前置课程
第一课 什么是norm?(An Evolutionary Approach to Norms)
An Evolutionary Approach to Norms
这个是第二部分的内容,在之前我们已经讲解了什么是norm
Simulation of the Norms Game
前文所说,norms game有两个dimensions,boldness和vengefulness,作者把这两个分成8个等级,从0/7到7/7. 所以一个agent的策略可以用六个比特来表示,三个表示boldness,三个表示vengefulness。
simulation包含5个步骤,下面我们一一细说:
first step
一开始有20个玩家,每个玩家的初始策略是随机的从
2
6
2^6
26种策略中选择。
second step
每个玩家有四次作弊的机会,最终的得分是由别的玩家的选择和自己的选择来决定的;此外被发现作弊的概率服从0到1之间的均匀分布。含义就是四次的话,一次是0.25,0.5,0.75,1。
我们来举一个例子,假设有一个玩家叫LEE:
Lee has a boldness level of 2/7 and vengefulness level of 4/7. The total
payoff Lee achieved was the result of four different kinds of events, as shown in Table 1. Lee defected only once because only one of the four opportunities had a chance of being seen that was less than Lee’s boldness of 2/7. This defection gave a temptation payoff of T = 3 points. Unfortunately for Lee, one of the other players observed the defection and chose to punish it, leading to a loss for Lee of P = -9 points. In addition the other players defected a total of 36 times, each hurting Lee H = -1 point. Finally, Lee observed who was responsible for about half of these defections and chose to punish each of them with a probability determined by his vengefulness of 4/7.This lead to a punishment of 9 of the defections at an enforcement cost of E = -2 each, for a further loss of 18 points. The net result of these four types of events was a total score of -60 for Lee.
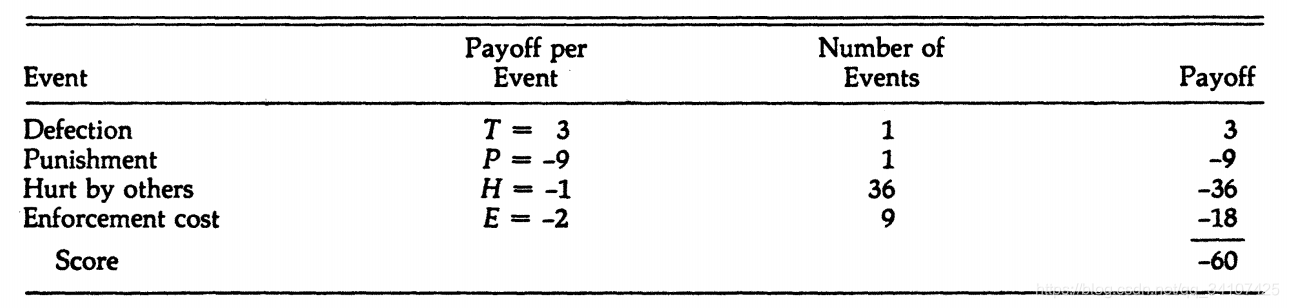
Lee由2/7的boldness和4/7的vengefulness。因为只有0.25小于boldness,所以Lee只作弊一次,获得了3;但是有一个人发现了并且决定惩罚Lee,所以-9;然后别的19个人总共欺骗了36次,然后lee根据自己的vengefulness惩罚了9次,所以最后的结果是-60。
third step
fourth step
第二步和第三步重复100次,来看是如何进化的
fifth step
从第一步到第四步重复五次,来得到五次完整的模拟
结果分析
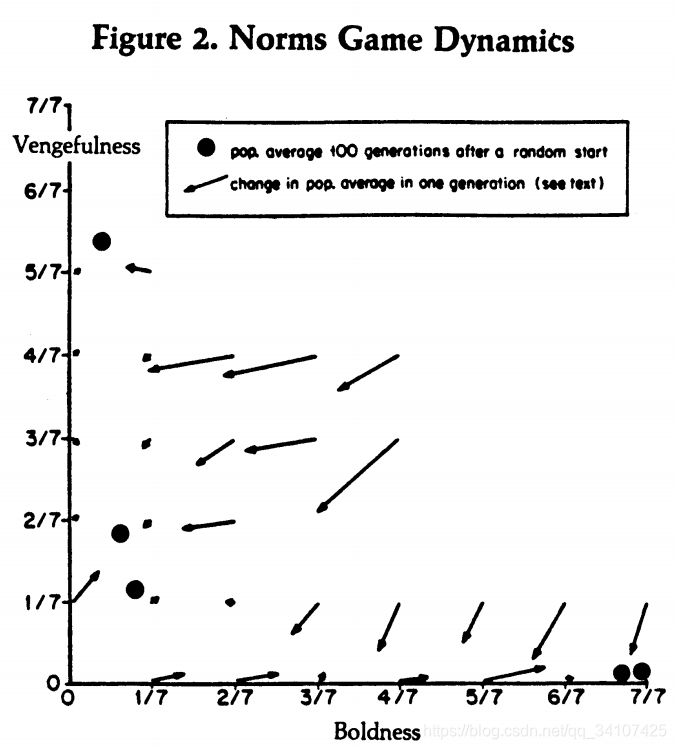
五个大黑点,是五次实验结果的平均boldness和vengefulness,
Three completely different outcomes appear possible. In one of the runs, there was a moderate level of vengefulness and almost no boldness, indicating the partial establishment of a norm against defection. On two other runs there was little boldness and little vengefulness, and on the remaining two runs, there was a great deal of boldness and almost no vengefulness-the very opposite of a norm against defection. What could be happening?
- 一次的结果是大vengefulness和小boldness,这个暗示了一个反对作弊的norm的产生;
- 有两次非常小的boldness和非常小的vengefulness;
- 有两次非常大的boldness和非常小的vengefulness
Now the various outcomes begin to fit into a common pattern. All five of the
runs begin near the middle of the field, with average boldness and vengefulness
levels near one-half. The first thing to happen is a dramatic fall in the boldness
level. The reason for the decline is that when there is enough vengefulness in the
population, it is very costly to be bold. Once the boldness level falls, the main
trend is a lowering of vengefulness. The reason for this is that to be vengeful and
punish an observed defection requires paying an enforcement cost without any
direct return to the individual. Finally, once the vengefulness level has fallen
nearly to zero, the players can be bold with impunity. This results in an increase
in boldness, destroying whatever restraint was established in the first stage of the
process-a sad but stable state in this norms game.
作者给出了一个common model:在一开始,所有的人都是平均的boldness和vengefulness,然后很快boldness快速下降因为vengefulness非常高,作弊的代价太大;然后boldness很低的时候,vengefulness下降,因为每一次都惩罚别人对自己没有什么好处;当vengefulness很低的时候,boldness又会快速上升。达到一个稳定状态,这是一个让人sad的结果。
目前为之,每一个人都是没incentive去惩罚别人的。假设我们加上这样的一种动机?这里我们引入metanorms
我们会在最后一章也就是下一部分,讲解什么是metanorms game