图是一种包括节点和边的数据结构,本文对图的构建、图的遍历给出详细的代码。其中,
图的表示方法有:
图的遍历方法有:
1. 图的表示
1.1 邻接矩阵
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
#define maxNodeNum 100 //最大顶点数
//定义图
struct GraphNode{
int nodeNum; //顶点数
int edgeNum; //边数
vector<vector<int>> graph;
/*vector<int> data; //多数情况下顶点无数据*/
GraphNode(): nodeNum(0),edgeNum(0),graph(maxNodeNum,vector<int>(maxNodeNum,0)){}
GraphNode(int n,int m): nodeNum(n),edgeNum(m),graph(maxNodeNum,vector<int>(maxNodeNum,0)){}
};
class Solution{
public:
GraphNode* buildGraph(){
GraphNode* g = new GraphNode();
cin>>g->nodeNum; //输入顶点数
cin>>g->edgeNum; //输入边数
if(g->edgeNum!=0){ //如果有边
//输入边,建图
for(int i=0;i<g->edgeNum;i++){
int node1,node2; //边连接的两个节点
int weight; //边权重,可以设为1,表示有连接,0表示无连接
cin>>node1>>node2>>weight;
g->graph[node1][node2] = weight; //插入边
g->graph[node2][node1] = weight; //此处模拟无向图
}
}
/*//如果有顶点数据的话,读入数据
for(int i=0;i<g->nodeNum;i++){
cin>>g->data[i];
}*/
return g;
}
//遍历图
void printGraph(GraphNode* g){
for(int i=0;i<g->nodeNum;i++){
for(int j=0;j<g->nodeNum;j++){
cout<<g->graph[i][j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
};
int main(){
Solution s;
GraphNode* g = s.buildGraph();
s.printGraph(g);
return 0;
}
/**
输入:
0 17
0 1 1
0 3 1
1 2 1
1 3 1
1 5 1
2 4 1
2 5 1
3 6 1
3 7 1
4 5 1
4 9 1
5 6 1
5 8 1
5 9 1
6 7 1
6 8 1
8 9 1
输出:
0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0
1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0
0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1
0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0
0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1
0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0
*/
1.2 邻接表
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
#define maxNodeNum 100 //最大顶点数
//图节点定义
struct VNode{
int nodeVal; //邻接点下标
int weight; //边权重
/*int data; //存顶点数据,这里省略*/
VNode* next; //指向下一个邻接点的指针
VNode():nodeVal(-1),weight(0),next(NULL){} // 这里的-1是随便设的
VNode(int node,int w,VNode* ptr):nodeVal(node),weight(w),next(ptr){}
};
//图定义
struct GraphNode{
int nodeNum; //顶点数
int edgeNum; //边数
vector<VNode*> graph; //邻接表
//下面的初始化逻辑是错误的,graph(maxNodeNum,new VNode())的意思是maxNodeNum个指针全都指向new Node()开辟的一个空间
//导致插入节点时都是在一个头节点上进行插入
GraphNode(): nodeNum(0),edgeNum(0){
for(int i=0;i<maxNodeNum;i++){
VNode* init = new VNode();
graph.push_back(init);
}
}
GraphNode(int n,int m): nodeNum(n),edgeNum(m),graph(maxNodeNum){
for(int i=0;i<maxNodeNum;i++){
VNode* init = new VNode();
graph.push_back(init);
}
}
};
class Solution{
public:
//插入边
void insertEdge(GraphNode* g,int node1,int node2,int weight){
VNode* newNode1 = new VNode();
/*插入边<node1,node2>*/
newNode1->nodeVal = node2;
newNode1->weight = weight;
//将node2插入node1的头节点
newNode1->next = g->graph[node1]->next;
g->graph[node1]->next = newNode1;
/*若是无向图,插入边<node2,node1>*/
VNode* newNode2 = new VNode();
newNode2->nodeVal = node1;
newNode2->weight = weight;
//将node1插入node2的头节点
newNode2->next = g->graph[node2]->next;
g->graph[node2]->next = newNode2;
}
//构建图
GraphNode* buildGraph(){
GraphNode* g = new GraphNode();
cin>>g->nodeNum;
cin>>g->edgeNum;
if(g->edgeNum!=0){ //边数不为零时
for(int i=0;i<g->edgeNum;i++){
int node1,node2; //边节点
int weight; //边权重
cin>>node1>>node2>>weight;
insertEdge(g,node1,node2,weight);
}
}
// 如果顶点有数据的话,读入数据
return g;
}
void printGraph(GraphNode* g){
VNode* cur;
for(int i=0;i<g->nodeNum;i++){
cout<<i<<" ";
cur = g->graph[i]->next;
while(cur){
cout<<cur->nodeVal<<" ";
cur = cur->next;
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
};
int main(){
Solution s;
GraphNode* g = s.buildGraph();
s.printGraph(g);
return 0;
}
/*
输入:
10 17
0 1 1
0 3 1
1 2 1
1 3 1
1 5 1
2 4 1
2 5 1
3 6 1
3 7 1
4 5 1
4 9 1
5 6 1
5 8 1
5 9 1
6 7 1
6 8 1
8 9 1
输出:
0 3 1
1 5 3 2 0
2 5 4 1
3 7 6 1 0
4 9 5 2
5 9 8 6 4 2 1
6 8 7 5 3
7 6 3
8 9 6 5
9 8 5 4
*/
2. 图的遍历
2.1 深度优先搜索
深度优先遍历图的方法是,从图中某顶点v出发:
- 访问顶点v;
- 依次从v的未被访问的邻接点出发,对图进行深度优先遍历,直至图中和v有路径相通的顶点都被访问;
- 若此时图中尚有顶点未被访问,则从一个未被访问的顶点出发,重新进行深度优先遍历,直到图中所有顶点均被访问过为止。
深度优先搜系类似于树的先序遍历,伪代码如下所示:
void DFS(Vertex V)
{
visited[V] = true;
for(V的每个邻接点W)
if (!visited[W])
DFS(W) ;
}
若有N个顶点、E条边,时间复杂度:
- 用邻接表存储图,为
O
(
N
+
E
)
O (N+E)
O(N+E)
- 用邻接矩阵存储图,为
O
(
N
2
)
O ( N^2 )
O(N2)
2.2 广度优先搜索
广度优先搜索的基本过程:BFS是从根节点开始,沿着树(图)的宽度遍历树(图)的节点。如果所有节点均被访问,则算法中止。一般用队列数据结构来辅助实现BFS算法。
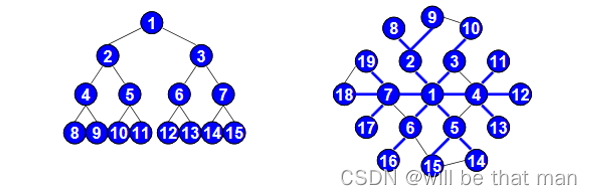
广度优先搜索类似于树的层序遍历,伪代码如下所示:
void BFS(Vertex V)
{
visited[V] = true;
Enqueue(V, Q);
while(!IsEmpty (Q)){
V = Dequeue(Q);
for (V的每个邻接点W){
if(!visited[W]){
visited[W]= true;
Enqueue (W, Q);
}
}
}
}
若有N个顶点、E条边,时间复杂度:
- 用邻接表存储图,为
O
(
N
+
E
)
O (N+E)
O(N+E)
- 用邻接矩阵存储图,为
O
(
N
2
)
O ( N^2 )
O(N2)
3. 图的遍历代码
3.1 邻接矩阵的遍历
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
#define maxNodeNum 100 //最大顶点数
//定义图
struct GraphNode{
int nodeNum; //顶点数
int edgeNum; //边数
vector<vector<int>> graph;
/*vector<int> data; //多数情况下顶点无数据*/
GraphNode(): nodeNum(0),edgeNum(0),graph(maxNodeNum,vector<int>(maxNodeNum,0)){}
GraphNode(int n,int m): nodeNum(n),edgeNum(m),graph(maxNodeNum,vector<int>(maxNodeNum,0)){}
};
class Solution{
public:
GraphNode* buildGraph(){
GraphNode* g = new GraphNode();
cin>>g->nodeNum; //输入顶点数
cin>>g->edgeNum; //输入边数
if(g->edgeNum!=0){ //如果有边
//输入边,建图
for(int i=0;i<g->edgeNum;i++){
int node1,node2; //边连接的两个节点
int weight; //边权重,可以设为1,表示有连接,0表示无连接
cin>>node1>>node2>>weight;
g->graph[node1][node2] = weight; //插入边
g->graph[node2][node1] = weight; //此处模拟无向图
}
}
/*//如果有顶点数据的话,读入数据
for(int i=0;i<g->nodeNum;i++){
cin>>g->data[i];
}*/
return g;
}
};
vector<bool> visit(maxNodeNum,false);
//深搜,类似于二叉树的递归遍历
void dfs(GraphNode* g,int val){
visit[val] = true;
cout<<"正在访问节点"<<val<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<g->nodeNum;i++){
if(!visit[i] && g->graph[val][i]){
dfs(g,i);
}
}
}
//广搜,类似于二叉树的层序遍历
void bfs(GraphNode* g,int val){
queue<int> que;
que.push(val);
visit[val] = true;
cout<<"正在访问节点"<<val<<endl;
while(!que.empty()){
int curVal = que.front();
que.pop();
for(int i=0;i<g->nodeNum;i++){
if(!visit[i] && g->graph[curVal][i]){
que.push(i);
visit[i] = true;
cout<<"正在访问节点"<<i<<endl;
}
}
}
}
int main(){
Solution s;
GraphNode* g = s.buildGraph();
dfs(g,0);
for(int i=0;i<maxNodeNum;i++){
visit[i] = false;
}
bfs(g,0);
return 0;
}
/*
输入:
10 17
0 1 1
0 3 1
1 2 1
1 3 1
1 5 1
2 4 1
2 5 1
3 6 1
3 7 1
4 5 1
4 9 1
5 6 1
5 8 1
5 9 1
6 7 1
6 8 1
8 9 1
输出:
正在访问节点0
正在访问节点1
正在访问节点2
正在访问节点4
正在访问节点5
正在访问节点6
正在访问节点3
正在访问节点7
正在访问节点8
正在访问节点9
正在访问节点0
正在访问节点1
正在访问节点3
正在访问节点2
正在访问节点5
正在访问节点6
正在访问节点7
正在访问节点4
正在访问节点8
正在访问节点9
*/
3.2 邻接表的遍历
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
#define maxNodeNum 100 //最大顶点数
//图节点定义
struct VNode{
int nodeVal; //邻接点下标
int weight; //边权重
/*int data; //存顶点数据,这里省略*/
VNode* next; //指向下一个邻接点的指针
VNode():nodeVal(-1),weight(0),next(NULL){} // 这里的-1是随便设的
VNode(int node,int w,VNode* ptr):nodeVal(node),weight(w),next(ptr){}
};
//图定义
struct GraphNode{
int nodeNum; //顶点数
int edgeNum; //边数
vector<VNode*> graph; //邻接表
//下面的初始化逻辑是错误的,graph(maxNodeNum,new VNode())的意思是maxNodeNum个指针全都指向new Node()开辟的一个空间
//导致插入节点时都是在一个头节点上进行插入
GraphNode(): nodeNum(0),edgeNum(0){
for(int i=0;i<maxNodeNum;i++){
VNode* init = new VNode(i,0,NULL);
graph.push_back(init);
}
}
GraphNode(int n,int m): nodeNum(n),edgeNum(m),graph(maxNodeNum){
for(int i=0;i<maxNodeNum;i++){
VNode* init = new VNode();
graph.push_back(init);
}
}
};
class Solution{
public:
//插入边
void insertEdge(GraphNode* g,int node1,int node2,int weight){
VNode* newNode1 = new VNode();
/*插入边<node1,node2>*/
newNode1->nodeVal = node2;
newNode1->weight = weight;
//将node2插入node1的头节点
newNode1->next = g->graph[node1]->next;
g->graph[node1]->next = newNode1;
/*若是无向图,插入边<node2,node1>*/
VNode* newNode2 = new VNode();
newNode2->nodeVal = node1;
newNode2->weight = weight;
//将node1插入node2的头节点
newNode2->next = g->graph[node2]->next;
g->graph[node2]->next = newNode2;
}
//构建图
GraphNode* buildGraph(){
GraphNode* g = new GraphNode();
cin>>g->nodeNum;
cin>>g->edgeNum;
if(g->edgeNum!=0){ //边数不为零时
for(int i=0;i<g->edgeNum;i++){
int node1,node2; //边节点
int weight; //边权重
cin>>node1>>node2>>weight;
insertEdge(g,node1,node2,weight);
}
}
// 如果顶点有数据的话,读入数据
return g;
}
void printGraph(GraphNode* g){
VNode* cur;
for(int i=0;i<g->nodeNum;i++){
cout<<i<<" ";
cur = g->graph[i]->next;
while(cur){
cout<<cur->nodeVal<<" ";
cur = cur->next;
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
};
vector<bool> visit(maxNodeNum,false);
//深搜,类似于二叉树的递归遍历
void dfs(GraphNode* g,int val){
cout<<"正在访问顶点"<<val<<endl;
visit[val] = true;
VNode* curNode = g->graph[val]->next;
while(curNode){
if(!visit[curNode->nodeVal]){
dfs(g,curNode->nodeVal);
}
curNode = curNode->next;
}
}
//广搜,类似于二叉树的层序遍历
void bfs(GraphNode* g,int val){
queue<VNode*> que;
que.push(g->graph[val]);
cout<<"正在访问节点"<<val<<endl;
visit[val] = true;
while(!que.empty()){
VNode* curNode = que.front();
que.pop();
VNode* nextNode = curNode->next;
while(nextNode){
if(!visit[nextNode->nodeVal]){
que.push(g->graph[nextNode->nodeVal]);
cout<<"正在访问节点"<<nextNode->nodeVal<<endl;
visit[nextNode->nodeVal] = true;
}
nextNode = nextNode->next;
}
}
}
int main(){
Solution s;
GraphNode* g = s.buildGraph();
dfs(g,0);
cout<<"=============="<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<maxNodeNum;i++){
visit[i] = false;
}
bfs(g,0);
return 0;
}
/**
输入:
10 17
0 1 1
0 3 1
1 2 1
1 3 1
1 5 1
2 4 1
2 5 1
3 6 1
3 7 1
4 5 1
4 9 1
5 6 1
5 8 1
5 9 1
6 7 1
6 8 1
8 9 1
输出:
正在访问顶点0
正在访问顶点3
正在访问顶点7
正在访问顶点6
正在访问顶点8
正在访问顶点9
正在访问顶点5
正在访问顶点4
正在访问顶点2
正在访问顶点1
==============
正在访问节点0
正在访问节点3
正在访问节点1
正在访问节点7
正在访问节点6
正在访问节点5
正在访问节点2
正在访问节点8
正在访问节点9
正在访问节点4
*/
参考
- 数据结构(四)—— 图(1):什么是图
- 数据结构(四)—— 图(2):图的遍历