目录
1. 检查网卡是否支持相应的时间戳
2. linuxptp的目录架构
3. ptp4l的大致流程分析
4. gptp协议对应的sync, follow-up, delay-request, delay-response消息在代码的位置
5.slave收到消息如何处理并调整时间:
6.一个完整的时间同步的例子
gptp的报文格式: 报文格式地图——重庆网管博客
1. 检查网卡是否支持相应的时间戳
否则可能出现以下这种:eth0网卡不支持软时间戳(-S)对应的SOF_TIMESTAMPING_TX_SOFTWARE,SOF_TIMESTAMPING_RX_SOFTWARE,SOF_TIMESTAMPING_SOFTWARE,
/usrdata # ./ptp4l -i eth0 -m -S
ptp4l[5430.909]: interface 'eth0' does not support requested timestamping mode
/* Check the time stamping mode on each interface. */
c->timestamping = timestamping;
required_modes = clock_required_modes(c);
STAILQ_FOREACH(iface, &config->interfaces, list) {
memset(ts_label, 0, sizeof(ts_label));
if (!rtnl_get_ts_device(interface_name(iface), ts_label))
interface_set_label(iface, ts_label);
interface_get_tsinfo(iface);
if (interface_tsinfo_valid(iface) &&
!interface_tsmodes_supported(iface, required_modes)) {
pr_err("interface '%s' does not support requested timestamping mode",
interface_name(iface));
return NULL;
}
config_get_int(config, NULL, "time_stamping"); // 配置的时间戳
----->clock_required_modes() //逻辑上需要支持的时间戳:比如SOF_TIMESTAMPING_SOFTWARE,
SOF_TIMESTAMPING_TX_SOFTWARE,//发包的时间戳
----->interface_get_tsinfo ----->sk_get_ts_info
- 创建socket---------------------fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_DGRAM, 0)
- 通过socket去把信息放到ifr--------ioctl(fd, SIOCETHTOOL, &ifr); //获取网卡支持的时间类型---和ethtool -T eth0 对应支持的时间戳应该一致
------>interface_tsinfo_valid() 和 interface_tsmodes_supported() 来确认这个网卡是否支持此时间模式
2. linuxptp的目录架构
研究目录下的makefile发现会编译出来几个APP:主要研究ptp4l, phc2sys这两个app
- ptp4l:主要是用来计算得出两个设备之间的时间误差(时间戳相差的大小),频率误差(时间走的快慢的差异)。
- phc2sys:主要是把两个时钟进行同步,比如把systime同步到phc时钟(ptp hardware clock)
3. ptp4l的大致流程分析
LinuxPTP的ptp4l.c文件有个int main()函数,makefile通过这个main函数会编译出来ptp4l的可执行程序。
- 简单的说就是通过getopt_long()函数拿到配置的参数,然后通过clock_create创建一个时钟,在通过poll处理这个时钟相关的事件。
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
......拿到配置对应的参数
while (EOF != (c = getopt_long(argc, argv, "MAEP246HSLf:i:p:sl:mqvh",
opts, &index))) { ......}
......创建时钟
clock = clock_create(type, cfg, req_phc);
......
while (is_running()) {
实时的处理poll得到的clock对应的事件
if (clock_poll(clock))
break;
}
......
}
struct clock *clock_create(enum clock_type type, struct config *config,
const char *phc_device)
{
....一些参数配置
....检查 -i [dev] -i参数指定的设备是否支持需要的时间戳类型
/* Check the time stamping mode on each interface. */
c->timestamping = timestamping;
required_modes = clock_required_modes(c);
STAILQ_FOREACH(iface, &config->interfaces, list) {
memset(ts_label, 0, sizeof(ts_label));
if (!rtnl_get_ts_device(interface_name(iface), ts_label))
interface_set_label(iface, ts_label);
interface_get_tsinfo(iface);
if (interface_tsinfo_valid(iface) &&
!interface_tsmodes_supported(iface, required_modes)) {
pr_err("interface '%s' does not support requested timestamping mode",
interface_name(iface));
return NULL;
}
}
...... 打开ptp hardware clock
c->clkid = phc_open(phc);
...... 通过拿到的clkid初始化clock
clockadj_init(c->clkid);
...... 创建时间控制器,通过makefile的
SERVOS = linreg.o ntpshm.o nullf.o pi.o servo.o
可知,servos是一个接口类,通过servo_create()创建不同的控制器,
比如比例积分(pi)控制器,线性(linreg)控制器
c->servo = servo_create(c->config, servo, -fadj, max_adj, sw_ts);
...... port_open通过指定不同的phc_device来创建相应的回调函数:
p->dispatch 和 p->event
c->uds_ro_port = port_open(phc_device, phc_index, timestamping, 0,
c->uds_ro_if, c);
}
clock_create函数最重要的两点:
1. 检查指定的网卡设备是否支持需要的时间戳模式
2. 通过port_open指定p->dispatch(事件处理分发机制)和p->event(事件有限元状态机的变化)
4. gptp协议对应的sync, follow-up, delay-request, delay-response消息在代码的位置
参考:以 ptp4l、E2E 为例的 Linuxptp 代码分析_悠扬侠的博客-CSDN博客_linuxptp源码分析
之前说了clock_create创建了时钟:在port_open函数指定了事件处理的函数,因为我用到的是bc_event和bc_dispatch,所以以这两个为例子.
参考的文章已经写的很清楚了:自己也大概的写下:
- port_dispatch接口函数里面调用了clock_create函数的p->dispatch方法,而 port_dispatch(p, event, 0);在clock_poll()函数中被一直调用,那么正常的运行状态,所有的事件都是从clock_poll()函数调用port_dispatch--->bc_dispatch
- 个人感觉:bc_dispatch做了一些预处理的操作,可以暂时忽略.
- 然后就在clock_poll函数调用port_event()接口函数,同样的会一路调用到bc_event()函数
- master发送sync消息:port_tx_sync()函数:这个函数发送了sync和follow-up报文
--->port_prepare_and_send函数执行发送消息
--->transport_send或者transport_sendto调用t->send方法发送数据
{
以UDP为例
t->send(t, fda, event, 0, msg, len, NULL, &msg->hwts); 对应的是 udp->t.send = udp_send;
--->udpsend调用sendto发送数据
--->立刻调用sk_receive接收反馈的消息,这里是最开始的ioctrl函数指定了发送一条报文,需要从网口设备返回一个时间戳给应用层,如果网口对应的driver有问题,可能会收不到时间戳
{
setsockopt(fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_TIMESTAMPING,×tamping, sizeof(timestamping));
setsockopt(fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_SELECT_ERR_QUEUE, &flags, sizeof(flags));
}
}
- master发送follow-up报文:port_tx_sync
- master发送delay-request报文:port_pdelay_request
- slave收到sync报文处理:process_sync
- slave收到follow-up报文处理:process_follow_up
5.slave收到消息如何处理并调整时间:
按照gptp协议的规定,master和slave之间交互了sync.follow-up,delay_requst, delay_response消息,会计算得出时间戳误差,频率误差。
- 可以查代码看出:在process_follow_up和process_sync函数会调用port_syfufsm(p, event, m);函数(这函数用来切换收到master发来的消息之后的状态机),其中调用了port_synchronize()函数来调整状态并通过port_dispatch分发事件
- 关键就是通过slave端的几个状态的跳变完成对时间的同步:
其中master offst对应的是clock_synchronize中的状态跳变,可以很容易看出:比较关键的就是S0到S1,调用了clockadj_step函数,完成对时间戳的改变
- 还有需要注意:clockadj_step()函数调整的是clkid对应的时间(如果调整的时间是phc对应的clkid的时间,那么同步到系统时间需要用phc2sys这个app)
switch (state) {
case SERVO_UNLOCKED: // S0
break;
case SERVO_JUMP: //s1
clockadj_set_freq(c->clkid, -adj);
//调整时间戳的差值
clockadj_step(c->clkid, -tmv_to_nanoseconds(c->master_offset));
c->ingress_ts = tmv_zero();
if (c->sanity_check) {
clockcheck_set_freq(c->sanity_check, -adj);
clockcheck_step(c->sanity_check,
-tmv_to_nanoseconds(c->master_offset));
}
tsproc_reset(c->tsproc, 0);
clock_step_window(c);
break;
case SERVO_LOCKED:
//调整频率
clock_synchronize_locked(c, adj);
break;
case SERVO_LOCKED_STABLE:
if (c->write_phase_mode) {
clockadj_set_phase(c->clkid, -offset);
adj = 0;
} else {
clock_synchronize_locked(c, adj);
}
break;
}
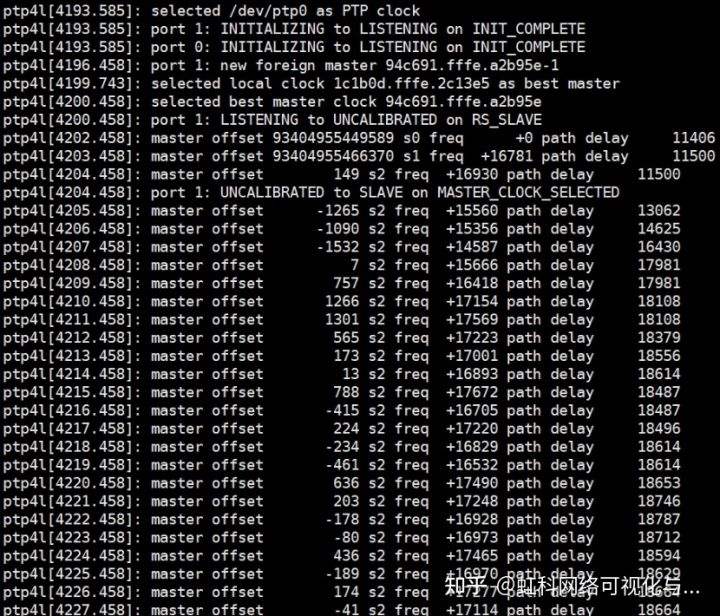
- s0,s1,s2 : 表示时钟伺服器的不同状态,s0表示未锁定,s1表示正在同步,s2表示锁定,锁定状态表示不会再发生阶跃行同步,只是缓慢调整
6.一个完整的时间同步的例子
/*
* PTP 1588 clock support - User space test program
*
* Copyright (C) 2010 OMICRON electronics GmbH
*
* This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify
* it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
* the Free Software Foundation; either version 2 of the License, or
* (at your option) any later version.
*
* This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
* GNU General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
* along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software
* Foundation, Inc., 675 Mass Ave, Cambridge, MA 02139, USA.
*/
#define _GNU_SOURCE
#define __SANE_USERSPACE_TYPES__ /* For PPC64, to get LL64 types */
#include <errno.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <inttypes.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/timex.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <linux/ptp_clock.h>
#define DEVICE "/dev/ptp0"
#ifndef ADJ_SETOFFSET
#define ADJ_SETOFFSET 0x0100
#endif
#ifndef CLOCK_INVALID
#define CLOCK_INVALID -1
#endif
/* clock_adjtime is not available in GLIBC < 2.14 */
#if !__GLIBC_PREREQ(2, 14)
#include <sys/syscall.h>
static int clock_adjtime(clockid_t id, struct timex *tx)
{
return syscall(__NR_clock_adjtime, id, tx);
}
#endif
static clockid_t get_clockid(int fd)
{
#define CLOCKFD 3
#define FD_TO_CLOCKID(fd) ((~(clockid_t) (fd) << 3) | CLOCKFD)
return FD_TO_CLOCKID(fd);
}
static void handle_alarm(int s)
{
printf("received signal %d\n", s);
}
static int install_handler(int signum, void (*handler)(int))
{
struct sigaction action;
sigset_t mask;
/* Unblock the signal. */
sigemptyset(&mask);
sigaddset(&mask, signum);
sigprocmask(SIG_UNBLOCK, &mask, NULL);
/* Install the signal handler. */
action.sa_handler = handler;
action.sa_flags = 0;
sigemptyset(&action.sa_mask);
sigaction(signum, &action, NULL);
return 0;
}
static long ppb_to_scaled_ppm(int ppb)
{
/*
* The 'freq' field in the 'struct timex' is in parts per
* million, but with a 16 bit binary fractional field.
* Instead of calculating either one of
*
* scaled_ppm = (ppb / 1000) << 16 [1]
* scaled_ppm = (ppb << 16) / 1000 [2]
*
* we simply use double precision math, in order to avoid the
* truncation in [1] and the possible overflow in [2].
*/
return (long) (ppb * 65.536);
}
static int64_t pctns(struct ptp_clock_time *t)
{
return t->sec * 1000000000LL + t->nsec;
}
static void usage(char *progname)
{
fprintf(stderr,
"usage: %s [options]\n"
" -a val request a one-shot alarm after 'val' seconds\n"
" -A val request a periodic alarm every 'val' seconds\n"
" -c query the ptp clock's capabilities\n"
" -d name device to open\n"
" -e val read 'val' external time stamp events\n"
" -f val adjust the ptp clock frequency by 'val' ppb\n"
" -g get the ptp clock time\n"
" -h prints this message\n"
" -i val index for event/trigger\n"
" -k val measure the time offset between system and phc clock\n"
" for 'val' times (Maximum 25)\n"
" -l list the current pin configuration\n"
" -L pin,val configure pin index 'pin' with function 'val'\n"
" the channel index is taken from the '-i' option\n"
" 'val' specifies the auxiliary function:\n"
" 0 - none\n"
" 1 - external time stamp\n"
" 2 - periodic output\n"
" -p val enable output with a period of 'val' nanoseconds\n"
" -P val enable or disable (val=1|0) the system clock PPS\n"
" -s set the ptp clock time from the system time\n"
" -S set the system time from the ptp clock time\n"
" -t val shift the ptp clock time by 'val' seconds\n"
" -T val set the ptp clock time to 'val' seconds\n",
progname);
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct ptp_clock_caps caps;
struct ptp_extts_event event;
struct ptp_extts_request extts_request;
struct ptp_perout_request perout_request;
struct ptp_pin_desc desc;
struct timespec ts;
struct timex tx;
static timer_t timerid;
struct itimerspec timeout;
struct sigevent sigevent;
struct ptp_clock_time *pct;
struct ptp_sys_offset *sysoff;
char *progname;
unsigned int i;
int c, cnt, fd;
char *device = DEVICE;
clockid_t clkid;
int adjfreq = 0x7fffffff;
int adjtime = 0;
int capabilities = 0;
int extts = 0;
int gettime = 0;
int index = 0;
int list_pins = 0;
int oneshot = 0;
int pct_offset = 0;
int n_samples = 0;
int periodic = 0;
int perout = -1;
int pin_index = -1, pin_func;
int pps = -1;
int seconds = 0;
int settime = 0;
int64_t t1, t2, tp;
int64_t interval, offset;
progname = strrchr(argv[0], '/');
progname = progname ? 1+progname : argv[0];
while (EOF != (c = getopt(argc, argv, "a:A:cd:e:f:ghi:k:lL:p:P:sSt:T:v"))) {
switch (c) {
case 'a':
oneshot = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'A':
periodic = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'c':
capabilities = 1;
break;
case 'd':
device = optarg;
break;
case 'e':
extts = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'f':
adjfreq = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'g':
gettime = 1;
break;
case 'i':
index = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'k':
pct_offset = 1;
n_samples = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'l':
list_pins = 1;
break;
case 'L':
cnt = sscanf(optarg, "%d,%d", &pin_index, &pin_func);
if (cnt != 2) {
usage(progname);
return -1;
}
break;
case 'p':
perout = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'P':
pps = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 's':
settime = 1;
break;
case 'S':
settime = 2;
break;
case 't':
adjtime = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'T':
settime = 3;
seconds = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'h':
usage(progname);
return 0;
case '?':
default:
usage(progname);
return -1;
}
}
fd = open(device, O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "opening %s: %s\n", device, strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
clkid = get_clockid(fd);
if (CLOCK_INVALID == clkid) {
fprintf(stderr, "failed to read clock id\n");
return -1;
}
if (capabilities) {
if (ioctl(fd, PTP_CLOCK_GETCAPS, &caps)) {
perror("PTP_CLOCK_GETCAPS");
} else {
printf("capabilities:\n"
" %d maximum frequency adjustment (ppb)\n"
" %d programmable alarms\n"
" %d external time stamp channels\n"
" %d programmable periodic signals\n"
" %d pulse per second\n"
" %d programmable pins\n"
" %d cross timestamping\n",
caps.max_adj,
caps.n_alarm,
caps.n_ext_ts,
caps.n_per_out,
caps.pps,
caps.n_pins,
caps.cross_timestamping);
}
}
if (0x7fffffff != adjfreq) {
memset(&tx, 0, sizeof(tx));
tx.modes = ADJ_FREQUENCY;
tx.freq = ppb_to_scaled_ppm(adjfreq);
if (clock_adjtime(clkid, &tx)) {
perror("clock_adjtime");
} else {
puts("frequency adjustment okay");
}
}
if (adjtime) {
memset(&tx, 0, sizeof(tx));
tx.modes = ADJ_SETOFFSET;
tx.time.tv_sec = adjtime;
tx.time.tv_usec = 0;
if (clock_adjtime(clkid, &tx) < 0) {
perror("clock_adjtime");
} else {
puts("time shift okay");
}
}
if (gettime) {
if (clock_gettime(clkid, &ts)) {
perror("clock_gettime");
} else {
printf("clock time: %ld.%09ld or %s",
ts.tv_sec, ts.tv_nsec, ctime(&ts.tv_sec));
}
}
if (settime == 1) {
clock_gettime(CLOCK_REALTIME, &ts);
if (clock_settime(clkid, &ts)) {
perror("clock_settime");
} else {
puts("set time okay");
}
}
if (settime == 2) {
clock_gettime(clkid, &ts);
if (clock_settime(CLOCK_REALTIME, &ts)) {
perror("clock_settime");
} else {
puts("set time okay");
}
}
if (settime == 3) {
ts.tv_sec = seconds;
ts.tv_nsec = 0;
if (clock_settime(clkid, &ts)) {
perror("clock_settime");
} else {
puts("set time okay");
}
}
if (extts) {
memset(&extts_request, 0, sizeof(extts_request));
extts_request.index = index;
extts_request.flags = PTP_ENABLE_FEATURE;
if (ioctl(fd, PTP_EXTTS_REQUEST, &extts_request)) {
perror("PTP_EXTTS_REQUEST");
extts = 0;
} else {
puts("external time stamp request okay");
}
for (; extts; extts--) {
cnt = read(fd, &event, sizeof(event));
if (cnt != sizeof(event)) {
perror("read");
break;
}
printf("event index %u at %lld.%09u\n", event.index,
event.t.sec, event.t.nsec);
fflush(stdout);
}
/* Disable the feature again. */
extts_request.flags = 0;
if (ioctl(fd, PTP_EXTTS_REQUEST, &extts_request)) {
perror("PTP_EXTTS_REQUEST");
}
}
if (list_pins) {
int n_pins = 0;
if (ioctl(fd, PTP_CLOCK_GETCAPS, &caps)) {
perror("PTP_CLOCK_GETCAPS");
} else {
n_pins = caps.n_pins;
}
for (i = 0; i < n_pins; i++) {
desc.index = i;
if (ioctl(fd, PTP_PIN_GETFUNC, &desc)) {
perror("PTP_PIN_GETFUNC");
break;
}
printf("name %s index %u func %u chan %u\n",
desc.name, desc.index, desc.func, desc.chan);
}
}
if (oneshot) {
install_handler(SIGALRM, handle_alarm);
/* Create a timer. */
sigevent.sigev_notify = SIGEV_SIGNAL;
sigevent.sigev_signo = SIGALRM;
if (timer_create(clkid, &sigevent, &timerid)) {
perror("timer_create");
return -1;
}
/* Start the timer. */
memset(&timeout, 0, sizeof(timeout));
timeout.it_value.tv_sec = oneshot;
if (timer_settime(timerid, 0, &timeout, NULL)) {
perror("timer_settime");
return -1;
}
pause();
timer_delete(timerid);
}
if (periodic) {
install_handler(SIGALRM, handle_alarm);
/* Create a timer. */
sigevent.sigev_notify = SIGEV_SIGNAL;
sigevent.sigev_signo = SIGALRM;
if (timer_create(clkid, &sigevent, &timerid)) {
perror("timer_create");
return -1;
}
/* Start the timer. */
memset(&timeout, 0, sizeof(timeout));
timeout.it_interval.tv_sec = periodic;
timeout.it_value.tv_sec = periodic;
if (timer_settime(timerid, 0, &timeout, NULL)) {
perror("timer_settime");
return -1;
}
while (1) {
pause();
}
timer_delete(timerid);
}
if (perout >= 0) {
if (clock_gettime(clkid, &ts)) {
perror("clock_gettime");
return -1;
}
memset(&perout_request, 0, sizeof(perout_request));
perout_request.index = index;
perout_request.start.sec = ts.tv_sec + 2;
perout_request.start.nsec = 0;
perout_request.period.sec = 0;
perout_request.period.nsec = perout;
if (ioctl(fd, PTP_PEROUT_REQUEST, &perout_request)) {
perror("PTP_PEROUT_REQUEST");
} else {
puts("periodic output request okay");
}
}
if (pin_index >= 0) {
memset(&desc, 0, sizeof(desc));
desc.index = pin_index;
desc.func = pin_func;
desc.chan = index;
if (ioctl(fd, PTP_PIN_SETFUNC, &desc)) {
perror("PTP_PIN_SETFUNC");
} else {
puts("set pin function okay");
}
}
if (pps != -1) {
int enable = pps ? 1 : 0;
if (ioctl(fd, PTP_ENABLE_PPS, enable)) {
perror("PTP_ENABLE_PPS");
} else {
puts("pps for system time request okay");
}
}
if (pct_offset) {
if (n_samples <= 0 || n_samples > 25) {
puts("n_samples should be between 1 and 25");
usage(progname);
return -1;
}
sysoff = calloc(1, sizeof(*sysoff));
if (!sysoff) {
perror("calloc");
return -1;
}
sysoff->n_samples = n_samples;
if (ioctl(fd, PTP_SYS_OFFSET, sysoff))
perror("PTP_SYS_OFFSET");
else
puts("system and phc clock time offset request okay");
pct = &sysoff->ts[0];
for (i = 0; i < sysoff->n_samples; i++) {
t1 = pctns(pct+2*i);
tp = pctns(pct+2*i+1);
t2 = pctns(pct+2*i+2);
interval = t2 - t1;
offset = (t2 + t1) / 2 - tp;
printf("system time: %lld.%u\n",
(pct+2*i)->sec, (pct+2*i)->nsec);
printf("phc time: %lld.%u\n",
(pct+2*i+1)->sec, (pct+2*i+1)->nsec);
printf("system time: %lld.%u\n",
(pct+2*i+2)->sec, (pct+2*i+2)->nsec);
printf("system/phc clock time offset is %" PRId64 " ns\n"
"system clock time delay is %" PRId64 " ns\n",
offset, interval);
}
free(sysoff);
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
master:
- ./ptp4l -i eth0 -E -m -l 7 -S -4 &
把带时间戳的报文通过ptp报文发送给slave端,用的是systime
slave: [选择/dev/ptp1是发现在clokadj_step的时候对应的clkid对应的设备是/dev/ptp1,需要根据调试过程动态调整]
- ./testptp -d /dev/ptp1 -s //把systime设到/dev/ptp1时间
- ./ptp4l -i pfe2 -m -4 -E -S -s
拿到master过来的systime,计算得到的offset是master和slave之间的systime的误差,而在调用clockadj_step的时候用的是两边系统时间的offset。所以需要保证clockadj_step对应的clkid的时间和系统时间是一样的!!
- ./testptp -d /dev/ptp1 -S //把/dev/ptp1时间设到systime
或者
- ./phc2sys -l 7 -m -c CLOCK_REALTIME -s /dev/ptp1 -w &
把/dev/ptp1对应的phc时间同步到systime,
-w是等待ptp4l: 通过pmc_create()来创建进程间通信,-w当收到了来自ptp4l的消息,就会跳出 Waiting for ptp4l...的循环,然后执行do_loop来执行 update_clock()来跟新时间(把/dev/ptp1上的时间更新到CLOCK_REALTIME上!!)
- ./testptp -d /dev/ptp1 -k 1 //打印系统,/dev/ptp1时间
本文内容由网友自发贡献,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有涉嫌抄袭侵权的内容,请联系:hwhale#tublm.com(使用前将#替换为@)