上个月发布了四篇文章,主要讲了深度学习中的“hello world”----mnist图像识别,以及卷积神经网络的原理详解,包括基本原理、自己手写CNN和paddlepaddle的源码解析。这篇主要跟大家讲讲如何用PaddlePaddle和Tensorflow做图像分类。所有程序都在我的github里,可以自行下载训练。
在卷积神经网络中,有五大经典模型,分别是:LeNet-5,AlexNet,GoogleNet,Vgg和ResNet。本文首先自己设计一个小型CNN网络结构来对图像进行分类,再了解一下LeNet-5网络结构对图像做分类,并用比较流行的Tensorflow框架和百度的PaddlePaddle实现LeNet-5网络结构,并对结果对比。
什么是图像分类
图像分类是根据图像的语义信息将不同类别图像区分开来,是计算机视觉中重要的基本问题,也是图像检测、图像分割、物体跟踪、行为分析等其他高层视觉任务的基础。图像分类在很多领域有广泛应用,包括安防领域的人脸识别和智能视频分析等,交通领域的交通场景识别,互联网领域基于内容的图像检索和相册自动归类,医学领域的图像识别等(引用自官网)
cifar-10数据集
CIFAR-10分类问题是机器学习领域的一个通用基准,由60000张32*32的RGB彩色图片构成,共10个分类。50000张用于训练集,10000张用于测试集。其问题是将32X32像素的RGB图像分类成10种类别:飞机,手机,鸟,猫,鹿,狗,青蛙,马,船和卡车。更多信息可以参考CIFAR-10和Alex Krizhevsky的演讲报告。常见的还有cifar-100,分类物体达到100类,以及ILSVRC比赛的100类。
自己设计CNN
了解CNN的基本网络结构后,首先自己设计一个简单的CNN网络结构对cifar-10数据进行分类。
网络结构
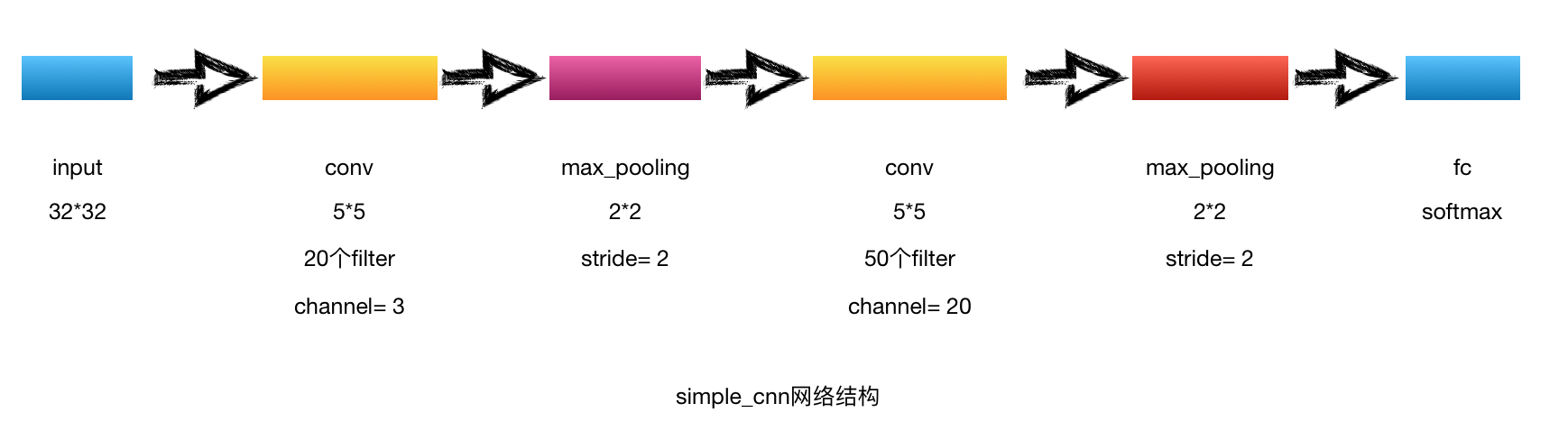
代码实现
1.网络结构:simple_cnn.py

1 #coding:utf-8
2 '''
3 Created by huxiaoman 2017.11.27
4 simple_cnn.py:自己设计的一个简单的cnn网络结构
5 '''
6
7 import os
8 from PIL import Image
9 import numpy as np
10 import paddle.fluid as fluid
11 from paddle.trainer_config_helpers import *
12
13 with_gpu = os.getenv('WITH_GPU', '0') != '1'
14
15 def simple_cnn(img):
16 conv_pool_1 = paddle.networks.simple_img_conv_pool(
17 input=img,
18 filter_size=5,
19 num_filters=20,
20 num_channel=3,
21 pool_size=2,
22 pool_stride=2,
23 act=paddle.activation.Relu())
24 conv_pool_2 = paddle.networks.simple_img_conv_pool(
25 input=conv_pool_1,
26 filter_size=5,
27 num_filters=50,
28 num_channel=20,
29 pool_size=2,
30 pool_stride=2,
31 act=paddle.activation.Relu())
32 fc = paddle.layer.fc(
33 input=conv_pool_2, size=512, act=paddle.activation.Softmax())

2.训练程序:train_simple_cnn.py

1 #coding:utf-8
2 '''
3 Created by huxiaoman 2017.11.27
4 train_simple—_cnn.py:训练simple_cnn对cifar10数据集进行分类
5 '''
6 import sys, os
7
8 import paddle.v2 as paddle
9 from simple_cnn import simple_cnn
10
11 with_gpu = os.getenv('WITH_GPU', '0') != '1'
12
13
14 def main():
15 datadim = 3 * 32 * 32
16 classdim = 10
17
18 # PaddlePaddle init
19 paddle.init(use_gpu=with_gpu, trainer_count=7)
20
21 image = paddle.layer.data(
22 name="image", type=paddle.data_type.dense_vector(datadim))
23
24 # Add neural network config
25 # option 1. resnet
26 # net = resnet_cifar10(image, depth=32)
27 # option 2. vgg
28 net = simple_cnn(image)
29
30 out = paddle.layer.fc(
31 input=net, size=classdim, act=paddle.activation.Softmax())
32
33 lbl = paddle.layer.data(
34 name="label", type=paddle.data_type.integer_value(classdim))
35 cost = paddle.layer.classification_cost(input=out, label=lbl)
36
37 # Create parameters
38 parameters = paddle.parameters.create(cost)
39
40 # Create optimizer
41 momentum_optimizer = paddle.optimizer.Momentum(
42 momentum=0.9,
43 regularization=paddle.optimizer.L2Regularization(rate=0.0002 * 128),
44 learning_rate=0.1 / 128.0,
45 learning_rate_decay_a=0.1,
46 learning_rate_decay_b=50000 * 100,
47 learning_rate_schedule='discexp')
48
49 # End batch and end pass event handler
50 def event_handler(event):
51 if isinstance(event, paddle.event.EndIteration):
52 if event.batch_id % 100 == 0:
53 print "\nPass %d, Batch %d, Cost %f, %s" % (
54 event.pass_id, event.batch_id, event.cost, event.metrics)
55 else:
56 sys.stdout.write('.')
57 sys.stdout.flush()
58 if isinstance(event, paddle.event.EndPass):
59 # save parameters
60 with open('params_pass_%d.tar' % event.pass_id, 'w') as f:
61 parameters.to_tar(f)
62
63 result = trainer.test(
64 reader=paddle.batch(
65 paddle.dataset.cifar.test10(), batch_size=128),
66 feeding={'image': 0,
67 'label': 1})
68 print "\nTest with Pass %d, %s" % (event.pass_id, result.metrics)
69
70 # Create trainer
71 trainer = paddle.trainer.SGD(
72 cost=cost, parameters=parameters, update_equation=momentum_optimizer)
73
74 # Save the inference topology to protobuf.
75 inference_topology = paddle.topology.Topology(layers=out)
76 with open("inference_topology.pkl", 'wb') as f:
77 inference_topology.serialize_for_inference(f)
78
79 trainer.train(
80 reader=paddle.batch(
81 paddle.reader.shuffle(
82 paddle.dataset.cifar.train10(), buf_size=50000),
83 batch_size=128),
84 num_passes=200,
85 event_handler=event_handler,
86 feeding={'image': 0,
87 'label': 1})
88
89 # inference
90 from PIL import Image
91 import numpy as np
92 import os
93
94 def load_image(file):
95 im = Image.open(file)
96 im = im.resize((32, 32), Image.ANTIALIAS)
97 im = np.array(im).astype(np.float32)
98 # The storage order of the loaded image is W(widht),
99 # H(height), C(channel). PaddlePaddle requires
100 # the CHW order, so transpose them.
101 im = im.transpose((2, 0, 1)) # CHW
102 # In the training phase, the channel order of CIFAR
103 # image is B(Blue), G(green), R(Red). But PIL open
104 # image in RGB mode. It must swap the channel order.
105 im = im[(2, 1, 0), :, :] # BGR
106 im = im.flatten()
107 im = im / 255.0
108 return im
109
110 test_data = []
111 cur_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))
112 test_data.append((load_image(cur_dir + '/image/dog.png'), ))
113
114 # users can remove the comments and change the model name
115 # with open('params_pass_50.tar', 'r') as f:
116 # parameters = paddle.parameters.Parameters.from_tar(f)
117
118 probs = paddle.infer(
119 output_layer=out, parameters=parameters, input=test_data)
120 lab = np.argsort(-probs) # probs and lab are the results of one batch data
121 print "Label of image/dog.png is: %d" % lab[0][0]
122
123
124 if __name__ == '__main__':
125 main()

3.结果输出

1 I1128 21:44:30.218085 14733 Util.cpp:166] commandline: --use_gpu=True --trainer_count=7
2 [INFO 2017-11-28 21:44:35,874 layers.py:2539] output for __conv_pool_0___conv: c = 20, h = 28, w = 28, size = 15680
3 [INFO 2017-11-28 21:44:35,874 layers.py:2667] output for __conv_pool_0___pool: c = 20, h = 14, w = 14, size = 3920
4 [INFO 2017-11-28 21:44:35,875 layers.py:2539] output for __conv_pool_1___conv: c = 50, h = 10, w = 10, size = 5000
5 [INFO 2017-11-28 21:44:35,876 layers.py:2667] output for __conv_pool_1___pool: c = 50, h = 5, w = 5, size = 1250
6 I1128 21:44:35.881502 14733 MultiGradientMachine.cpp:99] numLogicalDevices=1 numThreads=7 numDevices=8
7 I1128 21:44:35.928449 14733 GradientMachine.cpp:85] Initing parameters..
8 I1128 21:44:36.056259 14733 GradientMachine.cpp:92] Init parameters done.
9
10 Pass 0, Batch 0, Cost 2.302628, {'classification_error_evaluator': 0.9296875}
11 ................................................................................
12 ```
13 Pass 199, Batch 200, Cost 0.869726, {'classification_error_evaluator': 0.3671875}
14 ...................................................................................................
15 Pass 199, Batch 300, Cost 0.801396, {'classification_error_evaluator': 0.3046875}
16 ..........................................................................................I1128 23:21:39.443141 14733 MultiGradientMachine.cpp:99] numLogicalDevices=1 numThreads=7 numDevices=8
17
18 Test with Pass 199, {'classification_error_evaluator': 0.5248000025749207}
19 Label of image/dog.png is: 9

我开了7个线程,用了8个Tesla K80 GPU训练,batch_size = 128,迭代次数200次,耗时1h37min,错误分类率为0.5248,这个结果,emm,不算很高,我们可以把它作为一个baseline,后面对其进行调优。
LeNet-5网络结构
Lenet-5网络结构来源于Yan LeCun提出的,原文为《Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition》,论文里使用的是mnist手写数字作为输入数据(32 * 32)进行验证。我们来看一下网络结构。
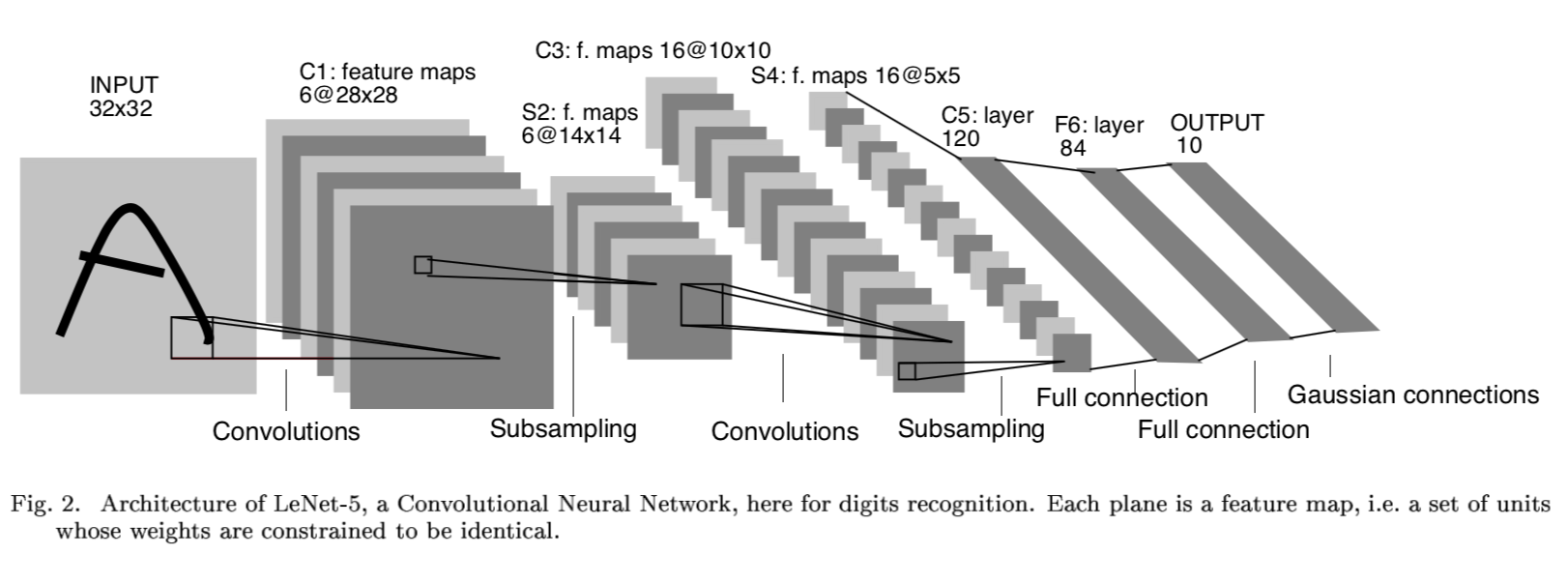
LeNet-5一共有8层: 1个输入层+3个卷积层(C1、C3、C5)+2个下采样层(S2、S4)+1个全连接层(F6)+1个输出层,每层有多个feature map(自动提取的多组特征)。
Input输入层
cifar10 数据集,每一张图片尺寸:32 * 32
C1 卷积层
- 6个feature_map,卷积核大小 5 * 5 ,feature_map尺寸:28 * 28
- 每个卷积神经元的参数数目:5 * 5 = 25个和一个bias参数
- 连接数目:(5*5+1)* 6 *(28*28) = 122,304
- 参数共享:每个feature_map内共享参数,∴∴共(5*5+1)*6 = 156个参数
S2 下采样层(池化层)
- 6个14*14的feature_map,pooling大小 2* 2
- 每个单元与上一层的feature_map中的一个2*2的滑动窗口连接,不重叠,因此S2每个feature_map大小是C1中feature_map大小的1/4
- 连接数:(2*2+1)*1*14*14*6 = 5880个
- 参数共享:每个feature_map内共享参数,有2 * 6 = 12个训练参数
C3 卷积层
这层略微复杂,S2神经元与C3是多对多的关系,比如最简单方式:用S2的所有feature map与C3的所有feature map做全连接(也可以对S2抽样几个feature map出来与C3某个feature map连接),这种全连接方式下:6个S2的feature map使用6个独立的5×5卷积核得到C3中1个feature map(生成每个feature map时对应一个bias),C3中共有16个feature map,所以该层需要学习的参数个数为:(5×5×6+1)×16=2416个,神经元连接数为:2416×8×8=154624个。
S4 下采样层
同S2,如果采用Max Pooling/Mean Pooling,则该层需要学习的参数个数为0个,神经元连接数为:(2×2+1)×16×4×4=1280个。
C5卷积层
类似C3,用S4的所有feature map与C5的所有feature map做全连接,这种全连接方式下:16个S4的feature map使用16个独立的1×1卷积核得到C5中1个feature map(生成每个feature map时对应一个bias),C5中共有120个feature map,所以该层需要学习的参数个数为:(1×1×16+1)×120=2040个,神经元连接数为:2040个。
F6 全连接层
将C5层展开得到4×4×120=1920个节点,并接一个全连接层,考虑bias,该层需要学习的参数和连接个数为:(1920+1)*84=161364个。
输出层
该问题是个10分类问题,所以有10个输出单元,通过softmax做概率归一化,每个分类的输出单元对应84个输入。
LeNet-5的PaddlePaddle实现
1.网络结构 lenet.py

1 #coding:utf-8
2 '''
3 Created by huxiaoman 2017.11.27
4 lenet.py:LeNet-5
5 '''
6
7 import os
8 from PIL import Image
9 import numpy as np
10 import paddle.v2 as paddle
11 from paddle.trainer_config_helpers import *
12
13 with_gpu = os.getenv('WITH_GPU', '0') != '1'
14
15 def lenet(img):
16 conv_pool_1 = paddle.networks.simple_img_conv_pool(
17 input=img,
18 filter_size=5,
19 num_filters=6,
20 num_channel=3,
21 pool_size=2,
22 pool_stride=2,
23 act=paddle.activation.Relu())
24 conv_pool_2 = paddle.networks.simple_img_conv_pool(
25 input=conv_pool_1,
26 filter_size=5,
27 num_filters=16,
28 pool_size=2,
29 pool_stride=2,
30 act=paddle.activation.Relu())
31 conv_3 = img_conv_layer(
32 input = conv_pool_2,
33 filter_size = 1,
34 num_filters = 120,
35 stride = 1)
36 fc = paddle.layer.fc(
37 input=conv_3, size=84, act=paddle.activation.Sigmoid())
38 return fc

2.训练代码 train_lenet.py

1 #coding:utf-8
2 '''
3 Created by huxiaoman 2017.11.27
4 train_lenet.py:训练LeNet-5对cifar10数据集进行分类
5 '''
6
7 import sys, os
8
9 import paddle.v2 as paddle
10 from lenet import lenet
11
12 with_gpu = os.getenv('WITH_GPU', '0') != '1'
13
14
15 def main():
16 datadim = 3 * 32 * 32
17 classdim = 10
18
19 # PaddlePaddle init
20 paddle.init(use_gpu=with_gpu, trainer_count=7)
21
22 image = paddle.layer.data(
23 name="image", type=paddle.data_type.dense_vector(datadim))
24
25 # Add neural network config
26 # option 1. resnet
27 # net = resnet_cifar10(image, depth=32)
28 # option 2. vgg
29 net = lenet(image)
30
31 out = paddle.layer.fc(
32 input=net, size=classdim, act=paddle.activation.Softmax())
33
34 lbl = paddle.layer.data(
35 name="label", type=paddle.data_type.integer_value(classdim))
36 cost = paddle.layer.classification_cost(input=out, label=lbl)
37
38 # Create parameters
39 parameters = paddle.parameters.create(cost)
40
41 # Create optimizer
42 momentum_optimizer = paddle.optimizer.Momentum(
43 momentum=0.9,
44 regularization=paddle.optimizer.L2Regularization(rate=0.0002 * 128),
45 learning_rate=0.1 / 128.0,
46 learning_rate_decay_a=0.1,
47 learning_rate_decay_b=50000 * 100,
48 learning_rate_schedule='discexp')
49
50 # End batch and end pass event handler
51 def event_handler(event):
52 if isinstance(event, paddle.event.EndIteration):
53 if event.batch_id % 100 == 0:
54 print "\nPass %d, Batch %d, Cost %f, %s" % (
55 event.pass_id, event.batch_id, event.cost, event.metrics)
56 else:
57 sys.stdout.write('.')
58 sys.stdout.flush()
59 if isinstance(event, paddle.event.EndPass):
60 # save parameters
61 with open('params_pass_%d.tar' % event.pass_id, 'w') as f:
62 parameters.to_tar(f)
63
64 result = trainer.test(
65 reader=paddle.batch(
66 paddle.dataset.cifar.test10(), batch_size=128),
67 feeding={'image': 0,
68 'label': 1})
69 print "\nTest with Pass %d, %s" % (event.pass_id, result.metrics)
70
71 # Create trainer
72 trainer = paddle.trainer.SGD(
73 cost=cost, parameters=parameters, update_equation=momentum_optimizer)
74
75 # Save the inference topology to protobuf.
76 inference_topology = paddle.topology.Topology(layers=out)
77 with open("inference_topology.pkl", 'wb') as f:
78 inference_topology.serialize_for_inference(f)
79
80 trainer.train(
81 reader=paddle.batch(
82 paddle.reader.shuffle(
83 paddle.dataset.cifar.train10(), buf_size=50000),
84 batch_size=128),
85 num_passes=200,
86 event_handler=event_handler,
87 feeding={'image': 0,
88 'label': 1})
89
90 # inference
91 from PIL import Image
92 import numpy as np
93 import os
94
95 def load_image(file):
96 im = Image.open(file)
97 im = im.resize((32, 32), Image.ANTIALIAS)
98 im = np.array(im).astype(np.float32)
99 # The storage order of the loaded image is W(widht),
100 # H(height), C(channel). PaddlePaddle requires
101 # the CHW order, so transpose them.
102 im = im.transpose((2, 0, 1)) # CHW
103 # In the training phase, the channel order of CIFAR
104 # image is B(Blue), G(green), R(Red). But PIL open
105 # image in RGB mode. It must swap the channel order.
106 im = im[(2, 1, 0), :, :] # BGR
107 im = im.flatten()
108 im = im / 255.0
109 return im
110
111 test_data = []
112 cur_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))
113 test_data.append((load_image(cur_dir + '/image/dog.png'), ))
114
115 # users can remove the comments and change the model name
116 # with open('params_pass_50.tar', 'r') as f:
117 # parameters = paddle.parameters.Parameters.from_tar(f)
118
119 probs = paddle.infer(
120 output_layer=out, parameters=parameters, input=test_data)
121 lab = np.argsort(-probs) # probs and lab are the results of one batch data
122 print "Label of image/dog.png is: %d" % lab[0][0]
123
124
125 if __name__ == '__main__':
126 main()

3.结果输出

1 I1129 14:52:44.314946 15153 Util.cpp:166] commandline: --use_gpu=True --trainer_count=7
2 [INFO 2017-11-29 14:52:50,490 layers.py:2539] output for __conv_pool_0___conv: c = 6, h = 28, w = 28, size = 4704
3 [INFO 2017-11-29 14:52:50,491 layers.py:2667] output for __conv_pool_0___pool: c = 6, h = 14, w = 14, size = 1176
4 [INFO 2017-11-29 14:52:50,491 layers.py:2539] output for __conv_pool_1___conv: c = 16, h = 10, w = 10, size = 1600
5 [INFO 2017-11-29 14:52:50,492 layers.py:2667] output for __conv_pool_1___pool: c = 16, h = 5, w = 5, size = 400
6 [INFO 2017-11-29 14:52:50,493 layers.py:2539] output for __conv_0__: c = 120, h = 5, w = 5, size = 3000
7 I1129 14:52:50.498749 15153 MultiGradientMachine.cpp:99] numLogicalDevices=1 numThreads=7 numDevices=8
8 I1129 14:52:50.545882 15153 GradientMachine.cpp:85] Initing parameters..
9 I1129 14:52:50.651103 15153 GradientMachine.cpp:92] Init parameters done.
10
11 Pass 0, Batch 0, Cost 2.331898, {'classification_error_evaluator': 0.9609375}
12 ```
13 ......
14 Pass 199, Batch 300, Cost 0.004373, {'classification_error_evaluator': 0.0}
15 ..........................................................................................I1129 16:17:08.678097 15153 MultiGradientMachine.cpp:99] numLogicalDevices=1 numThreads=7 numDevices=8
16
17 Test with Pass 199, {'classification_error_evaluator': 0.39579999446868896}
18 Label of image/dog.png is: 7

同样是7个线程,8个Tesla K80 GPU,batch_size = 128,迭代次数200次,耗时1h25min,错误分类率为0.3957,相比与simple_cnn的0.5248提高了12.91%。当然,这个结果也并不是很好,如果输出详细的日志,可以看到在训练的过程中loss先降后升,说明有一定程度的过拟合,对于如何防止过拟合,我们在后面会详细讲解。
有一个可视化CNN的网站可以对mnist和cifar10分类的网络结构进行可视化,这是cifar-10 BaseCNN的网络结构:

LeNet-5的Tensorflow实现
tensorflow版本的LeNet-5版本的可以参照models/tutorials/image/cifar10/(https://github.com/tensorflow/models/tree/master/tutorials/image/cifar10)的步骤来训练,不过这里面的代码包含了很多数据处理、权重衰减以及正则化的一些方法防止过拟合。按照官方写的,batch_size=128时在Tesla K40上迭代10w次需要4小时,准确率能达到86%。不过如果不对数据做处理,直接跑的话,效果应该没有这么好。不过可以仔细借鉴cifar10_inputs.py里的distorted_inouts函数对数据预处理增大数据集的思想,以及cifar10.py里对于权重和偏置的衰减设置等。目前迭代到1w次左右,cost是0.98,acc是78.4%
对于未进行数据处理的cifar10我准备也跑一次,看看效果如何,与paddle的结果对比一下。不过得等到周末再补上了 = =
总结
本节用常规的cifar-10数据集做图像分类,用了三种实现方式,第一种是自己设计的一个简单的cnn,第二种是LeNet-5,第三种是Tensorflow实现的LeNet-5,对比速度可以见一下表格:

可以看到LeNet-5相比于原始的simple_cnn在准确率和速度方面都有一定的的提升,等tensorflow版本跑完后可以把结果加上去再对比一下。不过用Lenet-5网络结构后,结果虽然有一定的提升,但是还是不够理想,在日志里看到loss的信息基本可以推断出是过拟合,对于神经网络训练过程中出现的过拟合情况我们应该如何避免,下期我们讲着重讲解。此外在下一节将介绍AlexNet,并对分类做一个实验,对比其效果。
参考文献
1.LeNet-5论文:《Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition》
2.可视化CNN:http://shixialiu.com/publications/cnnvis/demo/
作者:Charlotte77
出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/charlotte77/
本文以学习、研究和分享为主,如需转载,请联系本人,标明作者和出处,非商业用途!
关注【Charlotte数据挖掘】回复 '资料' 获取深度学习优质资料