert file: %d\n", status);
return 1;
}
// 将 DOS 格式的文件转换为 Unix 格式
status = dos2unix("input_dos.txt", "output_unix.txt");
if (status != 0)
{
printf("Failed to convert file: %d\n", status);
return 1;
}
printf("File conversion successful\n");
return 0;
}
int unix2dos(const char *src_file, const char *dst_file)
{
FILE *in = fopen(src_file, "r");
FILE *out = fopen(dst_file, "w");
if (in == NULL || out == NULL)
return -1;
int c;
while ((c = fgetc(in)) != EOF)
{
if (c == '\n')
fputc('\r', out);
fputc(c, out);
}
fclose(in);
fclose(out);
return 0;
}
int dos2unix(const char *src_file, const char *dst_file)
{
FILE *in = fopen(src_file, "r");
FILE *out = fopen(dst_file, "w");
if (in == NULL || out == NULL)
return -1;
int c;
int prev = -1;
while ((c = fgetc(in)) != EOF)
{
if (prev == '\r' && c == '\n')
{
// skip CR character
prev = c;
continue;
}
fputc(c, out);
prev = c;
}
fclose(in);
fclose(out);
return 0;
}
5. unlink
5.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 |
函数功能 |
int unlink(const char *pathname); |
用于删除指定文件 |
参数:
5.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
int status;
// 删除指定文件
status = unlink("huazie.txt");
if (status != 0)
{
printf("Failed to delete file: %d\n", status);
return 1;
}
printf("File deletion successful\n");
return 0;
}
在上面的示例代码中,我们使用 unlink() 函数删除了当前目录下名为 huazie.txt 的文件。如果 unlink() 函数返回值不为 0,则说明删除操作失败,可能是由于权限不足、文件不存在或其他原因导致的。如果删除操作成功,则会输出一条简短的提示信息 "File deletion successful"。
注意: 由于删除操作无法撤销,并且被删除的文件内容将无法恢复,因此在使用 unlink() 函数删除文件时需要小心谨慎,建议在执行此类敏感操作之前进行备份或确认。
5.3 运行结果
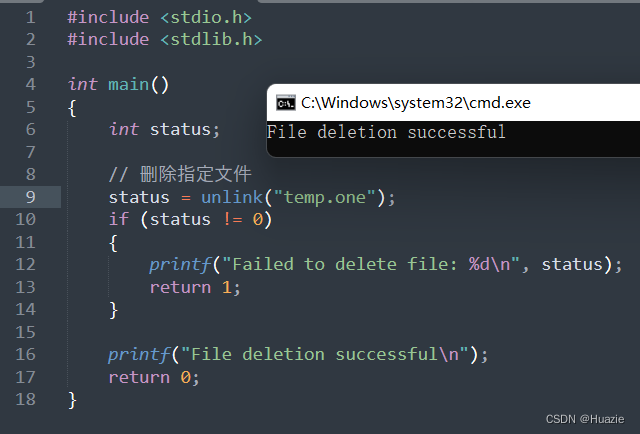
6. unlock
6.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 |
函数功能 |
int unlock(int handle, long offset, long length); |
它不是标准 C 库中的函数,而是 Linux/Unix 系统下用于文件锁定和解锁的函数 |
参数:
-
handle : 要解锁的文件句柄
-
offset: 解锁操作的起始偏移量(以字节为单位)。通常情况下,偏移量应该为正整数,代表从文件开头开始的偏移量。如果
offset 参数小于零,则将从文件末尾开始向前计算偏移量。
-
length: 要解锁的字节数
6.2 演示示例
#include <io.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys\stat.h>
#include <process.h>
#include <share.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys\locking.h>
int main(void)
{
int handle, status;
long length;
// 打开名为 test.txt 的文件
handle = sopen("test.txt",O_RDONLY,SH_DENYNO,S_IREAD);
if (handle < 0)
{
printf("sopen failed\n");
exit(1);
}
// 获取文件长度
length = filelength(handle);
// 锁定上面打开的文件
status = lock(handle,0L,length/2);
// 检查锁定操作是否成功,返回0,表示成功,返回非0,则加锁失败
if (status == 0)
printf("lock succeeded\n");
else
printf("lock failed\n");
// 对上面锁定的文件进行解除锁定
status = unlock(handle,0L,length/2);
// 检查解除锁定操作是否成功,返回0,表示成功,返回非0,则解锁失败
if (status == 0)
printf("unlock succeeded\n");
else
printf("unlock failed\n");
// 关闭文件句柄
close(handle);
return 0;
}
7. UnlockFile
7.1 函数说明
| 函数声明 |
函数功能 |
BOOL UnlockFile(HANDLE hFile, DWORD dwFileOffsetLow, DWORD dwFileOffsetHigh, DWORD nNumberOfBytesToUnlockLow, DWORD nNumberOfBytesToUnlockHigh); |
用于对文件进行解锁操作 |
参数:
-
hFile : 要解锁的文件句柄
-
dwFileOffsetLow 和 dwFileOffsetHigh: 解锁操作的起始偏移量(以字节为单位)。由于文件大小可能超过
4GB,因此需要使用两个参数表示完整的偏移量
-
nNumberOfBytesToUnlockLow 和 nNumberOfBytesToUnlockHigh: 要解锁的字节数。同样地,这些参数也需要使用两个参数表示完整的字节数
7.2 演示示例
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
HANDLE file_handle;
DWORD bytes_written;
OVERLAPPED overlapped = {0};
DWORD offset = 0;
DWORD length = 0;
BOOL status;
// 打开指定文件并获取文件句柄
file_handle = CreateFile("test.txt", GENERIC_WRITE, 0, NULL, CREATE_ALWAYS,
FILE_ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL, NULL);
if (file_handle == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
{
printf("Failed to open file\n");
return 1;
}
// 将字符串写入文件
const char *data = "Hello, world!";
status = WriteFile(file_handle, data, strlen(data), &bytes_written, &overlapped);
if (!status)
{
printf("Failed to write to file\n");
CloseHandle(file_handle);
return 1;
}
// 锁定文件的前半部分
length = GetFileSize(file_handle, NULL) / 2;
status = LockFile(file_handle, offset, 0, length, 0);
if (!status)
{
printf("Failed to lock file\n");
CloseHandle(file_handle);
return 1;
}
printf("File locked successfully\n");
// 解锁文件的前半部分
status = UnlockFile(file_handle, offset, 0, length, 0);
if (!status)
printf("Failed to unlock file\n");
else
printf("File unlocked successfully\n");
// 关闭文件句柄并返回
CloseHandle(file_handle);
return 0;
}
在上面的示例代码中,
- 我们首先使用
Windows API 中的 CreateFile() 函数打开名为 test.txt 的文件,并获取其文件句柄;
- 然后,我们使用
WriteFile() 函数将字符串写入文件;
- 接着,我们使用
LockFile() 函数对文件进行锁定操作,并使用 UnlockFile() 函数进行解锁操作;
- 最后,我们关闭文件句柄并退出程序。
注意:在使用 UnlockFile() 函数时,需要确保已经使用 CreateFile() 或其他文件打开函数打开了文件,并获得了有效的文件句柄。
7.3 运行结果
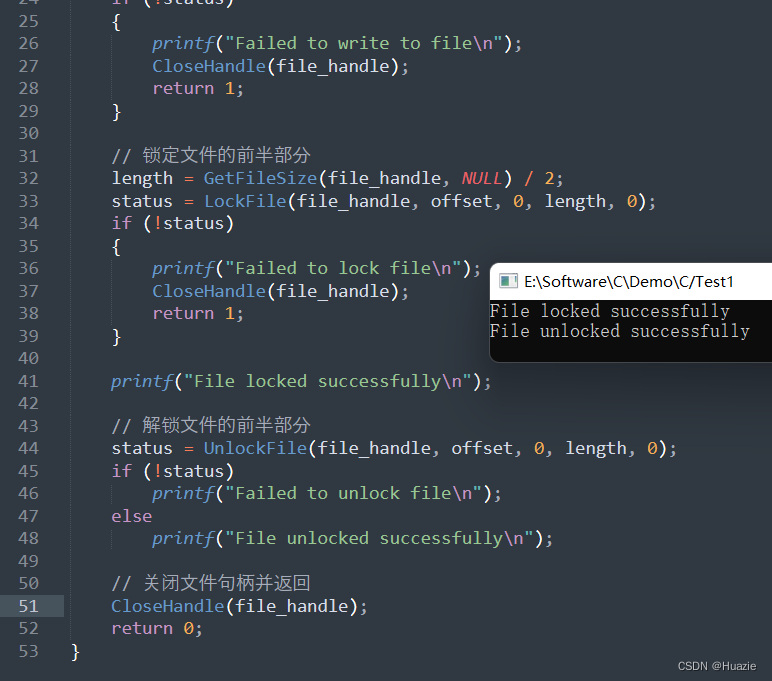
参考
- [API Reference Document]
- [LockFile function]