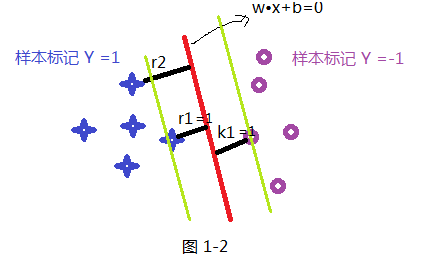
最近在学习svm算法,借此文章记录自己的学习过程,在学习很多处借鉴了z老师的讲义和李航的统计,若有不足的地方,请海涵;svm算法通俗的理解在二维上,就是找一分割线把两类分开,问题是如下图三条颜色都可以把点和星划开,但哪条线是最优的呢,这就是我们要考虑的问题;

首先我们先假设一条直线为 W•X+b =0 为最优的分割线,把两类分开如下图所示,那我们就要解决的是怎么获取这条最优直线呢?及W 和 b 的值;在SVM中最优分割面(超平面)就是:能使支持向量和超平面最小距离的最大值;
我们的目标是寻找一个超平面,使得离超平面比较近的点能有更大的间距。也就是我们不考虑所有的点都必须远离超平面,我们关心求得的超平面能够让所有点中离它最近的点具有最大间距。
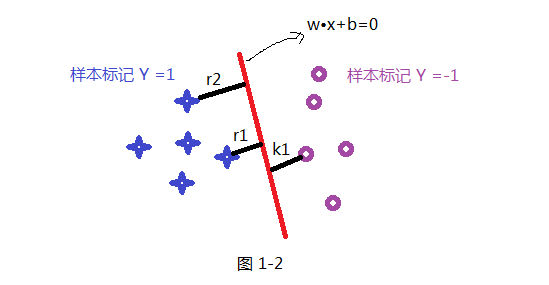
如上面假设蓝色的星星类有5个样本,并设定此类样本标记为Y =1,紫色圈类有5个样本,并设定此类标记为 Y =-1,共 T ={(X₁ ,Y₁) , (X₂,Y₂) (X₃,Y₃) .........} 10个样本,超平面(分割线)为wx+b=0; 样本点到超平面的几何距离为:
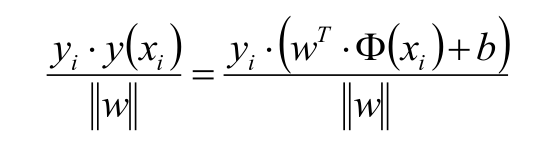
此处要说明一下:函数距离和几何距离的关系;定义上把 样本| w▪x₁+b|的距离叫做函数距离,而上面公式为几何距离,你会发现当w 和b 同倍数增加时候,函数距离也会通倍数增加;简单个例子就是,样本 X₁ 到 2wX₁+2b =0的函数距离是wX₁ +b =0的函数距离的 2倍;而几何矩阵不变;
下面我们就要谈谈怎么获取超平面了?!
超平面就是满足支持向量到其最小距离最大,及是求:max [支持向量到超平面的最小距离] ;那只要算出支持向量到超平面的距离就可以了吧 ,而支持向量到超平面的最小距离可以表示如下公式:
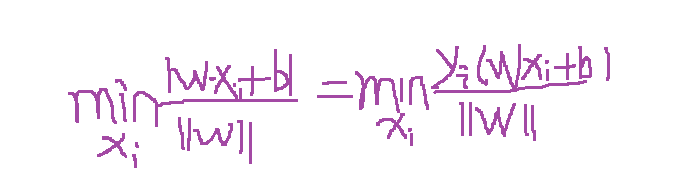
故最终优化的的公式为:
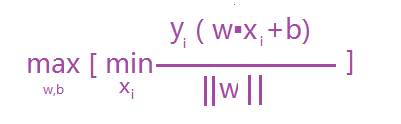
根据函数距离和几何距离可以得知,w和b增加时候,几何距离不变,故怎能通过同倍数增加w和 b使的支持向量(距离超平面最近的样本点)上样本代入 y(w*x+b) =1,而不影响上面公式的优化,样本点距离如下:如上图其r1函数距离为1,k1函数距离为1,而其它
样本点的函数距离大于1,及是:y(w•x+b)>=1,把此条件代入上面优化公式候,可以获取新的优化公式1-3:
公式1-3见下方:优化最大化分数,转化为优化最小化分母,为了优化方便转化为公式1-4
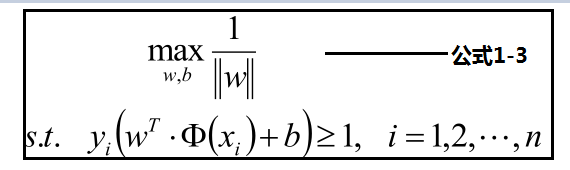
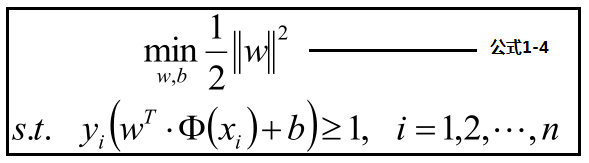
为了优化上面公式,使用拉格朗日公式和KTT条件优化公式转化为:
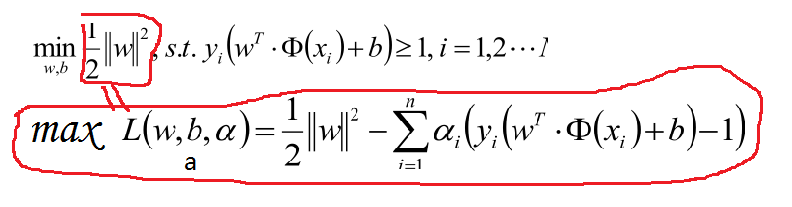
对于上面的优化公式在此说明一下:比如我们的目标问题是 minf(x)。可以构造函数L(a,b,x):
L(a,b,x)=f(x)+a⋅g(x)+b⋅h(x),a≥0
此时 f(x) 与 maxa,bL(a,b,x) 是等价的。因为 h(x)=0,g(x)≤0,a⋅g(x)≤0,所以只有在a⋅g(x)=0的情况下
L(a,b,x) 才能取得最大值,因此我们的目标函数可以写为minxmaxa,bL(a,b,x)。如果用对偶表达式:maxa,bminxL(a,b,x),
由于我们的优化是满足强对偶的(强对偶就是说对偶式子的最优值是等于原问题的最优值的),所以在取得最优值x∗ 的条件下,它满足 :
f(x∗)=maxa,bminxL(a,b,x)=minxmaxa,bL(a,b,x)=f(x∗),
结合上面的一度的对偶说明故我们的优化函数如下面,其中a >0

现在的优化方案到上面了,先求最小值,对 w 和 b 分别求偏导可以获取如下公式:

把上式获取的参数代入公式优化max值:
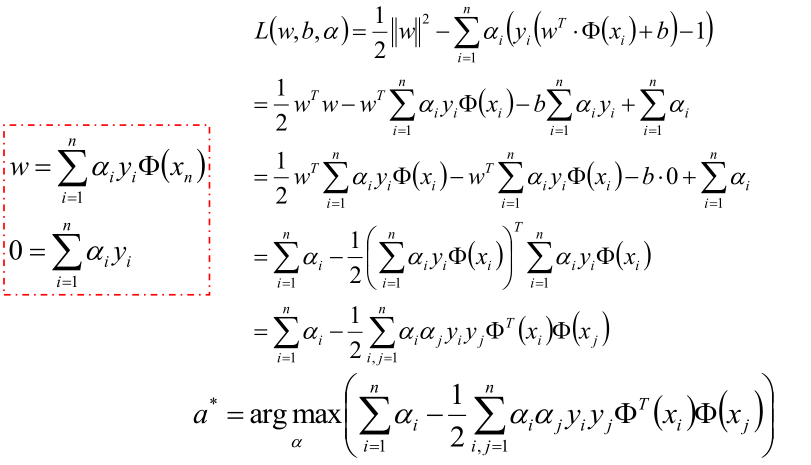
化解到最后一步,就可以获取最优的a值:


以上就可以获取超平面!
但在正常情况下可能存在一些特异点,将这些特异点去掉后,剩下的大部分点都能线性可分的,有些点线性不可以分,意味着此点的函数距离不是大于等于1,而是小于1的,为了解决这个问题,我们引进了松弛变量 ε>=0; 这样约束条件就会变成为:
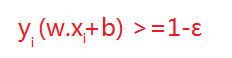
故原先的优化函数变为:

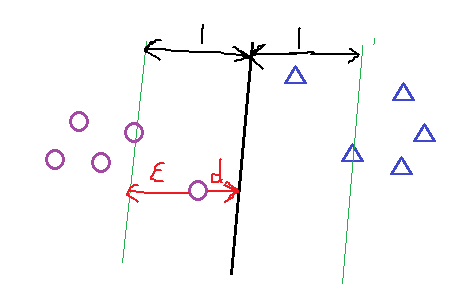
对加入松弛变量后有几点说明如下图所以;距离小于1的样本点离超平面的距离为d ,在绿线和超平面之间的样本点都是由损失的,
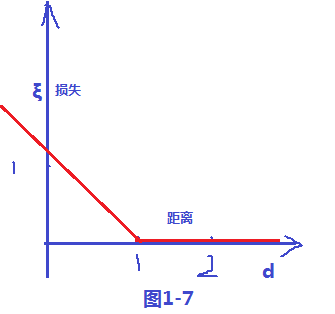
其损失变量和距离d 的关系,可以看出 ξ = 1-d , 当d >1的时候会发现ξ =0,当 d<1 的时候 ξ = 1-d ;故可以画出损失函数图,如下图1-7;样式就像翻书一样,我们把这个损失函数叫做 hinge损失;
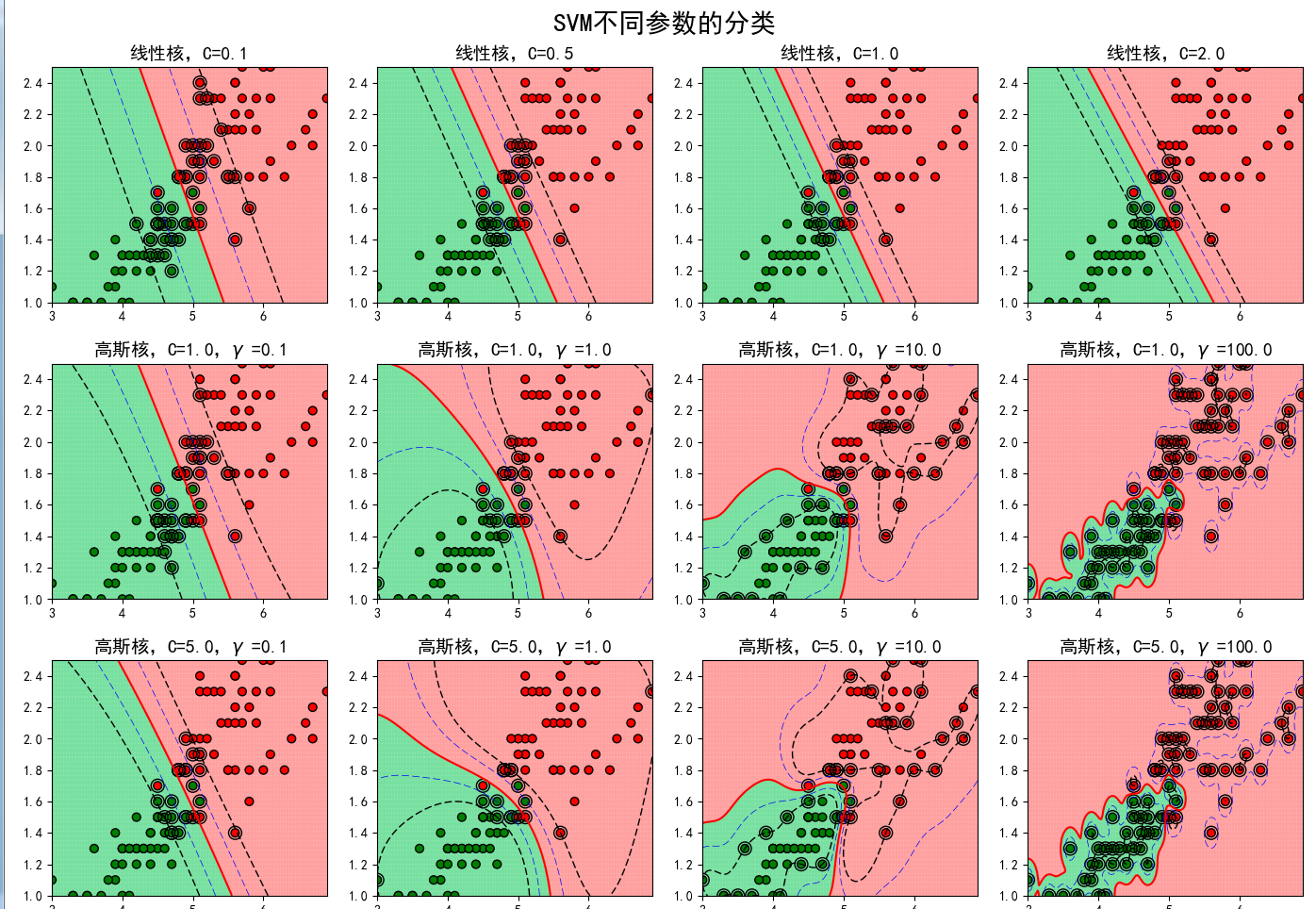
下面我们简单的就来讨论一下核函数:核函数的作用其实很简单就是把低维映射到高维中,便于分类。核函数有高斯核等,下面就直接上图看参数对模型的影响,从下图可以了解,当C变化时候,容错变小,泛化能力变小;当选择高斯核函数的时候,随时R参数调大,准确高提高,最终有过拟合风险;
% Project Title: Plant Leaf Disease Detection & Classification
function varargout = DetectDisease_GUI(varargin)
% DETECTDISEASE_GUI MATLAB code for DetectDisease_GUI.fig
% DETECTDISEASE_GUI, by itself, creates a new DETECTDISEASE_GUI or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = DETECTDISEASE_GUI returns the handle to a new DETECTDISEASE_GUI or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% DETECTDISEASE_GUI('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in DETECTDISEASE_GUI.M with the given input arguments.
%
% DETECTDISEASE_GUI('Property','Value',...) creates a new DETECTDISEASE_GUI or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before DetectDisease_GUI_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to DetectDisease_GUI_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help DetectDisease_GUI
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 26-Aug-2015 17:06:52
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @DetectDisease_GUI_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @DetectDisease_GUI_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before DetectDisease_GUI is made visible.
function DetectDisease_GUI_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to DetectDisease_GUI (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for DetectDisease_GUI
handles.output = hObject;
ss = ones(300,400);
axes(handles.axes1);
imshow(ss);
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(ss);
axes(handles.axes3);
imshow(ss);
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes DetectDisease_GUI wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = DetectDisease_GUI_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
%varargout{1} = handles.output;
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton1.
function pushbutton1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
%clear all
%close all
clc
[filename, pathname] = uigetfile({'*.*';'*.bmp';'*.jpg';'*.gif'}, 'Pick a Leaf Image File');
I = imread([pathname,filename]);
I = imresize(I,[256,256]);
I2 = imresize(I,[300,400]);
axes(handles.axes1);
imshow(I2);title('Query Image');
ss = ones(300,400);
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(ss);
axes(handles.axes3);
imshow(ss);
handles.ImgData1 = I;
guidata(hObject,handles);
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton3.
function pushbutton3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
I3 = handles.ImgData1;
I4 = imadjust(I3,stretchlim(I3));
I5 = imresize(I4,[300,400]);
axes(handles.axes2);
imshow(I5);title(' Contrast Enhanced ');
handles.ImgData2 = I4;
guidata(hObject,handles);
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton4.
function pushbutton4_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton4 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
I6 = handles.ImgData2;
I = I6;
%% Extract Features
% Function call to evaluate features
%[feat_disease seg_img] = EvaluateFeatures(I)
% Color Image Segmentation
% Use of K Means clustering for segmentation
% Convert Image from RGB Color Space to L*a*b* Color Space
% The L*a*b* space consists of a luminosity layer 'L*', chromaticity-layer 'a*' and 'b*'.
% All of the color information is in the 'a*' and 'b*' layers.
cform = makecform('srgb2lab');
% Apply the colorform
lab_he = applycform(I,cform);
% Classify the colors in a*b* colorspace using K means clustering.
% Since the image has 3 colors create 3 clusters.
% Measure the distance using Euclidean Distance Metric.
ab = double(lab_he(:,:,2:3));
nrows = size(ab,1);
ncols = size(ab,2);
ab = reshape(ab,nrows*ncols,2);
nColors = 3;
[cluster_idx cluster_center] = kmeans(ab,nColors,'distance','sqEuclidean', ...
'Replicates',3);
%[cluster_idx cluster_center] = kmeans(ab,nColors,'distance','sqEuclidean','Replicates',3);
% Label every pixel in tha image using results from K means
pixel_labels = reshape(cluster_idx,nrows,ncols);
%figure,imshow(pixel_labels,[]), title('Image Labeled by Cluster Index');
% Create a blank cell array to store the results of clustering
segmented_images = cell(1,3);
% Create RGB label using pixel_labels
rgb_label = repmat(pixel_labels,[1,1,3]);
for k = 1:nColors
colors = I;
colors(rgb_label ~= k) = 0;
segmented_images{k} = colors;
end
figure,subplot(2,3,2);imshow(I);title('Original Image'); subplot(2,3,4);imshow(segmented_images{1});title('Cluster 1'); subplot(2,3,5);imshow(segmented_images{2});title('Cluster 2');
subplot(2,3,6);imshow(segmented_images{3});title('Cluster 3');
set(gcf, 'Position', get(0,'Screensize'));
set(gcf, 'name','Segmented by K Means', 'numbertitle','off')
% Feature Extraction
pause(2)
x = inputdlg('Enter the cluster no. containing the ROI only:');
i = str2double(x);
% Extract the features from the segmented image
seg_img = segmented_images{i};
% Convert to grayscale if image is RGB
if ndims(seg_img) == 3
img = rgb2gray(seg_img);
end
%figure, imshow(img); title('Gray Scale Image');
% Evaluate the disease affected area
black = im2bw(seg_img,graythresh(seg_img));
%figure, imshow(black);title('Black & White Image');
m = size(seg_img,1);
n = size(seg_img,2);
zero_image = zeros(m,n);
%G = imoverlay(zero_image,seg_img,[1 0 0]);
cc = bwconncomp(seg_img,6);
diseasedata = regionprops(cc,'basic');
A1 = diseasedata.Area;
sprintf('Area of the disease affected region is : %g%',A1);
I_black = im2bw(I,graythresh(I));
kk = bwconncomp(I,6);
leafdata = regionprops(kk,'basic');
A2 = leafdata.Area;
sprintf(' Total leaf area is : %g%',A2);
%Affected_Area = 1-(A1/A2);
Affected_Area = (A1/A2);
if Affected_Area < 0.1
Affected_Area = Affected_Area+0.15;
end
sprintf('Affected Area is: %g%%',(Affected_Area*100))
Affect = Affected_Area*100;
% Create the Gray Level Cooccurance Matrices (GLCMs)
glcms = graycomatrix(img);
% Derive Statistics from GLCM
stats = graycoprops(glcms,'Contrast Correlation Energy Homogeneity');
Contrast = stats.Contrast;
Correlation = stats.Correlation;
Energy = stats.Energy;
Homogeneity = stats.Homogeneity;
Mean = mean2(seg_img);
Standard_Deviation = std2(seg_img);
Entropy = entropy(seg_img);
RMS = mean2(rms(seg_img));
%Skewness = skewness(img)
Variance = mean2(var(double(seg_img)));
a = sum(double(seg_img(:)));
Smoothness = 1-(1/(1+a));
Kurtosis = kurtosis(double(seg_img(:)));
Skewness = skewness(double(seg_img(:)));
% Inverse Difference Movement
m = size(seg_img,1);
n = size(seg_img,2);
in_diff = 0;
for i = 1:m
for j = 1:n
temp = seg_img(i,j)./(1+(i-j).^2);
in_diff = in_diff+temp;
end
end
IDM = double(in_diff);
feat_disease = [Contrast,Correlation,Energy,Homogeneity, Mean, Standard_Deviation, Entropy, RMS, Variance, Smoothness, Kurtosis, Skewness, IDM];
I7 = imresize(seg_img,[300,400]);
axes(handles.axes3);
imshow(I7);title('Segmented ROI');
%set(handles.edit3,'string',Affect);
set(handles.edit5,'string',Mean);
set(handles.edit6,'string',Standard_Deviation);
set(handles.edit7,'string',Entropy);
set(handles.edit8,'string',RMS);
set(handles.edit9,'string',Variance);
set(handles.edit10,'string',Smoothness);
set(handles.edit11,'string',Kurtosis);
set(handles.edit12,'string',Skewness);
set(handles.edit13,'string',IDM);
set(handles.edit14,'string',Contrast);
set(handles.edit15,'string',Correlation);
set(handles.edit16,'string',Energy);
set(handles.edit17,'string',Homogeneity);
handles.ImgData3 = feat_disease;
handles.ImgData4 = Affect;
% Update GUI
guidata(hObject,handles);
function edit2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit2 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit2 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit2_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function edit3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit3 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit3 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit3_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton5.
function pushbutton5_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton5 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
%% Evaluate Accuracy
load('Accuracy_Data.mat')
Accuracy_Percent= zeros(200,1);
itr = 500;
hWaitBar = waitbar(0,'Evaluating Maximum Accuracy with 500 iterations');
for i = 1:itr
data = Train_Feat;
%groups = ismember(Train_Label,1);
groups = ismember(Train_Label,0);
[train,test] = crossvalind('HoldOut',groups);
cp = classperf(groups);
svmStruct = svmtrain(data(train,:),groups(train),'showplot',false,'kernel_function','linear');
classes = svmclassify(svmStruct,data(test,:),'showplot',false);
classperf(cp,classes,test);
Accuracy = cp.CorrectRate;
Accuracy_Percent(i) = Accuracy.*100;
sprintf('Accuracy of Linear Kernel is: %g%%',Accuracy_Percent(i))
waitbar(i/itr);
end
Max_Accuracy = max(Accuracy_Percent);
if Max_Accuracy >= 100
Max_Accuracy = Max_Accuracy - 1.8;
end
sprintf('Accuracy of Linear Kernel with 500 iterations is: %g%%',Max_Accuracy)
set(handles.edit4,'string',Max_Accuracy);
delete(hWaitBar);
guidata(hObject,handles);
function edit4_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit4 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit4 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit4 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit4_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit4 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton6.
function pushbutton6_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton6 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
test = handles.ImgData3;
Affect = handles.ImgData4;
% Load All The Features
load('Training_Data.mat')
% Put the test features into variable 'test'
result = multisvm(Train_Feat,Train_Label,test);
%disp(result);
% Visualize Results
if result == 0
R1 = 'Alternaria Alternata';
set(handles.edit2,'string',R1);
set(handles.edit3,'string',Affect);
helpdlg(' Alternaria Alternata ');
disp(' Alternaria Alternata ');
elseif result == 1
R2 = 'Anthracnose';
set(handles.edit2,'string',R2);
set(handles.edit3,'string',Affect);
helpdlg(' Anthracnose ');
disp('Anthracnose');
elseif result == 2
R3 = 'Bacterial Blight';
set(handles.edit2,'string',R3);
set(handles.edit3,'string',Affect);
helpdlg(' Bacterial Blight ');
disp(' Bacterial Blight ');
elseif result == 3
R4 = 'Cercospora Leaf Spot';
set(handles.edit2,'string',R4);
set(handles.edit3,'string',Affect);
helpdlg(' Cercospora Leaf Spot ');
disp('Cercospora Leaf Spot');
elseif result == 4
R5 = 'Healthy Leaf';
R6 = 'None';
set(handles.edit2,'string',R5);
set(handles.edit3,'string',R6);
helpdlg(' Healthy Leaf ');
disp('Healthy Leaf ');
end
% Update GUI
guidata(hObject,handles);
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton7.
function pushbutton7_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton7 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
close all
function edit5_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit5 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit5 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit5 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit5_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit5 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function edit6_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit6 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit6 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit6 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit6_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit6 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function edit7_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit7 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit7 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit7 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit7_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit7 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function edit8_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit8 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit8 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit8 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit8_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit8 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function edit9_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit9 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit9 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit9 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit9_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit9 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function edit10_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit10 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit10 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit10 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit10_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit10 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function edit11_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit11 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit11 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit11 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit11_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit11 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function edit12_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit12 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit12 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit12 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit12_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit12 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function edit13_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit13 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit13 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit13 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit13_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit13 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function edit14_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit14 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit14 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit14 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit14_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit14 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function edit15_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit15 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit15 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit15 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit15_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit15 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function edit16_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit16 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit16 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit16 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit16_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit16 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
function edit17_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit17 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit17 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit17 as a double
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit17_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit17 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
