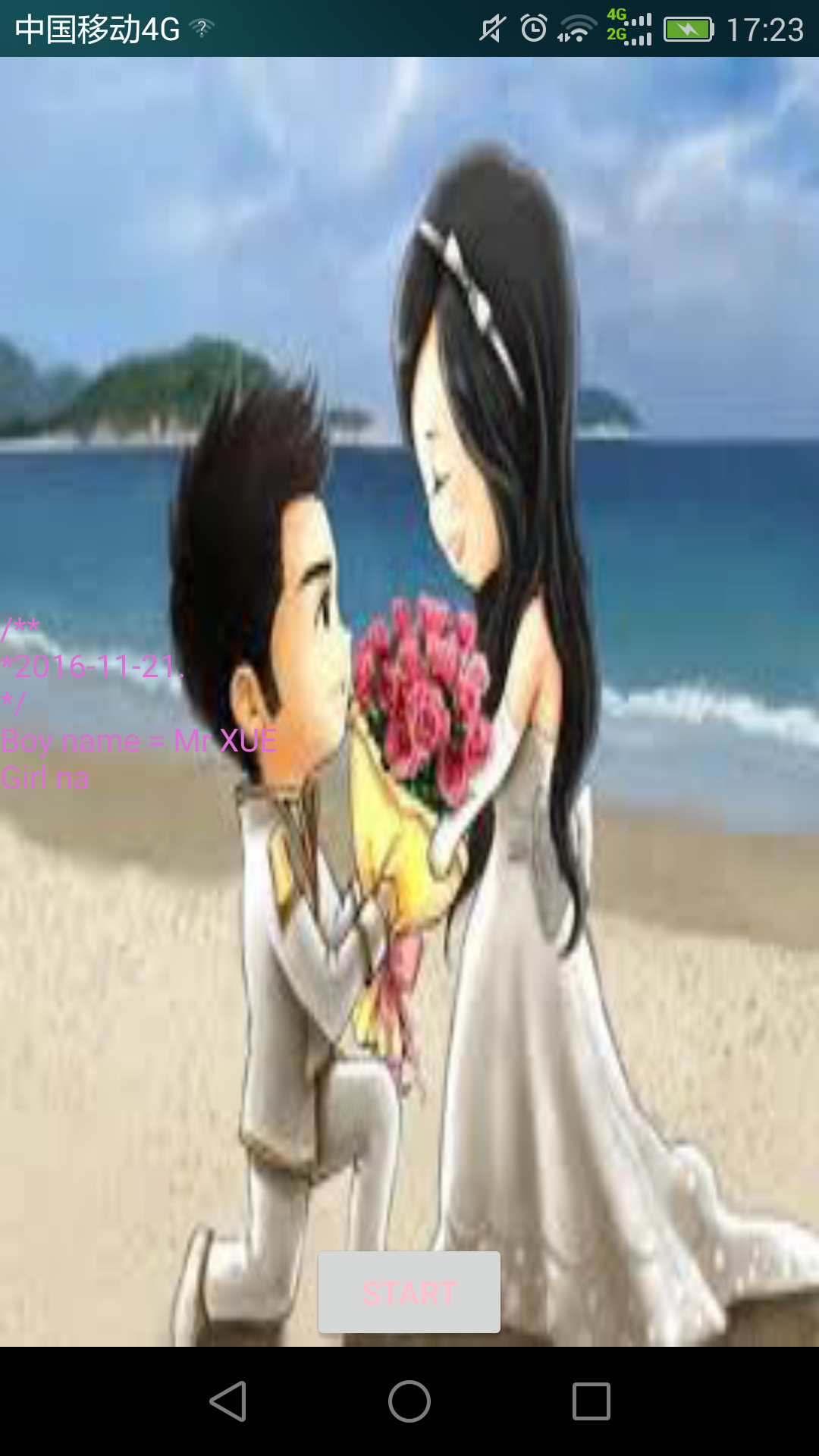
一年前,看到过有个牛人用HTML5绘制了浪漫的爱心表白动画,后来又在华超的这篇文章上看到大神用Android写出了相同的效果,于是也动手写了一下,并加了一些功能,感谢大神的指引,写给女票看她很开心呢。地址在这:浪漫程序员 HTML5爱心表白动画。发现原来程序员也是可以很浪……漫…..的。那么在Android怎么打造如此这个效果呢?参考了一下前面Html5的算法,在Android中实现了类似的效果。先贴上最终效果图:
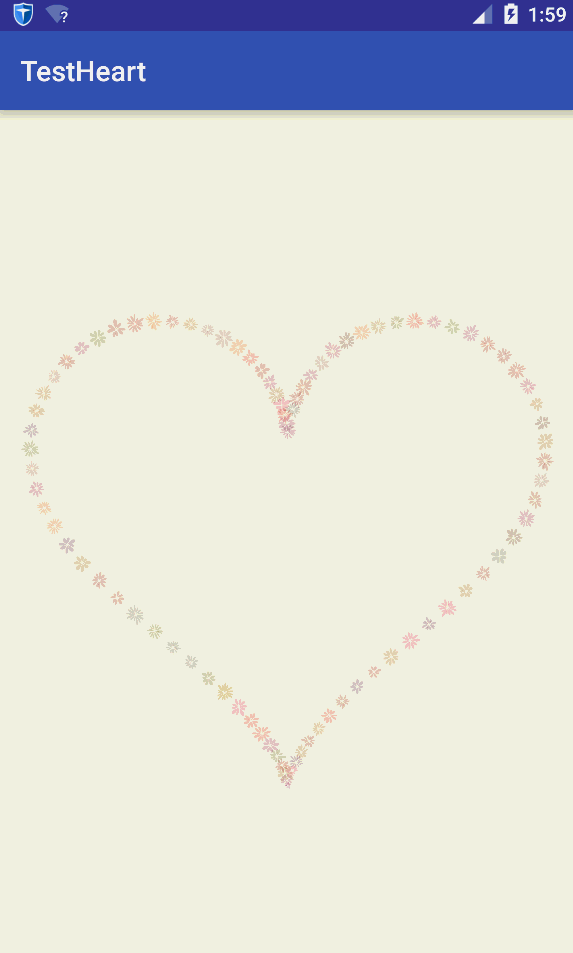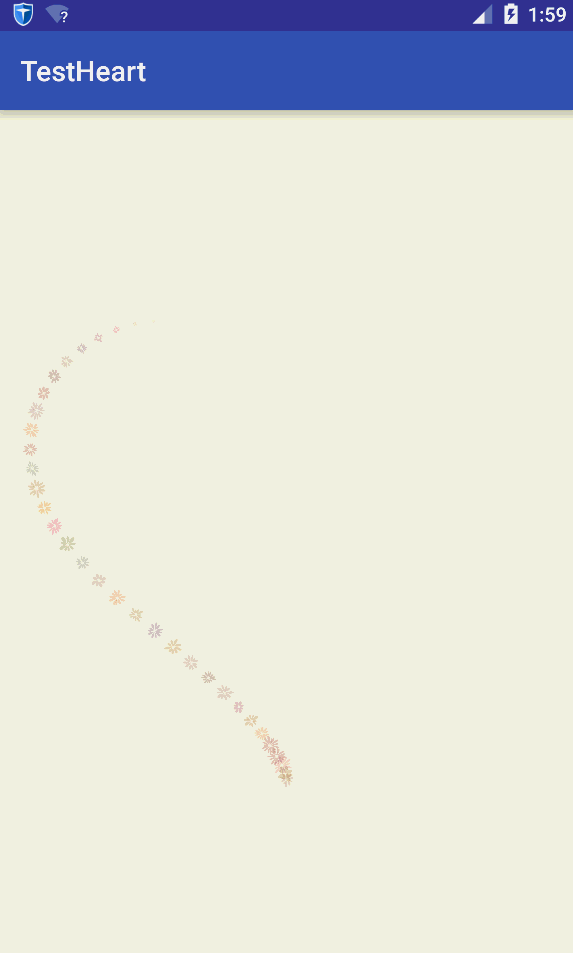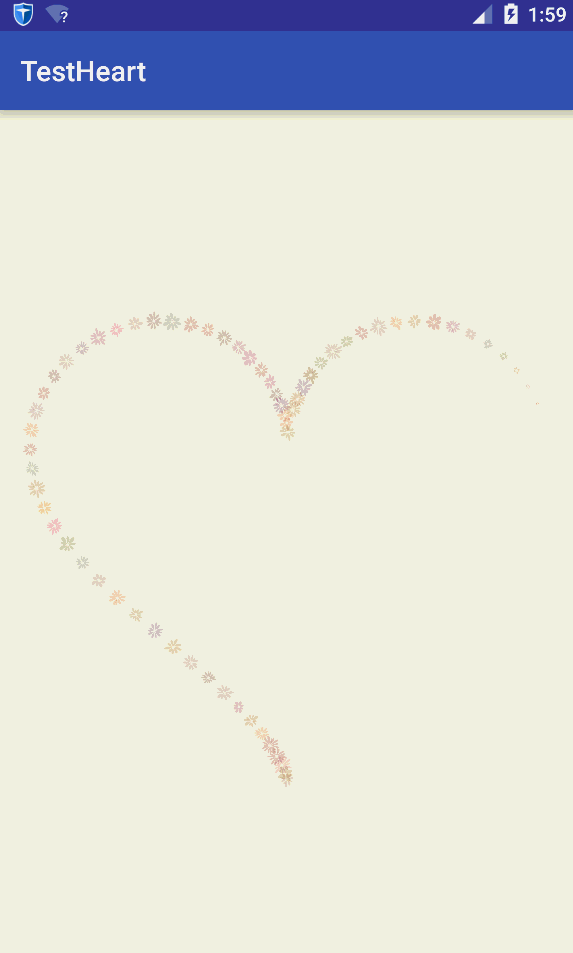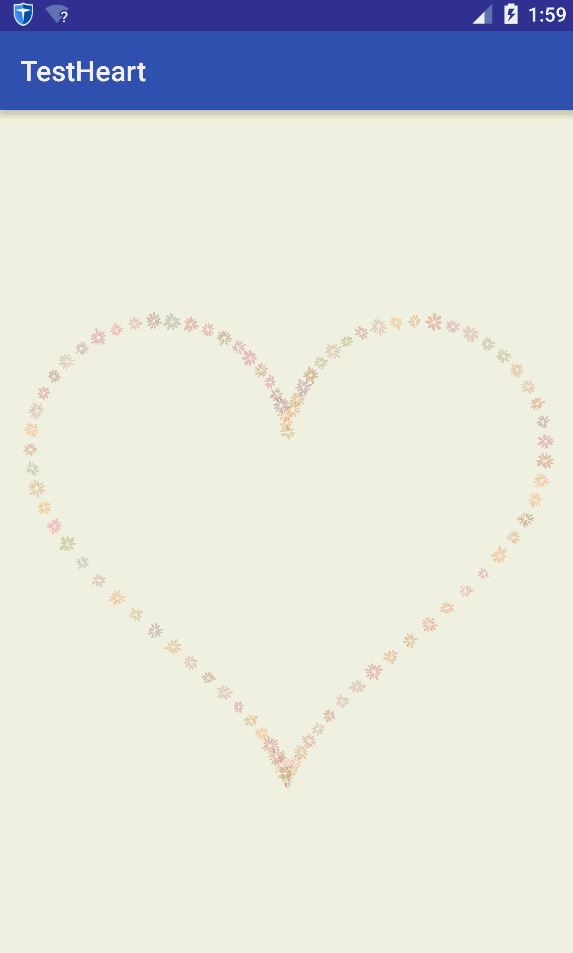




生成心形线
心形线的表达式可以参考:桃心线。里面对桃心线的表达式解析的挺好。可以通过使用极坐标的方式,传入角度和距离(常量)计算出对应的坐标点。其中距离是常量值,不需改变,变化的是角度。
桃心线极坐标方程式为:
x=16×sin3α
y=13×cosα−5×cos2α−2×cos3α−cos4α
如果生成的桃心线不够大,可以把x、y乘以一个常数,使之变大。考虑到大部分人都不愿去研究具体的数学问题,我们直接把前面HTML5的JS代码直接翻译成Java代码就好。代码如下:
public Point getHeartPoint(float angle) {
float t = (float) (angle / Math.PI);
float x = (float) (19.5 * (16 * Math.pow(Math.sin(t), 3)));
float y = (float) (-20 * (13 * Math.cos(t) - 5 * Math.cos(2 * t) - 2 * Math.cos(3 * t) - Math.cos(4 * t)));
return new Point(offsetX + (int) x, offsetY + (int) y);
}
其中offsetX和offsetY是偏移量。使用偏移量主要是为了能让心形线处于中央。offsetX和offsetY的值分别为:
offsetX = width / 2;
offsetY = height / 2 - 55;
通过这个函数,我们可以将角度从(0,180)变化,不断取点并画点将这个心形线显示出来。好了,我们自定义一个View,然后把这个心形线画出来吧!
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
float angle = 10;
while (angle < 180) {
Point p = getHeartPoint(angle);
canvas.drawPoint(p.x, p.y, paint);
angle = angle + 0.02f;
}
}
运行结果如下:
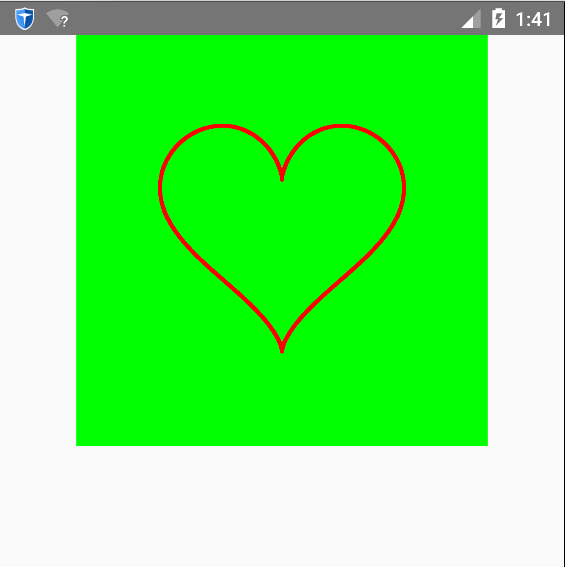
绘制花瓣原理
我们想要的并不是简单绘制一个桃心线,要的是将花朵在桃心线上摆放。首先,得要知道怎么绘制花朵,而花朵是由一个个花瓣组成。因此绘制花朵的核心是绘制花瓣。绘制花瓣的原理是:3次贝塞尔曲线。三次贝塞尔曲线是由两个端点和两个控制点决定。假设花芯是一个圆,有n个花瓣,那么两个端点与花芯的圆心连线之间的夹角即为360/n。因此可以根据花瓣数量和花芯半径确定每个花瓣的位置。将两个端点与花芯的圆心连线的延长线分别确定另外两个控制点。通过随机生成花芯半径、每个花瓣的起始角以及随机确定延长线得到两个控制点,可以绘制一个随机的花朵。参数的改变如下图所示:
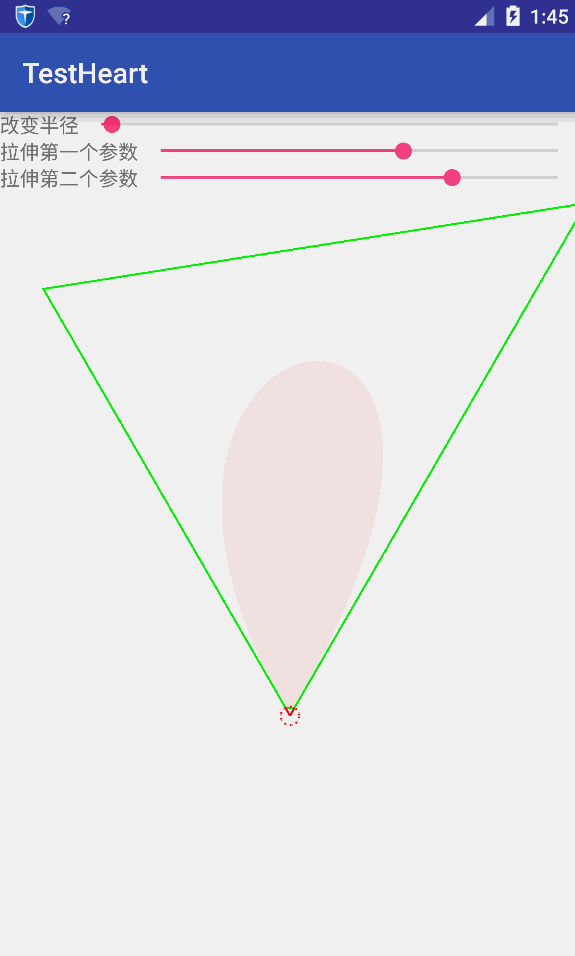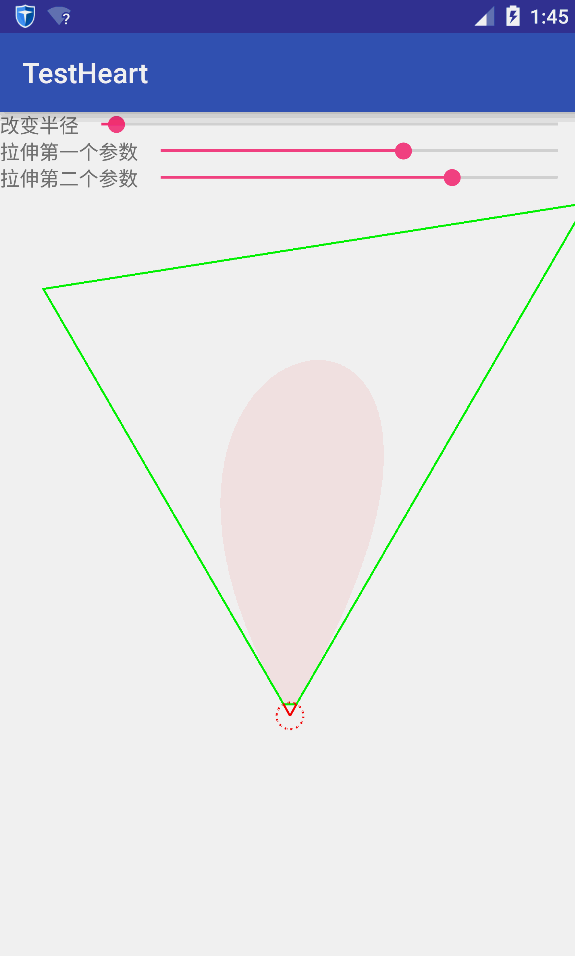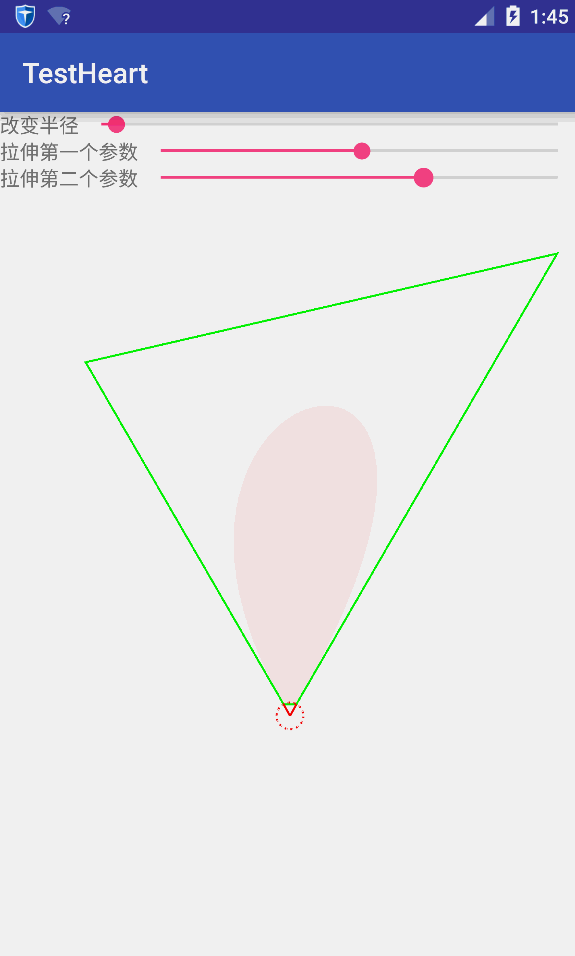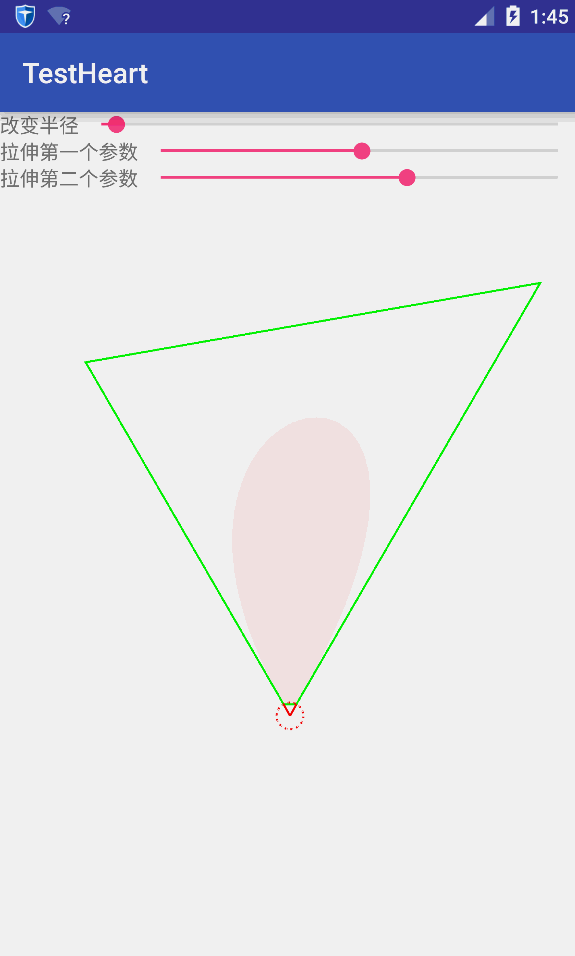
将花朵绘制到桃心线上
首先定义花瓣类Petal:
package com.example.administrator.testheart;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.Path;
public class Petal {
private float stretchA;
private float stretchB;
private float startAngle;
private float angle;
private int radius = 2;
private float growFactor;
private int color;
private boolean isFinished = false;
private Path path = new Path();
private Paint paint = new Paint();
public Petal(float stretchA, float stretchB, float startAngle, float angle, int color, float growFactor) {
this.stretchA = stretchA;
this.stretchB = stretchB;
this.startAngle = startAngle;
this.angle = angle;
this.color = color;
this.growFactor = growFactor;
paint.setColor(color);
}
public void render(Point p, int radius, Canvas canvas) {
if (this.radius <= radius) {
this.radius += growFactor;
} else {
isFinished = true;
}
this.draw(p, canvas);
}
private void draw(Point p, Canvas canvas) {
if (!isFinished) {
path = new Path();
Point t = new Point(0, this.radius).rotate(MyUtil.degrad(this.startAngle));
Point v1 = new Point(0, 3).rotate(MyUtil.degrad(this.startAngle));
Point v2 = t.clone().rotate(MyUtil.degrad(this.angle));
Point v3 = t.clone().mult(this.stretchA);
Point v4 = v2.clone().mult(this.stretchB);
v1.add(p);
v2.add(p);
v3.add(p);
v4.add(p);
path.moveTo(v1.x, v1.y);
path.cubicTo(v3.x, v3.y, v4.x, v4.y, v2.x, v2.y);
}
canvas.drawPath(path, paint);
}
}
花瓣类是最重要的类,因为真正绘制在屏幕上的是一个个小花瓣。每个花朵包含一系列花瓣,花朵类Bloom如下:
package com.example.administrator.testheart;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Bloom {
private int color;
private Point point;
private int radius;
private ArrayList<Petal> petals;
public Point getPoint() {
return point;
}
public Bloom(Point point, int radius, int color, int petalCount) {
this.point = point;
this.radius = radius;
this.color = color;
petals = new ArrayList<>(petalCount);
float angle = 360f / petalCount;
int startAngle = MyUtil.randomInt(0, 90);
for (int i = 0; i < petalCount; i++) {
float stretchA = MyUtil.random(Garden.Options.minPetalStretch, Garden.Options.maxPetalStretch);
float stretchB = MyUtil.random(Garden.Options.minPetalStretch, Garden.Options.maxPetalStretch);
int beginAngle = startAngle + (int) (i * angle);
float growFactor = MyUtil.random(Garden.Options.minGrowFactor, Garden.Options.maxGrowFactor);
this.petals.add(new Petal(stretchA, stretchB, beginAngle, angle, color, growFactor));
}
}
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
Petal p;
for (int i = 0; i < this.petals.size(); i++) {
p = petals.get(i);
p.render(point, this.radius, canvas);
}
}
public int getColor() {
return color;
}
}
接下来是花园类Garden,主要用于创建花朵以及一些相关配置:
package com.example.administrator.testheart;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Garden {
public Bloom createRandomBloom(int x, int y) {
int radius = MyUtil.randomInt(Options.minBloomRadius, Options.maxBloomRadius);
int color = MyUtil.randomrgba(Options.minRedColor, Options.maxRedColor, Options.minGreenColor, Options.maxGreenColor, Options.minBlueColor, Options.maxBlueColor, Options.opacity);
int petalCount = MyUtil.randomInt(Options.minPetalCount, Options.maxPetalCount);
return createBloom(x, y, radius, color, petalCount);
}
public Bloom createBloom(int x, int y, int radius, int color, int petalCount) {
return new Bloom(new Point(x, y), radius, color, petalCount);
}
static class Options {
public static int minPetalCount = 8;
public static int maxPetalCount = 15;
public static float minPetalStretch = 2f;
public static float maxPetalStretch = 3.5f;
public static float minGrowFactor = 1f;
public static float maxGrowFactor = 1.1f;
public static int minBloomRadius = 8;
public static int maxBloomRadius = 10;
public static int minRedColor = 128;
public static int maxRedColor = 255;
public static int minGreenColor = 0;
public static int maxGreenColor = 128;
public static int minBlueColor = 0;
public static int maxBlueColor = 128;
public static int opacity = 50;
}
}
考虑到刷新的比较频繁,选择使用SurfaceView作为显示视图。自定义一个HeartView继承SurfaceView。代码如下:
package com.example.administrator.testheart;
import android.content.Context;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.SurfaceHolder;
import android.view.SurfaceView;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class HeartView extends SurfaceView implements SurfaceHolder.Callback {
SurfaceHolder surfaceHolder;
int offsetX;
int offsetY;
private Garden garden;
private int width;
private int height;
private Paint backgroundPaint;
private boolean isDrawing = false;
private Bitmap bm;
private Canvas canvas;
private int heartRadio = 1;
public HeartView(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
public HeartView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
private void init() {
surfaceHolder = getHolder();
surfaceHolder.addCallback(this);
garden = new Garden();
backgroundPaint = new Paint();
backgroundPaint.setColor(Color.rgb(0xff, 0xff, 0xe0));
}
ArrayList<Bloom> blooms = new ArrayList<>();
public Point getHeartPoint(float angle) {
float t = (float) (angle / Math.PI);
float x = (float) (heartRadio * (16 * Math.pow(Math.sin(t), 3)));
float y = (float) (-heartRadio * (13 * Math.cos(t) - 5 * Math.cos(2 * t) - 2 * Math.cos(3 * t) - Math.cos(4 * t)));
return new Point(offsetX + (int) x, offsetY + (int) y);
}
private void drawHeart() {
canvas.drawRect(0, 0, width, height, backgroundPaint);
for (Bloom b : blooms) {
b.draw(canvas);
}
Canvas c = surfaceHolder.lockCanvas();
c.drawBitmap(bm, 0, 0, null);
surfaceHolder.unlockCanvasAndPost(c);
}
public void reDraw() {
blooms.clear();
drawOnNewThread();
}
@Override
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
super.draw(canvas);
}
private void drawOnNewThread() {
new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (isDrawing) return;
isDrawing = true;
float angle = 10;
while (true) {
Bloom bloom = getBloom(angle);
if (bloom != null) {
blooms.add(bloom);
}
if (angle >= 30) {
break;
} else {
angle += 0.2;
}
drawHeart();
try {
sleep(20);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
isDrawing = false;
}
}.start();
}
private Bloom getBloom(float angle) {
Point p = getHeartPoint(angle);
boolean draw = true;
/**循环比较新的坐标位置是否可以创建花朵,
* 为了防止花朵太密集
* */
for (int i = 0; i < blooms.size(); i++) {
Bloom b = blooms.get(i);
Point bp = b.getPoint();
float distance = (float) Math.sqrt(Math.pow(p.x - bp.x, 2) + Math.pow(p.y - bp.y, 2));
if (distance < Garden.Options.maxBloomRadius * 1.5) {
draw = false;
break;
}
}
if (draw) {
Bloom bloom = garden.createRandomBloom(p.x, p.y);
return bloom;
}
return null;
}
@Override
public void surfaceCreated(SurfaceHolder holder) {
}
@Override
public void surfaceChanged(SurfaceHolder holder, int format, int width, int height) {
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
heartRadio = width * 30 / 1080;
offsetX = width / 2;
offsetY = height / 2 - 55;
bm = Bitmap.createBitmap(width, height, Bitmap.Config.RGB_565);
canvas = new Canvas(bm);
drawOnNewThread();
}
@Override
public void surfaceDestroyed(SurfaceHolder holder) {
}
}
还有两个比较重要的工具类
Point.java保存点信息,或者说是向量信息。包含向量的基本运算。
package com.example.administrator.testheart;
public class Point {
public int x;
public int y;
public Point(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public Point rotate(float theta) {
int x = this.x;
int y = this.y;
this.x = (int) (Math.cos(theta) * x - Math.sin(theta) * y);
this.y = (int) (Math.sin(theta) * x + Math.cos(theta) * y);
return this;
}
public Point mult(float f) {
this.x *= f;
this.y *= f;
return this;
}
public Point clone() {
return new Point(this.x, this.y);
}
public float length() {
return (float) Math.sqrt(this.x * this.x + this.y * this.y);
}
public Point subtract(Point p) {
this.x -= p.x;
this.y -= p.y;
return this;
}
public Point add(Point p) {
this.x += p.x;
this.y += p.y;
return this;
}
public Point set(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
return this;
}
}
工具类MyUtil.java主要是产生随机数、颜色等
package com.example.administrator.testheart;
import android.graphics.Color;
public class MyUtil {
public static float circle = (float) (2 * Math.PI);
public static int rgba(int r, int g, int b, int a) {
return Color.argb(a, r, g, b);
}
public static int randomInt(int min, int max) {
return (int) Math.floor(Math.random() * (max - min + 1)) + min;
}
public static float random(float min, float max) {
return (float) (Math.random() * (max - min) + min);
}
public static int randomrgba(int rmin, int rmax, int gmin, int gmax, int bmin, int bmax, int a) {
int r = Math.round(random(rmin, rmax));
int g = Math.round(random(gmin, gmax));
int b = Math.round(random(bmin, bmax));
int limit = 5;
if (Math.abs(r - g) <= limit && Math.abs(g - b) <= limit && Math.abs(b - r) <= limit) {
return rgba(rmin, rmax, gmin, gmax);
} else {
return rgba(r, g, b, a);
}
}
public static float degrad(float angle) {
return circle / 360 * angle;
}
}
Activity自动跳转及日期计时及打字机效果实现类MainActivity
package com.example.administrator.testheart;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Handler;
import android.os.Message;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.RelativeLayout;
import android.widget.TextView;
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
HeartView heartView;
private TextView tv_text;
private TextView tv_text_1;
private TextView tv_text_2;
private int clo = 0;
private RelativeLayout countDown;
private TextView daysTv, hoursTv, minutesTv, secondsTv;
private long mDay = 652;
private long mHour = 15;
private long mMin = 37;
private long mSecond = 00;
private boolean isRun = true;
private Handler timeHandler = new Handler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
super.handleMessage(msg);
if (msg.what==1) {
computeTime();
daysTv.setText(mDay+"");
hoursTv.setText(mHour+"");
minutesTv.setText(mMin+"");
secondsTv.setText(mSecond+"");
if (mDay==0&&mHour==0&&mMin==0&&mSecond==0) {
countDown.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
}
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
heartView = (HeartView) findViewById(R.id.surfaceView);
tv_text = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.myword);
tv_text_1 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.myword_1);
tv_text_2 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.myword_2);
shark();
countDown = (RelativeLayout) findViewById(R.id.countdown_layout);
daysTv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.days_tv);
hoursTv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.hours_tv);
minutesTv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.minutes_tv);
secondsTv = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.seconds_tv);
startRun();
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
heartView.reDraw();
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
public void reDraw(View v) {
heartView.reDraw();
}
private void shark() {
Timer timer = new Timer();
TimerTask taskcc = new TimerTask() {
public void run() {
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
if (clo == 0) {
clo = 1;
tv_text.setTextColor(Color.TRANSPARENT);
tv_text_1.setTextColor(Color.TRANSPARENT);
tv_text_2.setTextColor(Color.TRANSPARENT);
} else {
if (clo == 1) {
clo = 2;
tv_text.setTextColor(Color.YELLOW);
tv_text_1.setTextColor(Color.YELLOW);
tv_text_2.setTextColor(Color.YELLOW);
} else if (clo == 2) {
clo = 3;
tv_text.setTextColor(Color.RED);
tv_text_1.setTextColor(Color.RED);
tv_text_2.setTextColor(Color.RED);
} else if (clo == 3){
clo = 4;
tv_text.setTextColor(Color.BLACK);
tv_text_1.setTextColor(Color.BLACK);
tv_text_2.setTextColor(Color.BLACK);
} else if (clo == 4){
clo = 5;
tv_text.setTextColor(Color.WHITE);
tv_text_1.setTextColor(Color.WHITE);
tv_text_2.setTextColor(Color.WHITE);
}else if (clo == 5){
clo = 6;
tv_text.setTextColor(Color.GREEN);
tv_text_1.setTextColor(Color.GREEN);
tv_text_2.setTextColor(Color.GREEN);
} else if (clo == 6){
clo = 7;
tv_text.setTextColor(Color.MAGENTA);
tv_text_1.setTextColor(Color.MAGENTA);
tv_text_2.setTextColor(Color.MAGENTA);
}else if (clo == 7){
clo = 8;
tv_text.setTextColor(Color.CYAN);
tv_text_1.setTextColor(Color.CYAN);
tv_text_2.setTextColor(Color.CYAN);
}else if (clo == 8){
clo = 9;
tv_text.setTextColor(Color.DKGRAY);
tv_text_1.setTextColor(Color.DKGRAY);
tv_text_2.setTextColor(Color.DKGRAY);
}
else if (clo == 9){
clo = 10;
tv_text.setTextColor(Color.GRAY);
tv_text_1.setTextColor(Color.GRAY);
tv_text_2.setTextColor(Color.GRAY);
}else if (clo == 10){
clo = 11;
tv_text.setTextColor(Color.LTGRAY);
tv_text_1.setTextColor(Color.LTGRAY);
tv_text_2.setTextColor(Color.LTGRAY);
}else {
clo = 0;
tv_text.setTextColor(Color.BLUE);
tv_text_1.setTextColor(Color.BLUE);
tv_text_2.setTextColor(Color.BLUE);
}
}
}
});
}
};
timer.schedule(taskcc, 1, 1500);
}
/**
* 开启计时
*/
private void startRun() {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (isRun) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
Message message = Message.obtain();
message.what = 1;
timeHandler.sendMessage(message);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}).start();
}
/**
* 倒计时计算
*/
private void computeTime() {
mSecond++;
if (mSecond > 60) {
mSecond = 0;
mMin++;
if (mMin > 60) {
mMin = 0;
mHour++;
if (mHour > 24) {
mHour = 0;
mDay++;
}
}
}
}
}
到了这一步就可以实现上面的效果了。
源码地址在这。
本文内容由网友自发贡献,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有涉嫌抄袭侵权的内容,请联系:hwhale#tublm.com(使用前将#替换为@)