面试题:两个线程打印
两个线程,一个线程打印1-52,另一个打印字母A-Z打印顺序为12A34B...5152Z,要求用线程间通信
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShareData05 shareData05 = new ShareData05();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
shareData05.printChar();
}
}).start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
shareData05.printNum();
}
}).start();
}
}
/**
* 两个线程,一个线程打印1-52,另一个打印字母A-Z打印顺序为12A34B...5152Z,要求用线程间通信
* A线程:
* int变量记录输出的数字
* B线程:
* int变量记录输出的字母的值
*
* 互斥:
* int变量
*
* 打印数字、打印字母 加锁
*/
class ShareData05{
private int num = 1;
private char c = 'A';
private int i = 0;//0打印数字、1打印字母
private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition numC = lock.newCondition();
private Condition cC = lock.newCondition();
public void printNum(){
lock.lock();
try {
while(i!=0){
numC.await();
}
System.out.print(num++);
System.out.print(num++);
i = 1;
cC.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void printChar(){
lock.lock();
try {
while(i!=1){
cC.await();
}
System.out.print(c++);
i = 0;
numC.signal();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
1. 回顾线程通信
先来简单案例:
两个线程操作一个初始值为0的变量,实现一个线程对变量增加1,一个线程对变量减少1,交替10轮。
线程间通信模型:
-
生产者+消费者
-
通知等待唤醒机制
多线程编程模板中:
-
判断
-
干活
-
通知
代码实现:
class ShareDataOne {
private Integer number = 0;
/**
* 增加1
*/
public synchronized void increment() throws InterruptedException {
// 1. 判断
if (number != 0) {
this.wait();
}
// 2. 干活
number++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + number);
// 3. 通知
this.notifyAll();
}
/**
* 减少1
*/
public synchronized void decrement() throws InterruptedException {
// 1. 判断
if (number != 1) {
this.wait();
}
// 2. 干活
number--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + number);
// 3. 通知
this.notifyAll();
}
}
/**
* 现在两个线程,
* 可以操作初始值为零的一个变量,
* 实现一个线程对该变量加1,一个线程对该变量减1,
* 交替,来10轮。
*
* 笔记:Java里面如何进行工程级别的多线程编写
* 1 多线编程模板(套路)-----上
* 1.1 线程 操作 资源类
* 1.2 高内聚 低耦合
* 2 多线程编程模板(套路)-----中
* 2.1 判断
* 2.2 干活
* 2.3 通知
*/
public class NotifyWaitDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShareDataOne shareDataOne = new ShareDataOne();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
shareDataOne.increment();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "AAA").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
shareDataOne.decrement();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "BBB").start();
}
}
部分打印结果:AAA和BBB交互执行,执行结果是1 0 1 0... 一共10轮
AAA: 1
BBB: 0
AAA: 1
BBB: 0
AAA: 1
BBB: 0
AAA: 1
BBB: 0
。。。。
如果换成4个线程会怎样?
改造mian方法,加入CCC和DDD两个线程:
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShareDataOne shareDataOne = new ShareDataOne();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
shareDataOne.increment();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "AAA").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
shareDataOne.decrement();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "BBB").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
shareDataOne.increment();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "CCC").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
shareDataOne.decrement();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "DDD").start();
}
打印结果,依然会有概率是,10101010...。但是,多执行几次,也会出现错乱的现象:
AAA: 1
BBB: 0
CCC: 1
AAA: 2
CCC: 3
BBB: 2
CCC: 3
DDD: 2
AAA: 3
DDD: 2
CCC: 3
BBB: 2
2. 虚假唤醒
换成4个线程会导致错误,虚假唤醒
原因:wait()会释放锁, 在java多线程判断时,不能用if,程序出事出在了判断上面。
注意,消费者被唤醒后是从wait()方法(被阻塞的地方)后面执行,而不是重新从同步块开头。
解决虚假唤醒:if换成while。中断和虚假唤醒是可能产生的,所以要用loop循环,if只判断一次,while是只要唤醒就要拉回来再判断一次。
class ShareDataOne {
private Integer number = 0;
/**
* 增加1
*/
public synchronized void increment() throws InterruptedException {
// 1. 判断
while (number != 0) {
this.wait();
}
// 2. 干活
number++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + number);
// 3. 通知
this.notifyAll();
}
/**
* 减少1
*/
public synchronized void decrement() throws InterruptedException {
// 1. 判断
while (number != 1) {
this.wait();
}
// 2. 干活
number--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + number);
// 3. 通知
this.notifyAll();
}
}
/**
* 现在两个线程,
* 可以操作初始值为零的一个变量,
* 实现一个线程对该变量加1,一个线程对该变量减1,
* 交替,来10轮。
*
* 笔记:Java里面如何进行工程级别的多线程编写
* 1 多线程编程模板(套路)-----上
* 1.1 线程 操作 资源类
* 1.2 高内聚 低耦合
* 2 多线程编程模板(套路)-----中
* 2.1 判断
* 2.2 干活
* 2.3 通知
* 3 多线程编程模板(套路)-----下
* 防止虚假唤醒(while)
*/
public class NotifyWaitDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShareDataOne shareDataOne = new ShareDataOne();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
shareDataOne.increment();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "AAA").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
shareDataOne.decrement();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "BBB").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
shareDataOne.increment();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "CCC").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
shareDataOne.decrement();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "DDD").start();
}
}
3. 线程通信(Condition)
使用Condition实现线程通信,改造之前的代码(只需要改造ShareDataOne):删掉increment和decrement方法的synchronized
class ShareDataOne {
private Integer number = 0;
final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock(); // 初始化lock锁
final Condition condition = lock.newCondition(); // 初始化condition对象
/**
* 增加1
*/
public void increment() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock(); // 加锁
try {
// 1. 判断
while (number != 0) {
// this.wait();
condition.await();
}
// 2. 干活
number++;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + number);
// 3. 通知
// this.notifyAll();
condition.signalAll();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* 减少1
*/
public void decrement() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
// 1. 判断
while (number != 1) {
// this.wait();
condition.await();
}
// 2. 干活
number--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ": " + number);
// 3. 通知
//this.notifyAll();
condition.signalAll();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
4. 定制化调用通信
① 案例:
多线程之间按顺序调用,实现A->B->C。三个线程启动,要求如下:
AA打印5次,BB打印10次,CC打印15次
接着
AA打印5次,BB打印10次,CC打印15次
。。。打印10轮
② 分析实现方式:
-
有一个锁Lock,3把钥匙Condition
-
有顺序通知(切换线程),需要有标识位
-
判断标志位
-
输出线程名 + 内容
-
修改标识符,通知下一个
③ 具体实现:
ReentrantLock 实现
class ShareDataTwo {
private Integer flag = 1; // 线程标识位,通过它区分线程切换
private final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private final Condition condition1 = lock.newCondition();
private final Condition condition2 = lock.newCondition();
private final Condition condition3 = lock.newCondition();
public void print5() {
lock.lock();
try {
while (flag != 1) {
condition1.await();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + (i + 1));
}
flag = 2;
condition2.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void print10() {
lock.lock();
try {
while (flag != 2) {
condition2.await();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + (i + 1));
}
flag = 3;
condition3.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void print15() {
lock.lock();
try {
while (flag != 3) {
condition3.await();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 15; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "\t" + (i + 1));
}
flag = 1;
condition1.signal();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
/**
* 多线程之间按顺序调用,实现A->B->C
* 三个线程启动,要求如下:
* AA打印5次,BB打印10次,CC打印15次
* 接着
* AA打印5次,BB打印10次,CC打印15次
* ......来10轮
*/
public class ThreadOrderAccess {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShareDataTwo sdt = new ShareDataTwo();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
sdt.print5();
}
}, "AAA").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
sdt.print10();
}
}, "BBB").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
sdt.print15();
}
}, "CCC").start();
}
}
Synchronized 实现
public class Demo10 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShareData04 shareData04 = new ShareData04();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
shareData04.printB();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"AA").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
shareData04.printA();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"BB").start();
new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
shareData04.printC();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"CC").start();
}
}
class ShareData04{
private int i = 0;
public synchronized void printA() throws InterruptedException {
while(i!=0){
this.wait();
}
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 5; i1++) {
System.out.print("AA\t");
}
i=1;
this.notifyAll();//唤醒的是所有线程
}
public synchronized void printB() throws InterruptedException {
while(i!=1){
this.wait();
}
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 10; i1++) {
System.out.print("BB\t");
}
i=2;
this.notifyAll();//唤醒的是所有线程
}
public synchronized void printC() throws InterruptedException {
while(i!=2){
this.wait();
}
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < 15; i1++) {
System.out.print("CC\t");
}
System.out.println();
i=0;
this.notifyAll();//唤醒的是所有线程
}
}
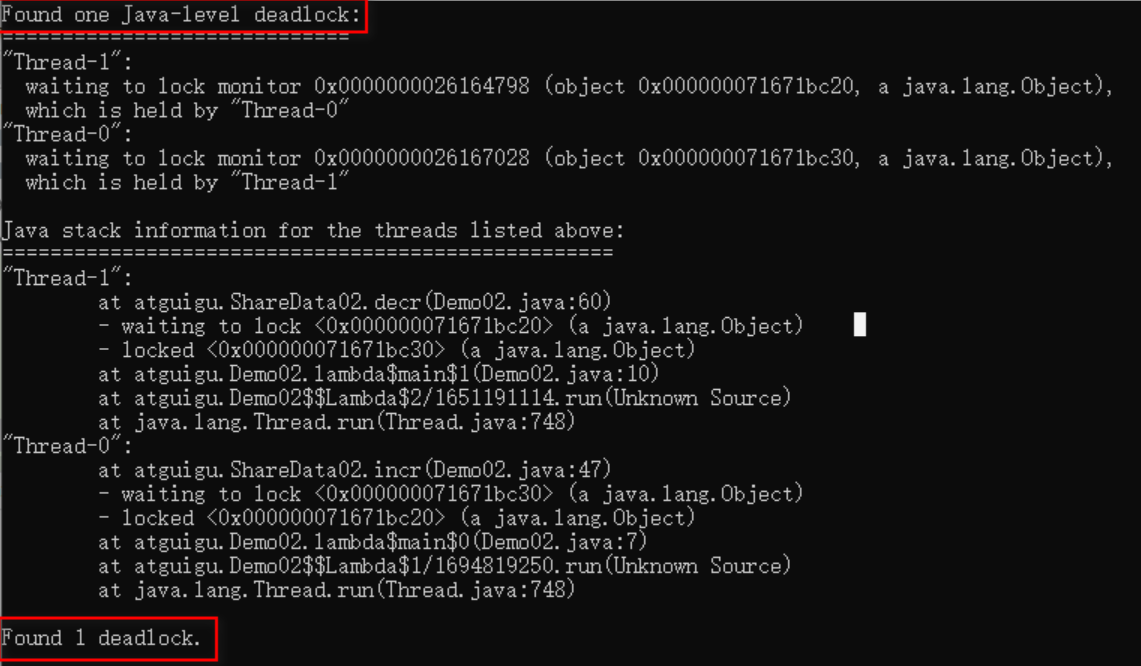
5. 死锁问题排查
jps(JVM Process Status Tool):显示当前系统的 Java 进程情况
jstack:java虚拟机自带的一种堆栈跟踪工具,查看Java进程内的线程堆栈信息,使用jstack命令查看线程堆栈信息时可能会看到的线程的几种状态:
如果出现:Found one Java-level deadlock 代表死锁
本文内容由网友自发贡献,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有涉嫌抄袭侵权的内容,请联系:hwhale#tublm.com(使用前将#替换为@)