Tensorflow
Tensorflow官方教程
由于Google Colab在国内无法使用,推荐deepnote代替
基本分类:对服装图像进行分类
# TensorFlow and tf.keras
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
# Helper libraries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
print(tf.__version__)
fashion_mnist = keras.datasets.fashion_mnist
(train_images, train_labels), (test_images, test_labels) = fashion_mnist.load_data()
class_names = ['T-shirt/top', 'Trouser', 'Pullover', 'Dress', 'Coat',
'Sandal', 'Shirt', 'Sneaker', 'Bag', 'Ankle boot']
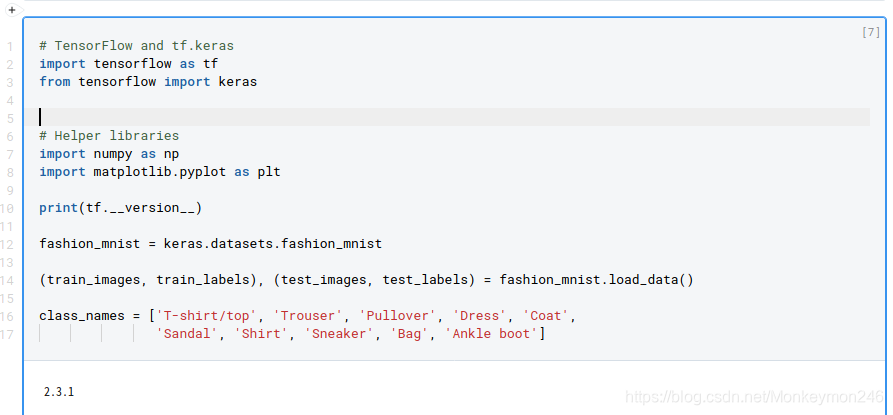
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(train_images[0])
plt.colorbar()
plt.grid(False)
plt.show()
train_images = train_images / 255.0
test_images = test_images / 255.0
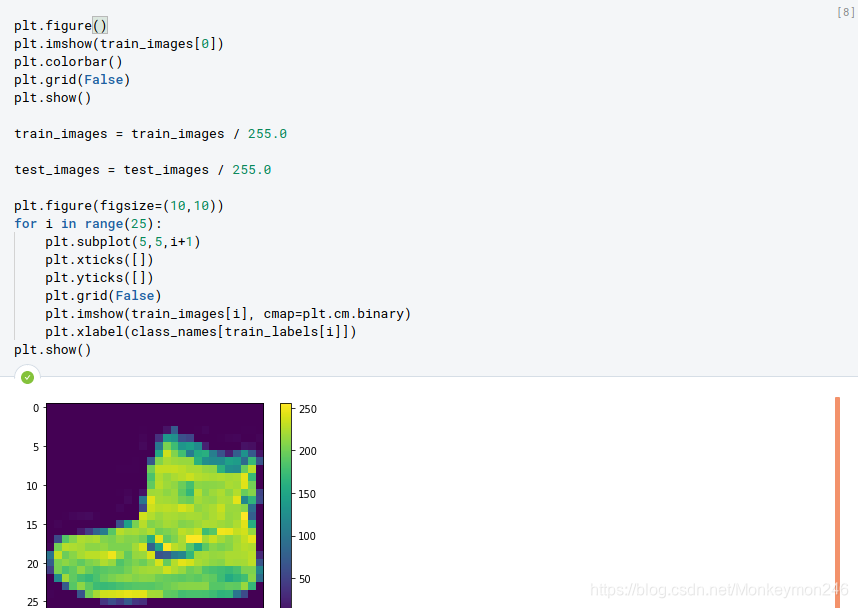
plt.figure(figsize=(10,10))
for i in range(25):
plt.subplot(5,5,i+1)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.grid(False)
plt.imshow(train_images[i], cmap=plt.cm.binary)
plt.xlabel(class_names[train_labels[i]])
plt.show()
 画图前:先使用 plt.figure() 来新创一个图片或者激活已经有的图片,而plt.colorbar()可以在图上加上那个深浅棒,plt.show()画出所有打开的图片
画图前:先使用 plt.figure() 来新创一个图片或者激活已经有的图片,而plt.colorbar()可以在图上加上那个深浅棒,plt.show()画出所有打开的图片
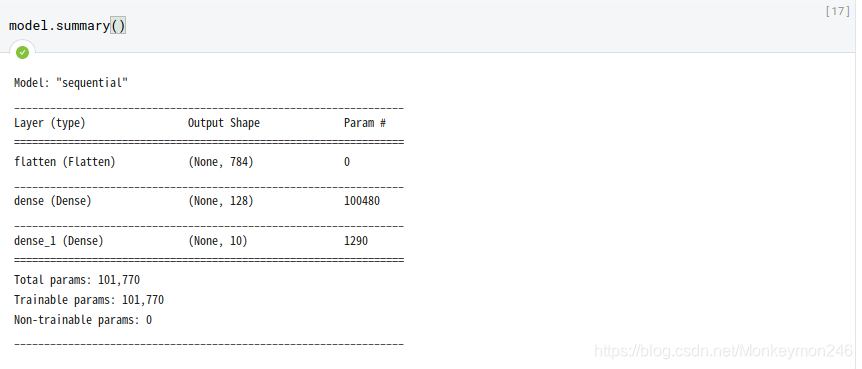
model = keras.Sequential([
keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28)),
keras.layers.Dense(128, activation='relu'),
keras.layers.Dense(10)
])
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=['accuracy'])
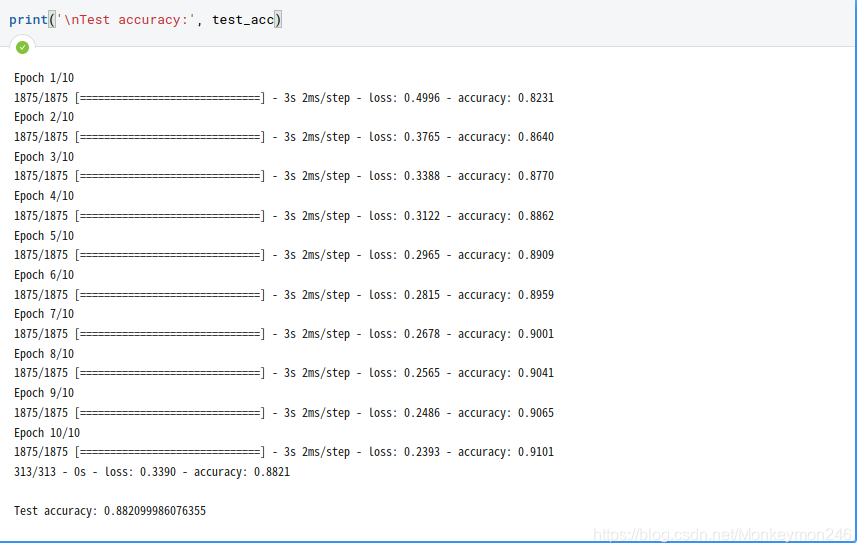
model.fit(train_images, train_labels, epochs=10)
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(test_images, test_labels, verbose=2)
print('\nTest accuracy:', test_acc)
probability_model = tf.keras.Sequential([model,
tf.keras.layers.Softmax()])
predictions = probability_model.predict(test_images)
print(predictions)
 这里有一个很有意思的事情,probability_model 是补充在model后的,按照正常的模型构建,理所当然以为应该在compile和fit前面,那是因为这层没有用到参数
这里有一个很有意思的事情,probability_model 是补充在model后的,按照正常的模型构建,理所当然以为应该在compile和fit前面,那是因为这层没有用到参数
 同理,flatten那层也没有用到参数
同理,flatten那层也没有用到参数
def plot_image(i, predictions_array, true_label, img):
predictions_array, true_label, img = predictions_array, true_label[i], img[i]
plt.grid(False)
plt.xticks([])
plt.yticks([])
plt.imshow(img, cmap=plt.cm.binary)
predicted_label = np.argmax(predictions_array)
if predicted_label == true_label:
color = 'blue'
else:
color = 'red'
plt.xlabel("{} {:2.0f}% ({})".format(class_names[predicted_label],
100*np.max(predictions_array),
class_names[true_label]),
color=color)
def plot_value_array(i, predictions_array, true_label):
predictions_array, true_label = predictions_array, true_label[i]
plt.grid(False)
plt.xticks(range(10))
plt.yticks([])
thisplot = plt.bar(range(10), predictions_array, color="#777777")
plt.ylim([0, 1])
predicted_label = np.argmax(predictions_array)
thisplot[predicted_label].set_color('red')
thisplot[true_label].set_color('blue')
i = 0
plt.figure(figsize=(6,3))
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plot_image(i, predictions[i], test_labels, test_images)
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plot_value_array(i, predictions[i], test_labels)
plt.show()
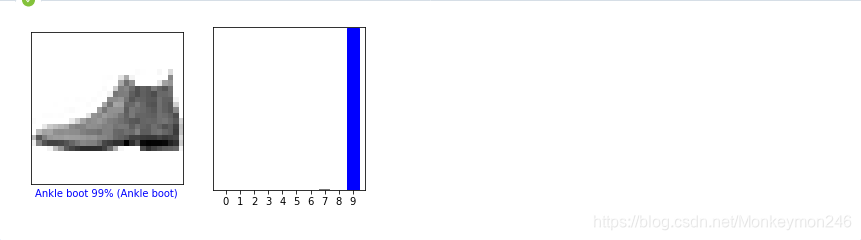
figsize 后面是inch。plt.subplot(1,2,1)和matlab的语法很像,1行2列中第一个
plt.xlabel X坐标写字
plt.imshow(img, cmap=plt.cm.binary) due to 图片是0-1
# Grab an image from the test dataset.
img = test_images[1]
print(img.shape)
# Add the image to a batch where it's the only member.
img = (np.expand_dims(img,0))
print(img.shape)
predictions_single = probability_model.predict(img)
print(predictions_single)
plot_value_array(1, predictions_single[0], test_labels)
_ = plt.xticks(range(10), class_names, rotation=45)
np.argmax(predictions_single[0])
官方说明:tf.keras 模型经过了优化,可同时对一个批或一组样本进行预测。因此,即便您只使用一个图像,您也需要将其添加到列表中:img = (np.expand_dims(img,0))
那个_ =是不要输出
电影评论文本分类
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
import numpy as np
print(tf.__version__)
imdb = keras.datasets.imdb
(train_data, train_labels), (test_data, test_labels) = imdb.load_data(num_words=10000)
print("Training entries: {}, labels: {}".format(len(train_data), len(train_labels)))
print(train_data[0])

len(train_data[0]), len(train_data[1])
# 一个映射单词到整数索引的词典
word_index = imdb.get_word_index()
# 保留第一个索引
word_index = {k:(v+3) for k,v in word_index.items()}
word_index["<PAD>"] = 0
word_index["<START>"] = 1
word_index["<UNK>"] = 2 # unknown
word_index["<UNUSED>"] = 3
reverse_word_index = dict([(value, key) for (key, value) in word_index.items()])
def decode_review(text):
return ' '.join([reverse_word_index.get(i, '?') for i in text])
decode_review(train_data[0])
train_data = keras.preprocessing.sequence.pad_sequences(train_data,
value=word_index["<PAD>"],
padding='post',
maxlen=256)
test_data = keras.preprocessing.sequence.pad_sequences(test_data,
value=word_index["<PAD>"],
padding='post',
maxlen=256)
影评——即整数数组必须在输入神经网络之前转换为张量。这种转换可以通过以下两种方式来完成:
将数组转换为表示单词出现与否的由 0 和 1 组成的向量,类似于 one-hot 编码。例如,序列[3, 5]将转换为一个 10,000 维的向量,该向量除了索引为 3 和 5 的位置是 1 以外,其他都为 0。然后,将其作为网络的首层——一个可以处理浮点型向量数据的稠密层。不过,这种方法需要大量的内存,需要一个大小为 num_words * num_reviews 的矩阵。
或者,我们可以填充数组来保证输入数据具有相同的长度,然后创建一个大小为 max_length * num_reviews 的整型张量。我们可以使用能够处理此形状数据的嵌入层作为网络中的第一层。
在本教程中,我们将使用第二种方法。
由于电影评论长度必须相同,我们将使用 pad_sequences 函数来使长度标准化
 train_data和test_data为什么能保证一样长度
train_data和test_data为什么能保证一样长度
# 输入形状是用于电影评论的词汇数目(10,000 词)
vocab_size = 10000
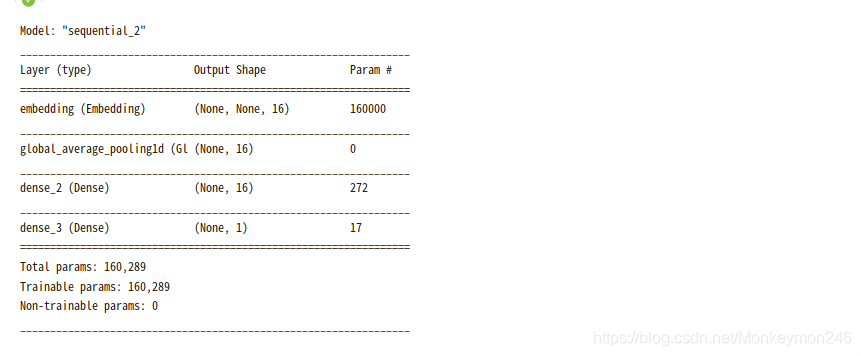
model = keras.Sequential()
model.add(keras.layers.Embedding(vocab_size, 16))
model.add(keras.layers.GlobalAveragePooling1D())
model.add(keras.layers.Dense(16, activation='relu'))
model.add(keras.layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
model.summary()
# 输入形状是用于电影评论的词汇数目(10,000 词)
vocab_size = 10000
model = keras.Sequential()
model.add(keras.layers.Embedding(vocab_size, 16))
model.add(keras.layers.GlobalAveragePooling1D())
model.add(keras.layers.Dense(16, activation='relu'))
model.add(keras.layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
model.summary()
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='binary_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
x_val = train_data[:10000]
partial_x_train = train_data[10000:]
y_val = train_labels[:10000]
partial_y_train = train_labels[10000:]
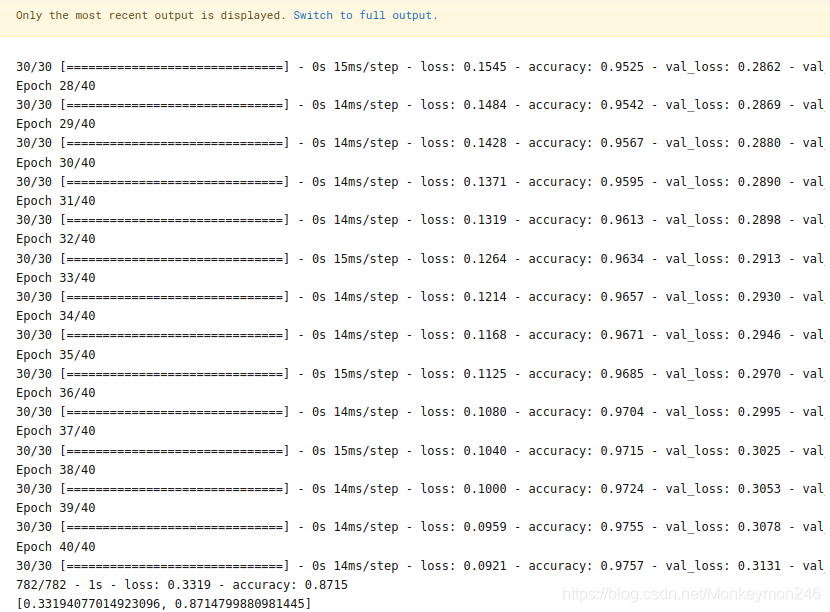
history = model.fit(partial_x_train,
partial_y_train,
epochs=40,
batch_size=512,
validation_data=(x_val, y_val),
verbose=1)
results = model.evaluate(test_data, test_labels, verbose=2)
print(results)
history_dict = history.history
history_dict.keys()
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
acc = history_dict['accuracy']
val_acc = history_dict['val_accuracy']
loss = history_dict['loss']
val_loss = history_dict['val_loss']
epochs = range(1, len(acc) + 1)
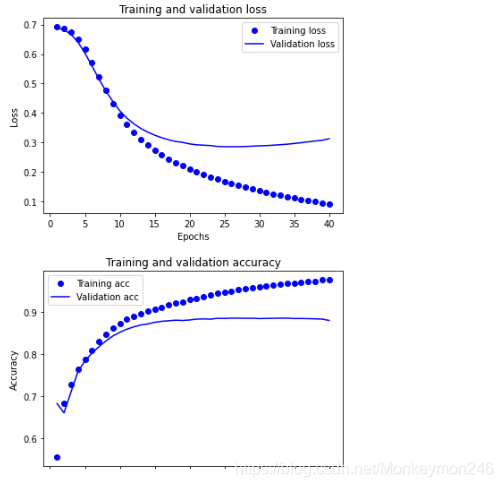
# “bo”代表 "蓝点"
plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'bo', label='Training loss')
# b代表“蓝色实线”
plt.plot(epochs, val_loss, 'b', label='Validation loss')
plt.title('Training and validation loss')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
plt.clf() # 清除数字
plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'bo', label='Training acc')
plt.plot(epochs, val_acc, 'b', label='Validation acc')
plt.title('Training and validation accuracy')
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
文本分类大概跑一下
validation_data=(x_val, y_val)验证集在这写
其中,history.history 该对象包含一个字典,其中包含训练阶段所发生的一切事件:
history_dict = history.history
history_dict.keys()
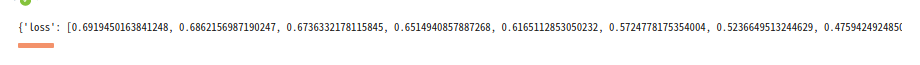
这个画loss的部分,可以学习下
Basic regression: Predict fuel efficiency
# 使用 seaborn 绘制矩阵图 (pairplot)
import pathlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import layers
print(tf.__version__)
dataset_path = keras.utils.get_file("auto-mpg.data", "http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/auto-mpg/auto-mpg.data")
dataset_path
下载UCI的数据 keras.utils.get_file,路径都写好了
‘/home/jovyan/.keras/datasets/auto-mpg.data’
column_names = ['MPG','Cylinders','Displacement','Horsepower','Weight',
'Acceleration', 'Model Year', 'Origin']
raw_dataset = pd.read_csv(dataset_path, names=column_names,
na_values = "?", comment='\t',
sep=" ", skipinitialspace=True)
dataset = raw_dataset.copy()
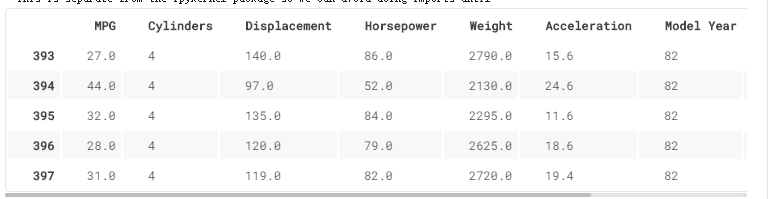
dataset.tail()
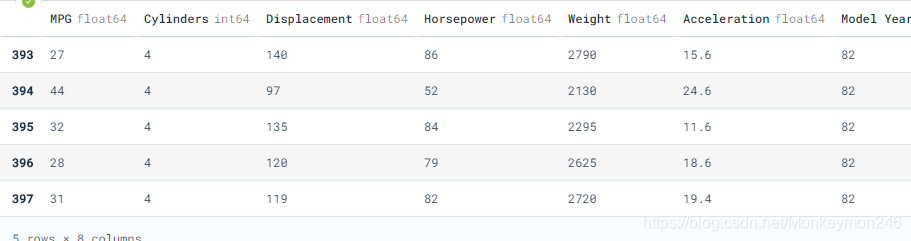
这个显示数据的方式太吊了:
dataset = raw_dataset.copy()
dataset.tail()
dataset.isna().sum()
dataset = dataset.dropna()
origin = dataset.pop('Origin')
snan判断是否nan(not a number)
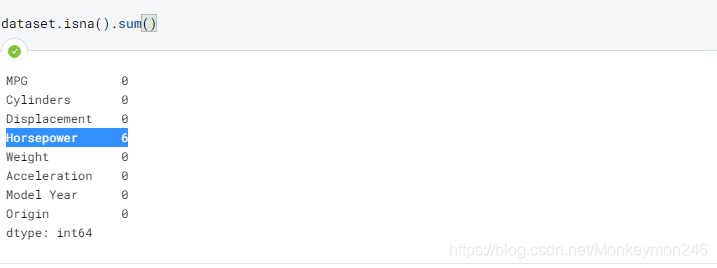
去掉之后,变成392 rows × 8 columns
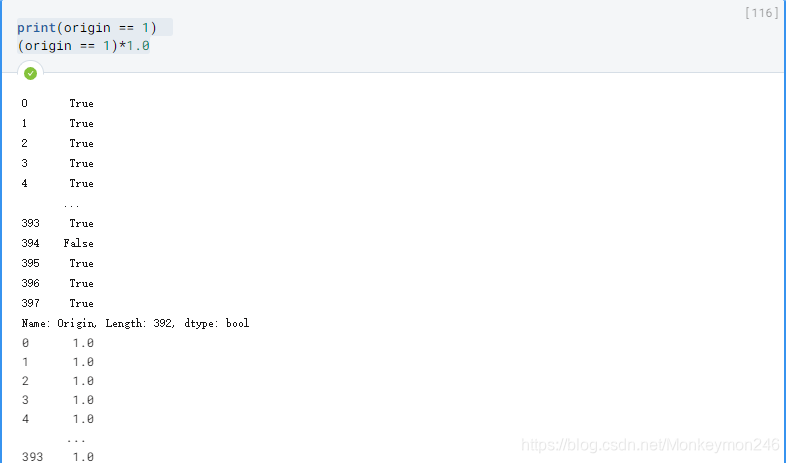
origin = dataset.pop('Origin')
dataset['USA'] = (origin == 1)*1.0
dataset['Europe'] = (origin == 2)*1.0
dataset['Japan'] = (origin == 3)*1.0
dataset.tail()
pop() 函数用于移除列表中的一个元素(默认最后一个元素),并且返回该元素的值。dataset[‘USA’]=392*1个数列,相当于赋值
dataset后三列,one hot
train_dataset = dataset.sample(frac=0.8,random_state=0)
test_dataset = dataset.drop(train_dataset.index)
快速查看训练集中几对列的联合分布。
这个地方,太酷了
train_dataset = dataset.sample(frac=0.8,random_state=0)
test_dataset = dataset.drop(train_dataset.index)
sns.pairplot(train_dataset[["MPG", "Cylinders", "Displacement", "Weight"]], diag_kind="kde")
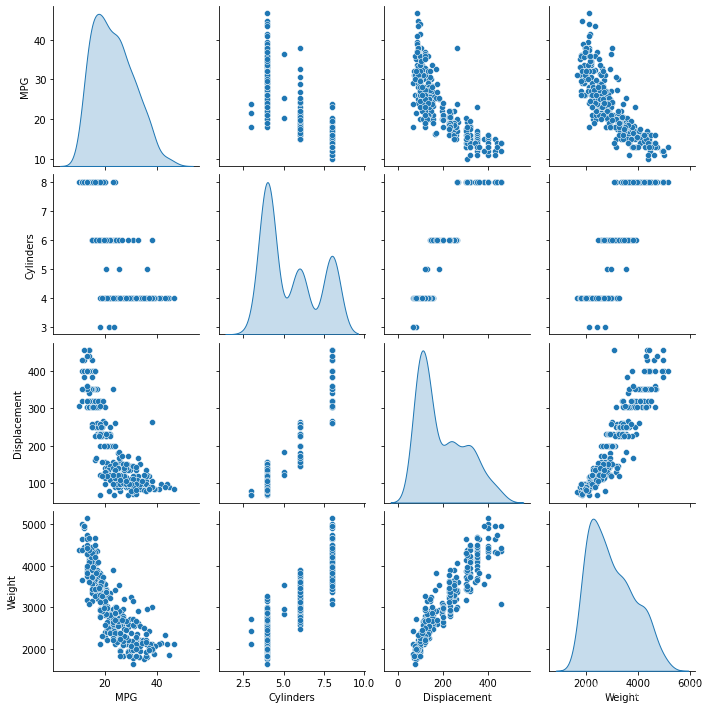
train_stats = train_dataset.describe()
train_stats.pop("MPG")
train_stats = train_stats.transpose()
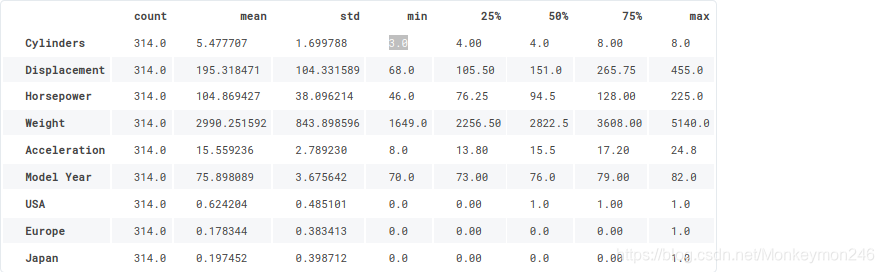
train_stats
查看总体的数据统计: 数量,平均值,方差,最小值,递增到最大值
train_labels = train_dataset.pop('MPG')
test_labels = test_dataset.pop('MPG')
一个很好的递归手段,利用describe()
再次审视下上面的 train_stats 部分,并注意每个特征的范围有什么不同。
使用不同的尺度和范围对特征归一化是好的实践。尽管模型可能 在没有特征归一化的情况下收敛,它会使得模型训练更加复杂,并会造成生成的模型依赖输入所使用的单位选择。
注意:尽管我们仅仅从训练集中有意生成这些统计数据,但是这些统计信息也会用于归一化的测试数据集。我们需要这样做,将测试数据集放入到与已经训练过的模型相同的分布中。
def norm(x):
return (x - train_stats['mean']) / train_stats['std']
normed_train_data = norm(train_dataset)
normed_test_data = norm(test_dataset)
模型是
def build_model():
model = keras.Sequential([
layers.Dense(64, activation='relu', input_shape=[len(train_dataset.keys())]),
layers.Dense(64, activation='relu'),
layers.Dense(1)
])
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.RMSprop(0.001)
model.compile(loss='mse',
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['mae', 'mse'])
return model
model = build_model()
model.summary()

example_batch = normed_train_data[:10]
example_result = model.predict(example_batch)
example_result
 训练模型
训练模型
对模型进行1000个周期的训练,并在 history 对象中记录训练和验证的准确性。
# 通过为每个完成的时期打印一个点来显示训练进度
class PrintDot(keras.callbacks.Callback):
def on_epoch_end(self, epoch, logs):
if epoch % 100 == 0: print('')
print('.', end='')
EPOCHS = 1000
history = model.fit(
normed_train_data, train_labels,
epochs=EPOCHS, validation_split = 0.2, verbose=0,
callbacks=[PrintDot()])
hist = pd.DataFrame(history.history)
hist['epoch'] = history.epoch
hist.tail()
def plot_history(history):
hist = pd.DataFrame(history.history)
hist['epoch'] = history.epoch
plt.figure()
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Mean Abs Error [MPG]')
plt.plot(hist['epoch'], hist['mae'],
label='Train Error')
plt.plot(hist['epoch'], hist['val_mae'],
label = 'Val Error')
plt.ylim([0,5])
plt.legend()
plt.figure()
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Mean Square Error [$MPG^2$]')
plt.plot(hist['epoch'], hist['mse'],
label='Train Error')
plt.plot(hist['epoch'], hist['val_mse'],
label = 'Val Error')
plt.ylim([0,20])
plt.legend()
plt.show()
plot_history(history)
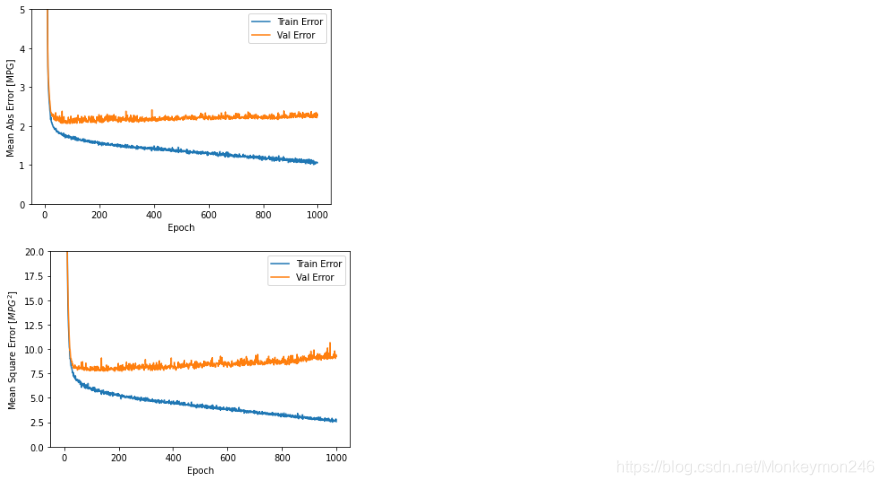
该图表显示在约100个 epochs 之后误差非但没有改进,反而出现恶化。 让我们更新 model.fit 调用,当验证值没有提高上是自动停止训练。 我们将使用一个 EarlyStopping callback 来测试每个 epoch 的训练条件。如果经过一定数量的 epochs 后没有改进,则自动停止训练。
model = build_model()
# patience 值用来检查改进 epochs 的数量
early_stop = keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(monitor='val_loss', patience=10)
history = model.fit(normed_train_data, train_labels, epochs=EPOCHS,
validation_split = 0.2, verbose=0, callbacks=[early_stop, PrintDot()])
plot_history(history)
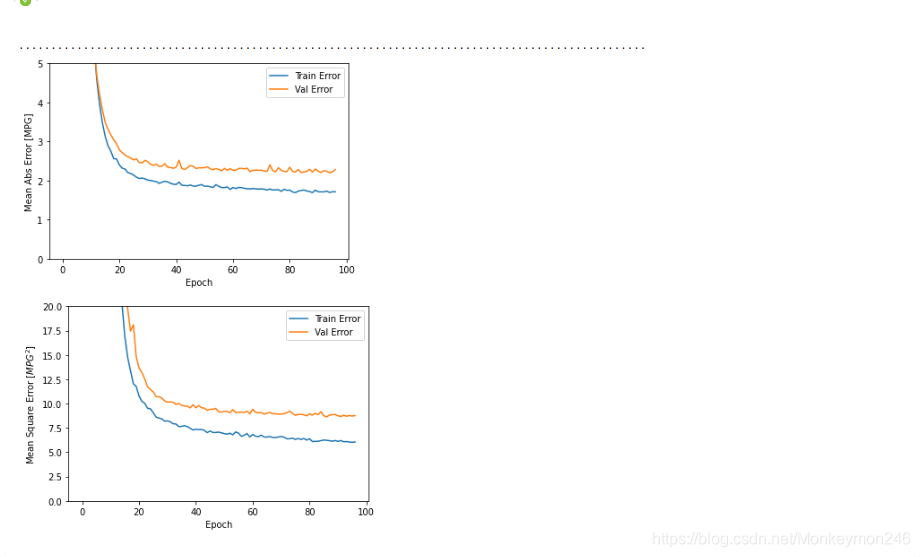
这个很好用啊,有木有,检测epochs 的数量
如图所示,验证集中的平均的误差通常在 +/- 2 MPG左右。 这个结果好么? 我们将决定权留给你。
给我?
loss, mae, mse = model.evaluate(normed_test_data, test_labels, verbose=2)
print("Testing set Mean Abs Error: {:5.2f} MPG".format(mae))
test_predictions = model.predict(normed_test_data).flatten()
plt.scatter(test_labels, test_predictions)
plt.xlabel('True Values [MPG]')
plt.ylabel('Predictions [MPG]')
plt.axis('equal')
plt.axis('square')
plt.xlim([0,plt.xlim()[1]])
plt.ylim([0,plt.ylim()[1]])
_ = plt.plot([-100, 100], [-100, 100])


error = test_predictions - test_labels
plt.hist(error, bins = 25)
plt.xlabel("Prediction Error [MPG]")
_ = plt.ylabel("Count")

过拟合和欠拟合
过拟合好理解,欠拟合的意思是在训练集上还有提升的空间
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import layers
from tensorflow.keras import regularizers
print(tf.__version__)
!pip install -q git+https://github.com/tensorflow/docs
import tensorflow_docs as tfdocs
import tensorflow_docs.modeling
import tensorflow_docs.plots
from IPython import display
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pathlib
import shutil
import tempfile
logdir = pathlib.Path(tempfile.mkdtemp())/"tensorboard_logs"
shutil.rmtree(logdir, ignore_errors=True)
The Higgs Dataset 包含11000000个示例,每个示例具有28个 features以及一个二进制类标签。
gz = tf.keras.utils.get_file('HIGGS.csv.gz', 'http://mlphysics.ics.uci.edu/data/higgs/HIGGS.csv.gz')
tf.data.experimental.CsvDataset类可用于直接从gzip文件读取csv记录,而无需中间的解压缩步骤。
FEATURES = 28
ds = tf.data.experimental.CsvDataset(gz,[float(),]*(FEATURES+1), compression_type="GZIP")
该csv阅读器类返回每个记录的标量列表。以下函数将该标量列表重新打包为(feature_vector,label)对。
def pack_row(*row):
label = row[0]
features = tf.stack(row[1:],1)
return features, label
packed_ds = ds.batch(10000).map(pack_row).unbatch()
当处理大量数据时,TensorFlow效率最高。因此,与其单独重新打包每一行,不如创建一个新的数据集,该数据集采用10000个examples的批次,将pack_row函数应用于每个批次,然后将这些批次拆分回各个记录:packed_ds = ds.batch(10000).map(pack_row).unbatch()
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
一些探索:
gz
‘/home/jovyan/.keras/datasets/HIGGS.csv.gz’
ds
<CsvDatasetV2 shapes: ((), (), (), (), (), (), (), (), (), (), (), (), (), (), (), (), (), (), (), (), (), (), (), (), (), (), (), (), ()), types: (tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32)>
ds.batch(10000)
<BatchDataset shapes: ((None,), (None,), (None,), (None,), (None,), (None,), (None,), (None,), (None,), (None,), (None,), (None,), (None,), (None,), (None,), (None,), (None,), (None,), (None,), (None,), (None,), (None,), (None,), (None,), (None,), (None,), (None,), (None,), (None,)), types: (tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32, tf.float32)>
ds.batch(10000).map(pack_row)
<MapDataset shapes: ((None, 28), (None,)), types: (tf.float32, tf.float32)>
ds.batch(10000).map(pack_row).unbatch()
<_UnbatchDataset shapes: ((28,), ()), types: (tf.float32, tf.float32)>
unbatch()将一个数据库分成多个元素
map()对每个数字进行处理
for features,label in packed_ds.batch(1000).take(1):
print(features[0])
plt.hist(features.numpy().flatten(), bins = 101)
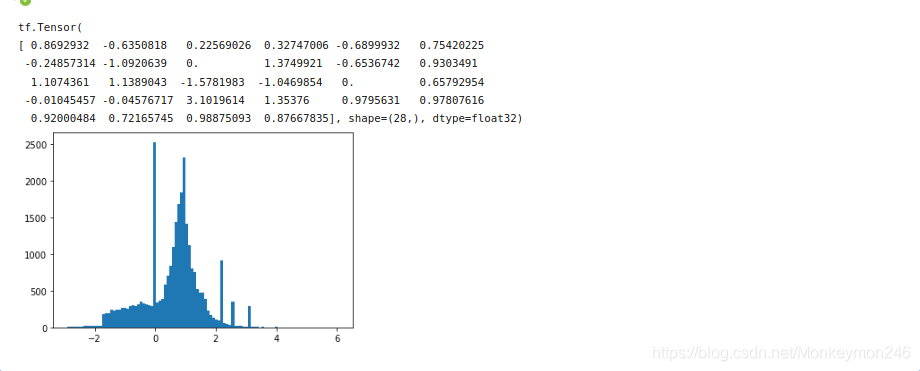
为了使本教程相对较短,仅使用前1000个样本进行验证,然后使用10000个样本进行培训:
N_VALIDATION = int(1e3)
N_TRAIN = int(1e4)
BUFFER_SIZE = int(1e4)
BATCH_SIZE = 500
STEPS_PER_EPOCH = N_TRAIN//BATCH_SIZE
train_ds
这些数据集返回单个示例。使用.batch方法可创建适当大小的批次进行训练。批处理之前,记得.shuffle和.repeat训练集。
validate_ds = validate_ds.batch(BATCH_SIZE)
train_ds = train_ds.shuffle(BUFFER_SIZE).repeat().batch(BATCH_SIZE)
过拟合
逐渐降低学习率
lr_schedule = tf.keras.optimizers.schedules.InverseTimeDecay(
0.001,
decay_steps=STEPS_PER_EPOCH*1000,
decay_rate=1,
staircase=False)
def get_optimizer():
return tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(lr_schedule)
step = np.linspace(0,100000)
lr = lr_schedule(step)
plt.figure(figsize = (8,6))
plt.plot(step/STEPS_PER_EPOCH, lr)
plt.ylim([0,max(plt.ylim())])
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
_ = plt.ylabel('Learning Rate')
上面的代码设置了一个schedules.InverseTimeDecay,以双曲线的方式将学习速率降低为1000周期时的基本速率的1 / 2、2000周期时的1/3等等。
 接下来 用callbacks.EarlyStopping以避免冗长和不必要的培训时间。请注意,此回调设置为监视val_binary_crossentropy,而不是val_loss。这种差异稍后将变得很重要。
接下来 用callbacks.EarlyStopping以避免冗长和不必要的培训时间。请注意,此回调设置为监视val_binary_crossentropy,而不是val_loss。这种差异稍后将变得很重要。
def get_callbacks(name):
return [
tfdocs.modeling.EpochDots(),
tf.keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(monitor='val_binary_crossentropy', patience=200),
tf.keras.callbacks.TensorBoard(logdir/name),
]
def compile_and_fit(model, name, optimizer=None, max_epochs=10000):
if optimizer is None:
optimizer = get_optimizer()
model.compile(optimizer=optimizer,
loss=tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=[
tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(
from_logits=True, name='binary_crossentropy'),
'accuracy'])
model.summary()
history = model.fit(
train_ds,
steps_per_epoch = STEPS_PER_EPOCH,
epochs=max_epochs,
validation_data=validate_ds,
callbacks=get_callbacks(name),
verbose=0)
return history
tiny_model = tf.keras.Sequential([
layers.Dense(16, activation='elu', input_shape=(FEATURES,)),
layers.Dense(1)
])
size_histories = {}
size_histories['Tiny'] = compile_and_fit(tiny_model, 'sizes/Tiny')
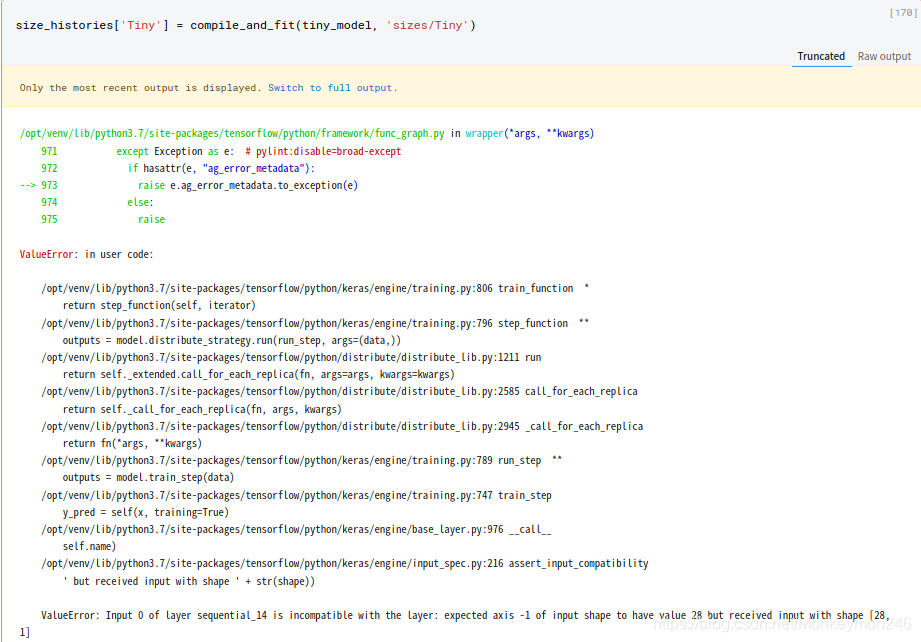
结果报错
原因出在这句
size_histories['Tiny'] = compile_and_fit(tiny_model, 'sizes/Tiny')