今天依然在放假中,在此将以前在学校写的四叉树的东西拿出来和大家分享。
四叉树索引的基本思想是将地理空间递归划分为不同层次的树结构。它将已知范围的空间等分成四个相等的子空间,如此递归下去,直至树的层次达到一定深度或者满足某种要求后停止分割。四叉树的结构比较简单,并且当空间数据对象分布比较均匀时,具有比较高的空间数据插入和查询效率,因此四叉树是GIS中常用的空间索引之一。常规四叉树的结构如图所示,地理空间对象都存储在叶子节点上,中间节点以及根节点不存储地理空间对象。
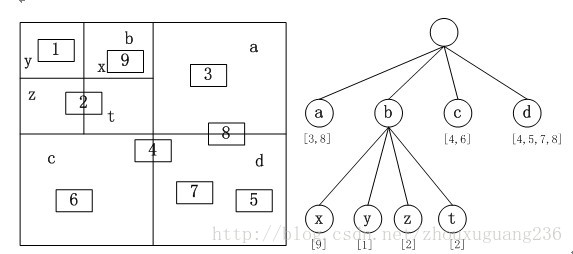
四叉树示意图
四叉树对于区域查询,效率比较高。但如果空间对象分布不均匀,随着地理空间对象的不断插入,四叉树的层次会不断地加深,将形成一棵严重不平衡的四叉树,那么每次查询的深度将大大的增多,从而导致查询效率的急剧下降。
本节将介绍一种改进的四叉树索引结构。四叉树结构是自顶向下逐步划分的一种树状的层次结构。传统的四叉树索引存在着以下几个缺点:
(1)空间实体只能存储在叶子节点中,中间节点以及根节点不能存储空间实体信息,随着空间对象的不断插入,最终会导致四叉树树的层次比较深,在进行空间数据窗口查询的时候效率会比较低下。
(2)同一个地理实体在四叉树的分裂过程中极有可能存储在多个节点中,这样就导致了索引存储空间的浪费。
(3)由于地理空间对象可能分布不均衡,这样会导致常规四叉树生成一棵极为不平衡的树,这样也会造成树结构的不平衡以及存储空间的浪费。
相应的改进方法,将地理实体信息存储在完全包含它的最小矩形节点中,不存储在它的父节点中,每个地理实体只在树中存储一次,避免存储空间的浪费。首先生成满四叉树,避免在地理实体插入时需要重新分配内存,加快插入的速度,最后将空的节点所占内存空间释放掉。改进后的四叉树结构如下图所示。四叉树的深度一般取经验值4-7之间为最佳。
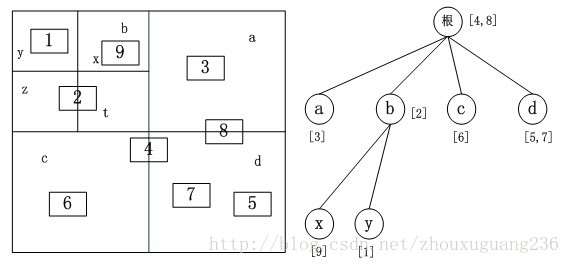
图改进的四叉树结构
为了维护空间索引与对存储在文件或数据库中的空间数据的一致性,作者设计了如下的数据结构支持四叉树的操作。
(1)四分区域标识
分别定义了一个平面区域的四个子区域索引号,右上为第一象限0,左上为第二象限1,左下为第三象限2,右下为第四象限3。
typedef enum
{
UR = 0,// UR第一象限
UL = 1, // UL为第二象限
LL = 2, // LL为第三象限
LR = 3 // LR为第四象限
}QuadrantEnum;
(2)空间对象数据结构
空间对象数据结构是对地理空间对象的近似,在空间索引中,相当一部分都是采用MBR作为近似。
/*空间对象MBR信息*/
typedef struct SHPMBRInfo
{
int nID; //空间对象ID号
MapRect Box; //空间对象MBR范围坐标
}SHPMBRInfo;
nID是空间对象的标识号,Box是空间对象的最小外包矩形(MBR)。
(3)四叉树节点数据结构
四叉树节点是四叉树结构的主要组成部分,主要用于存储空间对象的标识号和MBR,也是四叉树算法操作的主要部分。
/*四叉树节点类型结构*/
typedef struct QuadNode
{
MapRect Box; //节点所代表的矩形区域
int nShpCount; //节点所包含的所有空间对象个数
SHPMBRInfo* pShapeObj; //空间对象指针数组
int nChildCount; //子节点个数
QuadNode *children[4]; //指向节点的四个孩子
}QuadNode;
Box是代表四叉树对应区域的最小外包矩形,上一层的节点的最小外包矩形包含下一层最小外包矩形区域;nShpCount代表本节点包含的空间对象的个数;pShapeObj代表指向空间对象存储地址的首地址,同一个节点的空间对象在内存中连续存储;nChildCount代表节点拥有的子节点的数目;children是指向孩子节点指针的数组。
上述理论部分都都讲的差不多了,下面就贴上我的C语言实现版本代码。
头文件如下:
#ifndef __QUADTREE_H_59CAE94A_E937_42AD_AA27_794E467715BB__
#define __QUADTREE_H_59CAE94A_E937_42AD_AA27_794E467715BB__
/* 一个矩形区域的象限划分::
UL(1) | UR(0)
----------|-----------
LL(2) | LR(3)
以下对该象限类型的枚举
*/
typedef enum
{
UR = 0,
UL = 1,
LL = 2,
LR = 3
}QuadrantEnum;
/*空间对象MBR信息*/
typedef struct SHPMBRInfo
{
int nID; //空间对象ID号
MapRect Box; //空间对象MBR范围坐标
}SHPMBRInfo;
/* 四叉树节点类型结构 */
typedef struct QuadNode
{
MapRect Box; //节点所代表的矩形区域
int nShpCount; //节点所包含的所有空间对象个数
SHPMBRInfo* pShapeObj; //空间对象指针数组
int nChildCount; //子节点个数
QuadNode *children[4]; //指向节点的四个孩子
}QuadNode;
/* 四叉树类型结构 */
typedef struct quadtree_t
{
QuadNode *root;
int depth; // 四叉树的深度
}QuadTree;
//初始化四叉树节点
QuadNode *InitQuadNode();
//层次创建四叉树方法(满四叉树)
void CreateQuadTree(int depth,GeoLayer *poLayer,QuadTree* pQuadTree);
//创建各个分支
void CreateQuadBranch(int depth,MapRect &rect,QuadNode** node);
//构建四叉树空间索引
void BuildQuadTree(GeoLayer*poLayer,QuadTree* pQuadTree);
//四叉树索引查询(矩形查询)
void SearchQuadTree(QuadNode* node,MapRect &queryRect,vector<int>& ItemSearched);
//四叉树索引查询(矩形查询)并行查询
void SearchQuadTreePara(vector<QuadNode*> resNodes,MapRect &queryRect,vector<int>& ItemSearched);
//四叉树的查询(点查询)
void PtSearchQTree(QuadNode* node,double cx,double cy,vector<int>& ItemSearched);
//将指定的空间对象插入到四叉树中
void Insert(long key,MapRect &itemRect,QuadNode* pNode);
//将指定的空间对象插入到四叉树中
void InsertQuad(long key,MapRect &itemRect,QuadNode* pNode);
//将指定的空间对象插入到四叉树中
void InsertQuad2(long key,MapRect &itemRect,QuadNode* pNode);
//判断一个节点是否是叶子节点
bool IsQuadLeaf(QuadNode* node);
//删除多余的节点
bool DelFalseNode(QuadNode* node);
//四叉树遍历(所有要素)
void TraversalQuadTree(QuadNode* quadTree,vector<int>& resVec);
//四叉树遍历(所有节点)
void TraversalQuadTree(QuadNode* quadTree,vector<QuadNode*>& arrNode);
//释放树的内存空间
void ReleaseQuadTree(QuadNode** quadTree);
//计算四叉树所占的字节的大小
long CalByteQuadTree(QuadNode* quadTree,long& nSize);
#endif
源文件如下:
#include "QuadTree.h"
QuadNode *InitQuadNode()
{
QuadNode *node = new QuadNode;
node->Box.maxX = 0;
node->Box.maxY = 0;
node->Box.minX = 0;
node->Box.minY = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
node->children[i] = NULL;
}
node->nChildCount = 0;
node->nShpCount = 0;
node->pShapeObj = NULL;
return node;
}
void CreateQuadTree(int depth,GeoLayer *poLayer,QuadTree* pQuadTree)
{
pQuadTree->depth = depth;
GeoEnvelope env; //整个图层的MBR
poLayer->GetExtent(&env);
MapRect rect;
rect.minX = env.MinX;
rect.minY = env.MinY;
rect.maxX = env.MaxX;
rect.maxY = env.MaxY;
//创建各个分支
CreateQuadBranch(depth,rect,&(pQuadTree->root));
int nCount = poLayer->GetFeatureCount();
GeoFeature **pFeatureClass = new GeoFeature*[nCount];
for (int i = 0; i < poLayer->GetFeatureCount(); i ++)
{
pFeatureClass[i] = poLayer->GetFeature(i);
}
//插入各个要素
GeoEnvelope envObj; //空间对象的MBR
//#pragma omp parallel for
for (int i = 0; i < nCount; i ++)
{
pFeatureClass[i]->GetGeometry()->getEnvelope(&envObj);
rect.minX = envObj.MinX;
rect.minY = envObj.MinY;
rect.maxX = envObj.MaxX;
rect.maxY = envObj.MaxY;
InsertQuad(i,rect,pQuadTree->root);
}
//DelFalseNode(pQuadTree->root);
}
void CreateQuadBranch(int depth,MapRect &rect,QuadNode** node)
{
if (depth != 0)
{
*node = InitQuadNode(); //创建树根
QuadNode *pNode = *node;
pNode->Box = rect;
pNode->nChildCount = 4;
MapRect boxs[4];
pNode->Box.Split(boxs,boxs+1,boxs+2,boxs+3);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
//创建四个节点并插入相应的MBR
pNode->children[i] = InitQuadNode();
pNode->children[i]->Box = boxs[i];
CreateQuadBranch(depth-1,boxs[i],&(pNode->children[i]));
}
}
}
void BuildQuadTree(GeoLayer *poLayer,QuadTree* pQuadTree)
{
assert(poLayer);
GeoEnvelope env; //整个图层的MBR
poLayer->GetExtent(&env);
pQuadTree->root = InitQuadNode();
QuadNode* rootNode = pQuadTree->root;
rootNode->Box.minX = env.MinX;
rootNode->Box.minY = env.MinY;
rootNode->Box.maxX = env.MaxX;
rootNode->Box.maxY = env.MaxY;
//设置树的深度( 根据等比数列的求和公式)
//pQuadTree->depth = log(poLayer->GetFeatureCount()*3/8.0+1)/log(4.0);
int nCount = poLayer->GetFeatureCount();
MapRect rect;
GeoEnvelope envObj; //空间对象的MBR
for (int i = 0; i < nCount; i ++)
{
poLayer->GetFeature(i)->GetGeometry()->getEnvelope(&envObj);
rect.minX = envObj.MinX;
rect.minY = envObj.MinY;
rect.maxX = envObj.MaxX;
rect.maxY = envObj.MaxY;
InsertQuad2(i,rect,rootNode);
}
DelFalseNode(pQuadTree->root);
}
void SearchQuadTree(QuadNode* node,MapRect &queryRect,vector<int>& ItemSearched)
{
assert(node);
//int coreNum = omp_get_num_procs();
//vector<int> * pResArr = new vector<int>[coreNum];
if (NULL != node)
{
for (int i = 0; i < node->nShpCount; i ++)
{
if (queryRect.Contains(node->pShapeObj[i].Box)
|| queryRect.Intersects(node->pShapeObj[i].Box))
{
ItemSearched.push_back(node->pShapeObj[i].nID);
}
}
//并行搜索四个孩子节点
/*#pragma omp parallel sections
{
#pragma omp section
if ((node->children[0] != NULL) &&
(node->children[0]->Box.Contains(queryRect)
|| node->children[0]->Box.Intersects(queryRect)))
{
int tid = omp_get_thread_num();
SearchQuadTree(node->children[0],queryRect,pResArr[tid]);
}
#pragma omp section
if ((node->children[1] != NULL) &&
(node->children[1]->Box.Contains(queryRect)
|| node->children[1]->Box.Intersects(queryRect)))
{
int tid = omp_get_thread_num();
SearchQuadTree(node->children[1],queryRect,pResArr[tid]);
}
#pragma omp section
if ((node->children[2] != NULL) &&
(node->children[2]->Box.Contains(queryRect)
|| node->children[2]->Box.Intersects(queryRect)))
{
int tid = omp_get_thread_num();
SearchQuadTree(node->children[2],queryRect,pResArr[tid]);
}
#pragma omp section
if ((node->children[3] != NULL) &&
(node->children[3]->Box.Contains(queryRect)
|| node->children[3]->Box.Intersects(queryRect)))
{
int tid = omp_get_thread_num();
SearchQuadTree(node->children[3],queryRect,pResArr[tid]);
}
}*/
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
if ((node->children[i] != NULL) &&
(node->children[i]->Box.Contains(queryRect)
|| node->children[i]->Box.Intersects(queryRect)))
{
SearchQuadTree(node->children[i],queryRect,ItemSearched);
//node = node->children[i]; //非递归
}
}
}
/*for (int i = 0 ; i < coreNum; i ++)
{
ItemSearched.insert(ItemSearched.end(),pResArr[i].begin(),pResArr[i].end());
}*/
}
void SearchQuadTreePara(vector<QuadNode*> resNodes,MapRect &queryRect,vector<int>& ItemSearched)
{
int coreNum = omp_get_num_procs();
omp_set_num_threads(coreNum);
vector<int>* searchArrs = new vector<int>[coreNum];
for (int i = 0; i < coreNum; i ++)
{
searchArrs[i].clear();
}
#pragma omp parallel for
for (int i = 0; i < resNodes.size(); i ++)
{
int tid = omp_get_thread_num();
for (int j = 0; j < resNodes[i]->nShpCount; j ++)
{
if (queryRect.Contains(resNodes[i]->pShapeObj[j].Box)
|| queryRect.Intersects(resNodes[i]->pShapeObj[j].Box))
{
searchArrs[tid].push_back(resNodes[i]->pShapeObj[j].nID);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < coreNum; i ++)
{
ItemSearched.insert(ItemSearched.end(),
searchArrs[i].begin(),searchArrs[i].end());
}
delete [] searchArrs;
searchArrs = NULL;
}
void PtSearchQTree(QuadNode* node,double cx,double cy,vector<int>& ItemSearched)
{
assert(node);
if (node->nShpCount >0) //节点
{
for (int i = 0; i < node->nShpCount; i ++)
{
if (node->pShapeObj[i].Box.IsPointInRect(cx,cy))
{
ItemSearched.push_back(node->pShapeObj[i].nID);
}
}
}
else if (node->nChildCount >0) //节点
{
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
if (node->children[i]->Box.IsPointInRect(cx,cy))
{
PtSearchQTree(node->children[i],cx,cy,ItemSearched);
}
}
}
//找出重复元素的位置
sort(ItemSearched.begin(),ItemSearched.end()); //先排序,默认升序
vector<int>::iterator unique_iter =
unique(ItemSearched.begin(),ItemSearched.end());
ItemSearched.erase(unique_iter,ItemSearched.end());
}
void Insert(long key, MapRect &itemRect,QuadNode* pNode)
{
QuadNode *node = pNode; //保留根节点副本
SHPMBRInfo pShpInfo;
//节点有孩子
if (0 < node->nChildCount)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
//如果包含或相交,则将节点插入到此节点
if (node->children[i]->Box.Contains(itemRect)
|| node->children[i]->Box.Intersects(itemRect))
{
//node = node->children[i];
Insert(key,itemRect,node->children[i]);
}
}
}
//如果当前节点存在一个子节点时
else if (1 == node->nShpCount)
{
MapRect boxs[4];
node->Box.Split(boxs,boxs+1,boxs+2,boxs+3);
//创建四个节点并插入相应的MBR
node->children[UR] = InitQuadNode();
node->children[UL] = InitQuadNode();
node->children[LL] = InitQuadNode();
node->children[LR] = InitQuadNode();
node->children[UR]->Box = boxs[0];
node->children[UL]->Box = boxs[1];
node->children[LL]->Box = boxs[2];
node->children[LR]->Box = boxs[3];
node->nChildCount = 4;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
//将当前节点中的要素移动到相应的子节点中
for (int j = 0; j < node->nShpCount; j ++)
{
if (node->children[i]->Box.Contains(node->pShapeObj[j].Box)
|| node->children[i]->Box.Intersects(node->pShapeObj[j].Box))
{
node->children[i]->nShpCount += 1;
node->children[i]->pShapeObj =
(SHPMBRInfo*)malloc(node->children[i]->nShpCount*sizeof(SHPMBRInfo));
memcpy(node->children[i]->pShapeObj,&(node->pShapeObj[j]),sizeof(SHPMBRInfo));
free(node->pShapeObj);
node->pShapeObj = NULL;
node->nShpCount = 0;
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
//如果包含或相交,则将节点插入到此节点
if (node->children[i]->Box.Contains(itemRect)
|| node->children[i]->Box.Intersects(itemRect))
{
if (node->children[i]->nShpCount == 0) //如果之前没有节点
{
node->children[i]->nShpCount += 1;
node->pShapeObj =
(SHPMBRInfo*)malloc(sizeof(SHPMBRInfo)*node->children[i]->nShpCount);
}
else if (node->children[i]->nShpCount > 0)
{
node->children[i]->nShpCount += 1;
node->children[i]->pShapeObj =
(SHPMBRInfo *)realloc(node->children[i]->pShapeObj,
sizeof(SHPMBRInfo)*node->children[i]->nShpCount);
}
pShpInfo.Box = itemRect;
pShpInfo.nID = key;
memcpy(node->children[i]->pShapeObj,
&pShpInfo,sizeof(SHPMBRInfo));
}
}
}
//当前节点没有空间对象
else if (0 == node->nShpCount)
{
node->nShpCount += 1;
node->pShapeObj =
(SHPMBRInfo*)malloc(sizeof(SHPMBRInfo)*node->nShpCount);
pShpInfo.Box = itemRect;
pShpInfo.nID = key;
memcpy(node->pShapeObj,&pShpInfo,sizeof(SHPMBRInfo));
}
}
void InsertQuad(long key,MapRect &itemRect,QuadNode* pNode)
{
assert(pNode != NULL);
if (!IsQuadLeaf(pNode)) //非叶子节点
{
int nCorver = 0; //跨越的子节点个数
int iIndex = -1; //被哪个子节点完全包含的索引号
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
if (pNode->children[i]->Box.Contains(itemRect)
&& pNode->Box.Contains(itemRect))
{
nCorver += 1;
iIndex = i;
}
}
//如果被某一个子节点包含,则进入该子节点
if (/*pNode->Box.Contains(itemRect) ||
pNode->Box.Intersects(itemRect)*/1 <= nCorver)
{
InsertQuad(key,itemRect,pNode->children[iIndex]);
}
//如果跨越了多个子节点,直接放在这个节点中
else if (nCorver == 0)
{
if (pNode->nShpCount == 0) //如果之前没有节点
{
pNode->nShpCount += 1;
pNode->pShapeObj =
(SHPMBRInfo*)malloc(sizeof(SHPMBRInfo)*pNode->nShpCount);
}
else
{
pNode->nShpCount += 1;
pNode->pShapeObj =
(SHPMBRInfo *)realloc(pNode->pShapeObj,sizeof(SHPMBRInfo)*pNode->nShpCount);
}
SHPMBRInfo pShpInfo;
pShpInfo.Box = itemRect;
pShpInfo.nID = key;
memcpy(pNode->pShapeObj+pNode->nShpCount-1,&pShpInfo,sizeof(SHPMBRInfo));
}
}
//如果是叶子节点,直接放进去
else if (IsQuadLeaf(pNode))
{
if (pNode->nShpCount == 0) //如果之前没有节点
{
pNode->nShpCount += 1;
pNode->pShapeObj =
(SHPMBRInfo*)malloc(sizeof(SHPMBRInfo)*pNode->nShpCount);
}
else
{
pNode->nShpCount += 1;
pNode->pShapeObj =
(SHPMBRInfo *)realloc(pNode->pShapeObj,sizeof(SHPMBRInfo)*pNode->nShpCount);
}
SHPMBRInfo pShpInfo;
pShpInfo.Box = itemRect;
pShpInfo.nID = key;
memcpy(pNode->pShapeObj+pNode->nShpCount-1,&pShpInfo,sizeof(SHPMBRInfo));
}
}
void InsertQuad2(long key,MapRect &itemRect,QuadNode* pNode)
{
QuadNode *node = pNode; //保留根节点副本
SHPMBRInfo pShpInfo;
//节点有孩子
if (0 < node->nChildCount)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
//如果包含或相交,则将节点插入到此节点
if (node->children[i]->Box.Contains(itemRect)
|| node->children[i]->Box.Intersects(itemRect))
{
//node = node->children[i];
Insert(key,itemRect,node->children[i]);
}
}
}
//如果当前节点存在一个子节点时
else if (0 == node->nChildCount)
{
MapRect boxs[4];
node->Box.Split(boxs,boxs+1,boxs+2,boxs+3);
int cnt = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
//如果包含或相交,则将节点插入到此节点
if (boxs[i].Contains(itemRect))
{
cnt = i;
}
}
//如果有一个矩形包含此对象,则创建四个孩子节点
if (cnt > -1)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
//创建四个节点并插入相应的MBR
node->children[i] = InitQuadNode();
node->children[i]->Box = boxs[i];
}
node->nChildCount = 4;
InsertQuad2(key,itemRect,node->children[cnt]); //递归
}
//如果都不包含,则直接将对象插入此节点
if (cnt == -1)
{
if (node->nShpCount == 0) //如果之前没有节点
{
node->nShpCount += 1;
node->pShapeObj =
(SHPMBRInfo*)malloc(sizeof(SHPMBRInfo)*node->nShpCount);
}
else if (node->nShpCount > 0)
{
node->nShpCount += 1;
node->pShapeObj =
(SHPMBRInfo *)realloc(node->pShapeObj,
sizeof(SHPMBRInfo)*node->nShpCount);
}
pShpInfo.Box = itemRect;
pShpInfo.nID = key;
memcpy(node->pShapeObj,
&pShpInfo,sizeof(SHPMBRInfo));
}
}
//当前节点没有空间对象
/*else if (0 == node->nShpCount)
{
node->nShpCount += 1;
node->pShapeObj =
(SHPMBRInfo*)malloc(sizeof(SHPMBRInfo)*node->nShpCount);
pShpInfo.Box = itemRect;
pShpInfo.nID = key;
memcpy(node->pShapeObj,&pShpInfo,sizeof(SHPMBRInfo));
}*/
}
bool IsQuadLeaf(QuadNode* node)
{
if (NULL == node)
{
return 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
if (node->children[i] != NULL)
{
return 0;
}
}
return 1;
}
bool DelFalseNode(QuadNode* node)
{
//如果没有子节点且没有要素
if (node->nChildCount ==0 && node->nShpCount == 0)
{
ReleaseQuadTree(&node);
}
//如果有子节点
else if (node->nChildCount > 0)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
DelFalseNode(node->children[i]);
}
}
return 1;
}
void TraversalQuadTree(QuadNode* quadTree,vector<int>& resVec)
{
QuadNode *node = quadTree;
int i = 0;
if (NULL != node)
{
//将本节点中的空间对象存储数组中
for (i = 0; i < node->nShpCount; i ++)
{
resVec.push_back((node->pShapeObj+i)->nID);
}
//遍历孩子节点
for (i = 0; i < node->nChildCount; i ++)
{
if (node->children[i] != NULL)
{
TraversalQuadTree(node->children[i],resVec);
}
}
}
}
void TraversalQuadTree(QuadNode* quadTree,vector<QuadNode*>& arrNode)
{
deque<QuadNode*> nodeQueue;
if (quadTree != NULL)
{
nodeQueue.push_back(quadTree);
while (!nodeQueue.empty())
{
QuadNode* queueHead = nodeQueue.at(0); //取队列头结点
arrNode.push_back(queueHead);
nodeQueue.pop_front();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
if (queueHead->children[i] != NULL)
{
nodeQueue.push_back(queueHead->children[i]);
}
}
}
}
}
void ReleaseQuadTree(QuadNode** quadTree)
{
int i = 0;
QuadNode* node = *quadTree;
if (NULL == node)
{
return;
}
else
{
for (i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
ReleaseQuadTree(&node->children[i]);
}
free(node);
node = NULL;
}
node = NULL;
}
long CalByteQuadTree(QuadNode* quadTree,long& nSize)
{
if (quadTree != NULL)
{
nSize += sizeof(QuadNode)+quadTree->nChildCount*sizeof(SHPMBRInfo);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++)
{
if (quadTree->children[i] != NULL)
{
nSize += CalByteQuadTree(quadTree->children[i],nSize);
}
}
}
return 1;
}
代码有点长,有需要的朋友可以借鉴并自己优化。
本文内容由网友自发贡献,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有涉嫌抄袭侵权的内容,请联系:hwhale#tublm.com(使用前将#替换为@)