算法介绍
CNN的优势
相比于传统的全连接神经网络,CNN在图像处理方面表现更佳,原因在于:
- 局部连接:全连接层是一种稠密连接方式,而卷积层却只使用卷积核对局部进行处理,这种处理方式其实也刚好对应了图像的特点。在视觉识别中,关键性的图像特征、边缘、角点等只占据了整张图像的一小部分,相隔很远的像素之间存在联系和影响的可能性是很低的,而局部像素具有很强的相关性,也即:CNN可以保存更多的空间信息。
- 共享参数:如果借鉴全连接层的话,对于1000×1000大小的彩色图像,一层全连接层便对应于三百万数量级维的特征,即会导致庞大的参数量,不仅计算繁重,还会导致过拟合。而卷积层中,卷积核会与局部图像相互作用,是一种稀疏连接,大大减少了网络的参数量。另外从直观上理解,依靠卷积核的滑动去提取图像中不同位置的相同模式也刚好符合图像的特点,不同的卷积核提取不同的特征,组合起来后便可以提取到高级特征用于最后的识别检测了。
卷积操作
最简单的理解,卷积就是通过卷积核与输入相乘再相加,得到卷积操作之后的输出。它的作用如下:
- 图像增强:卷积可以通过一些滤波器对图像进行增强,比如锐化、平滑等。这有助于提高图像的视觉效果和品质。
- 特征提取:卷积可以通过滤波器提取出信号中的特征,比如边缘、纹理等。这些特征对于图像分类和识别任务非常重要。
- 降维:卷积可以通过池化操作减小图像的尺寸,从而降低数据的维度。这对于处理大规模图像和文本数据非常有用。
- 去噪:卷积可以通过滤波器去除信号中的噪声。这在信号处理和图像处理领域中非常常见,有助于提高数据的质量。
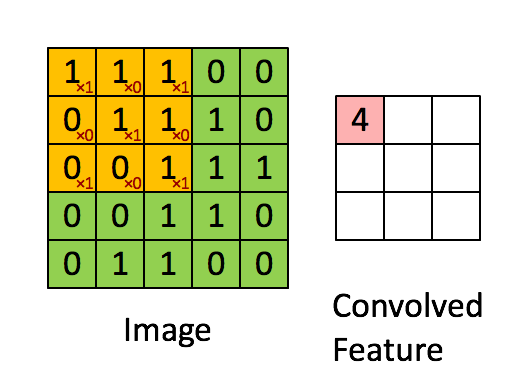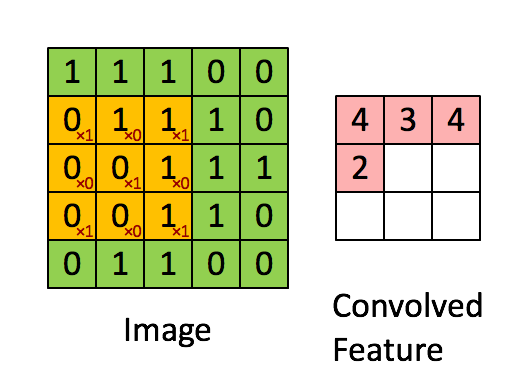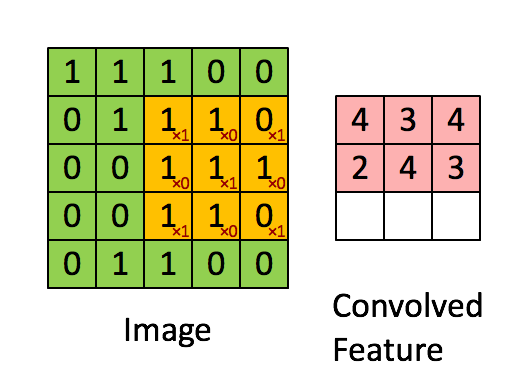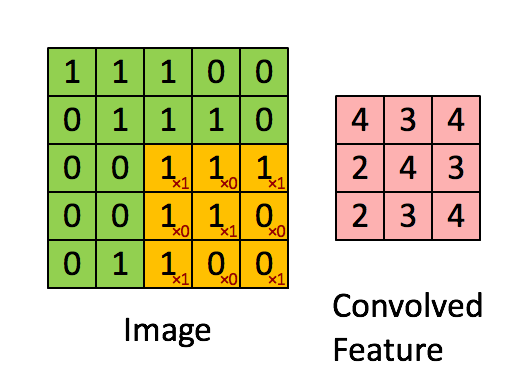
卷积操作的尺寸变化如图所示:

池化操作
池化操作通常在卷积层之后进行,其输入为卷积层的输出,输出为降采样后的特征图。其主要作用是:
-
减少数据量:在CNN中,每个卷积层的输出都是一个特征图,其大小通常比输入图像大很多。池化操作可以将特征图的大小降低,减少数据量,从而降低模型的计算复杂度。
-
提取重要特征:池化操作可以从输入数据中提取最显著的特征,将其保留下来,同时将其余特征舍弃。这样可以保留重要的特征,减少噪声的影响,提高模型的性能。
-
不变性:池化操作可以使模型对输入数据的变化具有一定的不变性。例如,最大池化操作可以使模型对输入数据的平移、旋转、缩放等变化具有一定的不变性。
-
防止过拟合:池化操作可以有效地减少模型的过拟合情况。过拟合是指模型在训练集上表现良好,但在测试集上表现差的情况。池化操作可以减少模型的参数量,从而降低过拟合的风险。
网络结构
- 输入层(Input layer):接收输入数据,通常是图像或其他多维数组形式的数据。
- 卷积层(Convolutional layer):卷积层是CNN的核心组件。每个卷积层包含多个卷积核(也称为滤波器),每个卷积核通过滑动窗口对输入数据进行卷积操作,提取特征。卷积操作通过局部感受野和权重参数实现对输入数据的局部特征提取。
- 激活函数层(Activation layer):在卷积层的输出上应用非线性激活函数(如ReLU),引入非线性特性。激活函数通过对卷积层的输出进行元素级的非线性变换,增加网络的表达能力。
- 池化层(Pooling layer):池化层对卷积层的输出进行下采样操作,减小特征图的空间尺寸,同时保留重要的特征。常见的池化操作包括最大池化和平均池化。
- 全连接层(Fully Connected layer):通过卷积层和池化层之后,通常会使用全连接层将高维的特征表示映射到目标类别的概率分布。全连接层中的神经元与前一层的所有神经元都连接起来,通过权重和偏差计算输出。
- 输出层(Output layer):最后一个全连接层的输出通过softmax函数进行概率归一化,将网络的输出转化为各个类别的概率分布。
训练过程
前向传播
- 输入数据:输入数据通常是图像或其他多维数组形式的数据。图像通常是由像素组成的三维数组,数据会通过网络中的各个层进行传递和处理。在本例中输入是(1,28,28)的数据。
- 卷积层、激活函数、池化层:卷积层生成特征图、激活函数引入非线性特性、池化层进行下采样保留重要特征
- 全连接层:全连接层中的神经元与前一层的所有神经元都连接起来,通过权重和偏差计算输出。(本例没有使用全连接层)
- 输出层:最后一个全连接层的输出通过softmax函数进行概率归一化,将网络的输出转化为各个类别的概率分布。
反向传播
- 损失函数:定义一个损失函数,用于度量网络输出与真实标签之间的差异。常见的损失函数包括交叉熵损失、均方误差等。这里使用的是均方误差
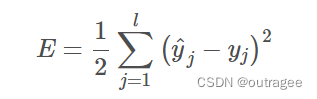
- 反向传播:根据损失函数计算网络参数的梯度。从输出层开始,通过链式法则逐层反向传播梯度,计算每个参数对于损失函数的梯度。梯度表示了参数的变化方向,以便于后续的参数更新。
- 参数更新:利用计算得到的梯度来更新网络的参数。通常使用梯度下降法或其变种进行参数更新。梯度下降法根据梯度的反方向调整参数的值,使损失函数逐渐减小。
- 重复迭代:通过不断重复前向传播、计算梯度和参数更新的过程,使网络逐渐学习到更好的参数配置,以减小损失函数。
代码实现
数据模型类Dataset
Dataset有三个主要的属性、负责读取文件的构造方法和一个内部类Instance,每个Instance对应着一条数据。
其中主要的方法有:append()添加一条数据、size()获取数据总数等常规方法。
package cnn;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Manage the dataset.
*
* @author Fan Min minfanphd@163.com.
*/
public class Dataset {
/**
* All instances organized by a list.
* 所有的数据使用list来保存
*/
private List<Instance> instances;
/**
* The label index.
* 当前数据的索引值
*/
private int labelIndex;
/**
* The max label (label start from 0).
*
*/
private double maxLabel = -1;
/**
***********************
* The first constructor.
***********************
*/
public Dataset() {
labelIndex = -1;
instances = new ArrayList<Instance>();
}// Of the first constructor
/**
***********************
* The second constructor.
*
* @param paraFilename
* The filename.
* @param paraSplitSign
* Often comma.
* @param paraLabelIndex
* Often the last column.
***********************
*/
public Dataset(String paraFilename, String paraSplitSign, int paraLabelIndex) {
instances = new ArrayList<Instance>();
labelIndex = paraLabelIndex;
File tempFile = new File(paraFilename);
try {
BufferedReader tempReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(tempFile));
String tempLine;
while ((tempLine = tempReader.readLine()) != null) {
String[] tempDatum = tempLine.split(paraSplitSign);
if (tempDatum.length == 0) {
continue;
} // Of if
double[] tempData = new double[tempDatum.length];
for (int i = 0; i < tempDatum.length; i++)
tempData[i] = Double.parseDouble(tempDatum[i]);
Instance tempInstance = new Instance(tempData);
append(tempInstance);
} // Of while
tempReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Unable to load " + paraFilename);
System.exit(0);
}//Of try
}// Of the second constructor
/**
***********************
* Append an instance.
*
* @param paraInstance
* The given record.
***********************
*/
public void append(Instance paraInstance) {
instances.add(paraInstance);
}// Of append
/**
***********************
* Append an instance specified by double values.
***********************
*/
public void append(double[] paraAttributes, Double paraLabel) {
instances.add(new Instance(paraAttributes, paraLabel));
}// Of append
/**
***********************
* Getter.
***********************
*/
public Instance getInstance(int paraIndex) {
return instances.get(paraIndex);
}// Of getInstance
/**
***********************
* Getter.
***********************
*/
public int size() {
return instances.size();
}// Of size
/**
***********************
* Getter.
***********************
*/
public double[] getAttributes(int paraIndex) {
return instances.get(paraIndex).getAttributes();
}// Of getAttrs
/**
***********************
* Getter.
***********************
*/
public Double getLabel(int paraIndex) {
return instances.get(paraIndex).getLabel();
}// Of getLabel
/**
***********************
* Unit test.
***********************
*/
public static void main(String args[]) {
Dataset tempData = new Dataset("C:\\Users\\hp\\Desktop\\deepLearning\\src\\main\\java\\resources\\train.format", ",", 784);
Instance tempInstance = tempData.getInstance(0);
System.out.println("The first instance is: " + tempInstance);
}// Of main
/**
***********************
* An instance.
***********************
*/
public class Instance {
/**
* Conditional attributes.
*/
private double[] attributes;
/**
* Label.
*/
private Double label;
/**
***********************
* The first constructor.
***********************
*/
private Instance(double[] paraAttrs, Double paraLabel) {
attributes = paraAttrs;
label = paraLabel;
}//Of the first constructor
/**
***********************
* The second constructor.
***********************
*/
public Instance(double[] paraData) {
if (labelIndex == -1)
// No label
attributes = paraData;
else {
label = paraData[labelIndex];
if (label > maxLabel) {
// It is a new label
maxLabel = label;
} // Of if
if (labelIndex == 0) {
// The first column is the label
attributes = Arrays.copyOfRange(paraData, 1, paraData.length);
} else {
// The last column is the label
attributes = Arrays.copyOfRange(paraData, 0, paraData.length - 1);
} // Of if
} // Of if
}// Of the second constructor
/**
***********************
* Getter.
***********************
*/
public double[] getAttributes() {
return attributes;
}// Of getAttributes
/**
***********************
* Getter.
***********************
*/
public Double getLabel() {
if (labelIndex == -1)
return null;
return label;
}// Of getLabel
/**
***********************
* toString.
***********************
*/
public String toString(){
return Arrays.toString(attributes) + ", " + label;
}//Of toString
}// Of class Instance
}// Of class Dataset
矩阵尺寸类Size
Size类主要用于表示卷积核与池化核的尺寸,并且封装了两组操作。
package cnn;
/**
* The size of a convolution core.
*
* @author Fan Min minfanphd@163.com.
*/
public class Size {
/**
* Cannot be changed after initialization.
*/
public final int width;
/**
* Cannot be changed after initialization.
*/
public final int height;
/**
***********************
* The first constructor.
*
* @param paraWidth
* The given width.
* @param paraHeight
* The given height.
***********************
*/
public Size(int paraWidth, int paraHeight) {
width = paraWidth;
height = paraHeight;
}// Of the first constructor
/**
***********************
* Divide a scale with another one. For example (4, 12) / (2, 3) = (2, 4).
*
* @param paraScaleSize
* The given scale size.
* @return The new size.
***********************
*/
public Size divide(Size paraScaleSize) {
int resultWidth = width / paraScaleSize.width;
int resultHeight = height / paraScaleSize.height;
if (resultWidth * paraScaleSize.width != width
|| resultHeight * paraScaleSize.height != height)
throw new RuntimeException("Unable to divide " + this + " with " + paraScaleSize);
return new Size(resultWidth, resultHeight);
}// Of divide
/**
***********************
* Subtract a scale with another one, and add a value. For example (4, 12) -
* (2, 3) + 1 = (3, 10).
*
* @param paraScaleSize
* The given scale size.
* @param paraAppend
* The appended size to both dimensions.
* @return The new size.
***********************
*/
public Size subtract(Size paraScaleSize, int paraAppend) {
int resultWidth = width - paraScaleSize.width + paraAppend;
int resultHeight = height - paraScaleSize.height + paraAppend;
return new Size(resultWidth, resultHeight);
}// Of subtract
/**
***********************
* @param The
* string showing itself.
***********************
*/
public String toString() {
String resultString = "(" + width + ", " + height + ")";
return resultString;
}// Of toString
/**
***********************
* Unit test.
***********************
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
Size tempSize1 = new Size(4, 6);
Size tempSize2 = new Size(2, 2);
System.out.println(
"" + tempSize1 + " divide " + tempSize2 + " = " + tempSize1.divide(tempSize2));
System.out.printf("a");
try {
System.out.println(
"" + tempSize2 + " divide " + tempSize1 + " = " + tempSize2.divide(tempSize1));
} catch (Exception ee) {
System.out.println(ee);
} // Of try
System.out.println(
"" + tempSize1 + " - " + tempSize2 + " + 1 = " + tempSize1.subtract(tempSize2, 1));
}// Of main
}// Of class Size
核心操作类MathUtils
Operator、OperatorOnTwo接口下的操作
在MathUtils类中有内部接口Operator和OperatorOnTwo,在大类中声明了很多实例实现了该接口,实现了一些功能,有:1-n运算、sigmoid运算以及对位加减乘运算
卷积操作
这里有两种卷积:
- double[][] convnValid(final double[][] matrix, double[][] kernel) 是常规的卷积操作,用于forword正向传递
- double[][] convnFull(double[][] matrix, final double[][] kernel) 用于backPropagation反向传递
/**
***********************
* Convolution operation, from a given matrix and a kernel, sliding and sum
* to obtain the result matrix. It is used in forward.
***********************
*/
public static double[][] convnValid(final double[][] matrix, double[][] kernel) {
// kernel = rot180(kernel);
int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
final int km = kernel.length;
final int kn = kernel[0].length;
int kns = n - kn + 1;
final int kms = m - km + 1;
final double[][] outMatrix = new double[kms][kns];
for (int i = 0; i < kms; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < kns; j++) {
double sum = 0.0;
for (int ki = 0; ki < km; ki++) {
for (int kj = 0; kj < kn; kj++)
sum += matrix[i + ki][j + kj] * kernel[ki][kj];
}
outMatrix[i][j] = sum;
}
}
return outMatrix;
}// Of convnValid
/**
***********************
* Convolution full to obtain a bigger size. It is used in back-propagation.
***********************
*/
public static double[][] convnFull(double[][] matrix, final double[][] kernel) {
int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
final int km = kernel.length;
final int kn = kernel[0].length;
final double[][] extendMatrix = new double[m + 2 * (km - 1)][n + 2 * (kn - 1)];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
extendMatrix[i + km - 1][j + kn - 1] = matrix[i][j];
} // Of for j
} // Of for i
return convnValid(extendMatrix, kernel);
}// Of convnFull
池化操作
- double[][] scaleMatrix(final double[][] matrix, final Size scale) 均值池化操作, 用于forward正向传播中对于值的预测.
- double[][] kronecker(final double[][] matrix, final Size scale) 均值反池化, 用于backPropagation逆向传播中对于惩罚信息的更新, 是卷积层更新惩罚信息进行上采样的关键函数.
/**
***********************
* Scale the matrix.
***********************
*/
public static double[][] scaleMatrix(final double[][] matrix, final Size scale) {
int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
final int sm = m / scale.width;
final int sn = n / scale.height;
final double[][] outMatrix = new double[sm][sn];
if (sm * scale.width != m || sn * scale.height != n)
throw new RuntimeException("scale matrix");
final int size = scale.width * scale.height;
for (int i = 0; i < sm; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < sn; j++) {
double sum = 0.0;
for (int si = i * scale.width; si < (i + 1) * scale.width; si++) {
for (int sj = j * scale.height; sj < (j + 1) * scale.height; sj++) {
sum += matrix[si][sj];
} // Of for sj
} // Of for si
outMatrix[i][j] = sum / size;
} // Of for j
} // Of for i
return outMatrix;
}// Of scaleMatrix
/**
***********************
* Extend the matrix to a bigger one (a number of times).
***********************
*/
public static double[][] kronecker(final double[][] matrix, final Size scale) {
final int m = matrix.length;
int n = matrix[0].length;
final double[][] outMatrix = new double[m * scale.width][n * scale.height];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
for (int ki = i * scale.width; ki < (i + 1) * scale.width; ki++) {
for (int kj = j * scale.height; kj < (j + 1) * scale.height; kj++) {
outMatrix[ki][kj] = matrix[i][j];
}
}
}
}
return outMatrix;
}// Of kronecker
其他数学处理
该类还封装了其他数学处理,如:
- double[][] randomMatrix(int x, int y) 生成一个x*y的矩阵, 矩阵内每个值是范围位于[-0.005, 0.095) 这里有意控制大小是为了避免Sigmoid出现梯度爆炸
- double[] randomArray(int len) 生成长度为len的随机值矩阵, 单个值范围依旧是[-0.005, 0.095)
- int[] randomPerm(int size, int batchSize) 在[0,size)的范围内随机生成batchSize个不重叠的值, 这个方法将会用到batch训练中. 代码中, 我们使用了Java的集合方法Set来回避区域重复.
- double[][] cloneMatrix(final double[][] matrix) 顾名思义 , 矩阵拷贝
- double sum(double[][] error) 惩罚信息矩阵每个元素求和, 并返回求和值
- double sum(double[][][][] errors, int j) 固定第二维为j, 然后进行全维求和, 并返回求和值
- int getMaxIndex(double[] out) 返回out数组最大下标
单层网络类CnnLayer
网络类型枚举
如下表示了四种不同的网络类型:输入层、输出层、卷积层和池化层
public enum LayerTypeEnum {
INPUT, CONVOLUTION, SAMPLING, OUTPUT;
}//Of enum LayerTypeEnum
/**
* The type of the layer.
*/
LayerTypeEnum type;
其他属性
outmaps[batchSize][outMapNum][mapSize.width][mapSize.height]是指当前网络层输出的特征图数量
errors[][][][]是存储反向传播时的错误信息
kernel[front map][out map][width][height]是存储卷积核信息
bias[]是一维的,用于表示本层的偏置信息
网络结构类LayerBuilder
LayerBuilder类是将CnnLayer类进行数组化封装,并实现了一系列操作。
public class LayerBuilder {
/**
* Layers.
*/
private List<CnnLayer> layers;
/**
***********************
* The first constructor.
***********************
*/
public LayerBuilder() {
layers = new ArrayList<CnnLayer>();
}// Of the first constructor
/**
***********************
* The second constructor.
***********************
*/
public LayerBuilder(CnnLayer paraLayer) {
this();
layers.add(paraLayer);
}// Of the second constructor
/**
***********************
* Add a layer.
*
* @param paraLayer
* The new layer.
***********************
*/
public void addLayer(CnnLayer paraLayer) {
layers.add(paraLayer);
}// Of addLayer
/**
***********************
* Get the specified layer.
*
* @param paraIndex
* The index of the layer.
***********************
*/
public CnnLayer getLayer(int paraIndex) throws RuntimeException{
if (paraIndex >= layers.size()) {
throw new RuntimeException("CnnLayer " + paraIndex + " is out of range: "
+ layers.size() + ".");
}//Of if
return layers.get(paraIndex);
}//Of getLayer
/**
***********************
* Get the output layer.
***********************
*/
public CnnLayer getOutputLayer() {
return layers.get(layers.size() - 1);
}//Of getOutputLayer
/**
***********************
* Get the number of layers.
***********************
*/
public int getNumLayers() {
return layers.size();
}//Of getNumLayers
}// Of class LayerBuilder
核心业务类FullCnn
FullCnn类则是完成如下工作:
- forward 预测
- backPropagation 设置惩罚信息
- 更新卷积核与偏差值
- 训练
训练
/**
***********************
* Train the cnn.
***********************
*/
public void train(Dataset paraDataset, int paraRounds) {
for (int t = 0; t < paraRounds; t++) {
System.out.println("Iteration: " + t);
int tempNumEpochs = paraDataset.size() / batchSize;
if (paraDataset.size() % batchSize != 0)
tempNumEpochs++;
double tempNumCorrect = 0;
int tempCount = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < tempNumEpochs; i++) {
int[] tempRandomPerm = MathUtils.randomPerm(paraDataset.size(), batchSize);
CnnLayer.prepareForNewBatch();
for (int index : tempRandomPerm) {
boolean isRight = train(paraDataset.getInstance(index));
if (isRight)
tempNumCorrect++;
tempCount++;
CnnLayer.prepareForNewRecord();
} // Of for index
updateParameters();
if (i % 50 == 0) {
System.out.print("..");
if (i + 50 > tempNumEpochs)
System.out.println();
}
}
double p = 1.0 * tempNumCorrect / tempCount;
if (t % 10 == 1 && p > 0.96) {
ALPHA = 0.001 + ALPHA * 0.9;
} // Of iff
System.out.println("Training precision: " + p);
} // Of for i
}// Of train
train方法首先根据数据集长度和batchsize得到迭代次数epochs,因此可以在循环中,使用封装好的训练方法进行训练,再统计准确率
这个封装好的训练方法就是使用了正向传播与反向传播,如下
/**
***********************
* Train the cnn with only one record.
*
* @param paraRecord
* The given record.
***********************
*/
private boolean train(Instance paraRecord) {
forward(paraRecord);
boolean result = backPropagation(paraRecord);
return result;
}// Of train
前向传播
前向传播就是按部就班,把所有的层分情况用switch语句实现,这里的情况有三种:卷积层、池化层和输出层,对应方法如下:
switch (tempCurrentLayer.getType()) {
case CONVOLUTION:
setConvolutionOutput(tempCurrentLayer, tempLastLayer);
break;
case SAMPLING:
setSampOutput(tempCurrentLayer, tempLastLayer);
break;
case OUTPUT:
setConvolutionOutput(tempCurrentLayer, tempLastLayer);
break;
反向传播
/**
***********************
* Back-propagation.
*
* @param paraRecord
* The given record.
***********************
*/
private boolean backPropagation(Instance paraRecord) {
boolean result = setOutputLayerErrors(paraRecord);
setHiddenLayerErrors();
return result;
}// Of backPropagation
反向传播也是按照顺序,先从输出层开始,再进行隐藏层的(卷积层、池化层、全连接层)
网络结构设计
LayerBuilder builder = new LayerBuilder();
// Input layer, the maps are 28*28
builder.addLayer(new CnnLayer(LayerTypeEnum.INPUT, -1, new Size(28, 28)));
// Convolution output has size 24*24, 24=28+1-5
builder.addLayer(new CnnLayer(LayerTypeEnum.CONVOLUTION, 6, new Size(5, 5)));
// Sampling output has size 12*12,12=24/2
builder.addLayer(new CnnLayer(LayerTypeEnum.SAMPLING, -1, new Size(2, 2)));
// Convolution output has size 8*8, 8=12+1-5
builder.addLayer(new CnnLayer(LayerTypeEnum.CONVOLUTION, 12, new Size(5, 5)));
// Sampling output has size4×4,4=8/2
builder.addLayer(new CnnLayer(LayerTypeEnum.SAMPLING, -1, new Size(2, 2)));
// output layer, digits 0 - 9.
builder.addLayer(new CnnLayer(LayerTypeEnum.OUTPUT, 10, null));
// Construct the full CNN.
FullCnn tempCnn = new FullCnn(builder, 10);
Dataset tempTrainingSet = new Dataset("C:\\Users\\hp\\Desktop\\deepLearning\\src\\main\\java\\resources\\train.format", ",", 784);
// Train the model.
tempCnn.train(tempTrainingSet, 10);