首先介绍nano板子上的i2c相关的硬件信息:

- 安装所需要的i2c库
sudo apt-get install l -y i2c-tools
- 完成nano中io与i2c设备的硬件接线。
本次案例使用的是PCA9685和MPU6050,这两个设备的SCL和SDA直连,其次完成与nano主板上IO连接,看图:

VCC ---接Nano引脚第17脚
GND ---接Nano 引脚第25脚
SCL ---接Nano 引脚第5脚(GEN2_I2C_SCL)
SDA ---接Nano 引脚第3脚(GEN2_I2C_SDA)
3.检测硬件地址:
sudo i2cdetect -y -r -a 1
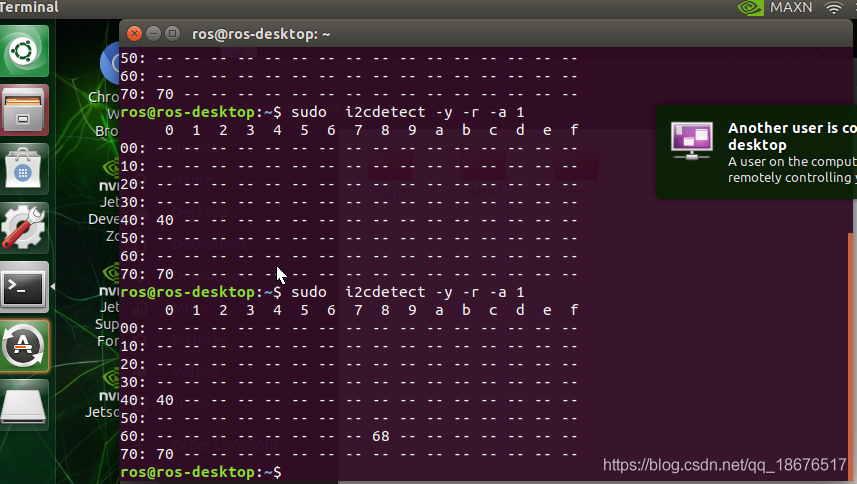 可以看到连接在i2c总线上的设备地址号
可以看到连接在i2c总线上的设备地址号
- 程序实现对i2c设备的访问:
"""This program handles the communication over I2C
between a Jetson Nano and a MPU-6050 Gyroscope / Accelerometer combo.
Made by: Dennis/TW
Released under the MIT License
Copyright 2019
"""
import smbus
import time
class mpu6050:
# Global Variables
GRAVITIY_MS2 = 9.80665
address = None
bus = smbus.SMBus(1)
# Scale Modifiers
ACCEL_SCALE_MODIFIER_2G = 16384.0
ACCEL_SCALE_MODIFIER_4G = 8192.0
ACCEL_SCALE_MODIFIER_8G = 4096.0
ACCEL_SCALE_MODIFIER_16G = 2048.0
GYRO_SCALE_MODIFIER_250DEG = 131.0
GYRO_SCALE_MODIFIER_500DEG = 65.5
GYRO_SCALE_MODIFIER_1000DEG = 32.8
GYRO_SCALE_MODIFIER_2000DEG = 16.4
# Pre-defined ranges
ACCEL_RANGE_2G = 0x00
ACCEL_RANGE_4G = 0x08
ACCEL_RANGE_8G = 0x10
ACCEL_RANGE_16G = 0x18
GYRO_RANGE_250DEG = 0x00
GYRO_RANGE_500DEG = 0x08
GYRO_RANGE_1000DEG = 0x10
GYRO_RANGE_2000DEG = 0x18
# MPU-6050 Registers
PWR_MGMT_1 = 0x6B
PWR_MGMT_2 = 0x6C
SELF_TEST_X = 0x0D
SELF_TEST_Y = 0x0E
SELF_TEST_Z = 0x0F
SELF_TEST_A = 0x10
ACCEL_XOUT0 = 0x3B
ACCEL_XOUT1 = 0x3C
ACCEL_YOUT0 = 0x3D
ACCEL_YOUT1 = 0x3E
ACCEL_ZOUT0 = 0x3F
ACCEL_ZOUT1 = 0x40
TEMP_OUT0 = 0x41
TEMP_OUT1 = 0x42
GYRO_XOUT0 = 0x43
GYRO_XOUT1 = 0x44
GYRO_YOUT0 = 0x45
GYRO_YOUT1 = 0x46
GYRO_ZOUT0 = 0x47
GYRO_ZOUT1 = 0x48
ACCEL_CONFIG = 0x1C
GYRO_CONFIG = 0x1B
def __init__(self, address):
self.address = address
# Wake up the MPU-6050 since it starts in sleep mode
self.bus.write_byte_data(self.address, self.PWR_MGMT_1, 0x00)
# I2C communication methods
def read_i2c_word(self, register):
"""Read two i2c registers and combine them.
register -- the first register to read from.
Returns the combined read results.
"""
# Read the data from the registers
high = self.bus.read_byte_data(self.address, register)
low = self.bus.read_byte_data(self.address, register + 1)
value = (high << 8) + low
if (value >= 0x8000):
return -((65535 - value) + 1)
else:
return value
# MPU-6050 Methods
def get_temp(self):
"""Reads the temperature from the onboard temperature sensor of the MPU-6050.
Returns the temperature in degrees Celcius.
"""
# Get the raw data
raw_temp = self.read_i2c_word(self.TEMP_OUT0)
# Get the actual temperature using the formule given in the
# MPU-6050 Register Map and Descriptions revision 4.2, page 30
actual_temp = (raw_temp / 340) + 36.53
# Return the temperature
return actual_temp
def set_accel_range(self, accel_range):
"""Sets the range of the accelerometer to range.
accel_range -- the range to set the accelerometer to. Using a
pre-defined range is advised.
"""
# First change it to 0x00 to make sure we write the correct value later
self.bus.write_byte_data(self.address, self.ACCEL_CONFIG, 0x00)
# Write the new range to the ACCEL_CONFIG register
self.bus.write_byte_data(self.address, self.ACCEL_CONFIG, accel_range)
def read_accel_range(self, raw=False):
"""Reads the range the accelerometer is set to.
If raw is True, it will return the raw value from the ACCEL_CONFIG
register
If raw is False, it will return an integer: -1, 2, 4, 8 or 16. When it
returns -1 something went wrong.
"""
# Get the raw value
raw_data = self.bus.read_byte_data(self.address, self.ACCEL_CONFIG)
if raw is True:
return raw_data
elif raw is False:
if raw_data == self.ACCEL_RANGE_2G:
return 2
elif raw_data == self.ACCEL_RANGE_4G:
return 4
elif raw_data == self.ACCEL_RANGE_8G:
return 8
elif raw_data == self.ACCEL_RANGE_16G:
return 16
else:
return -1
def get_accel_data(self, g=False):
"""Gets and returns the X, Y and Z values from the accelerometer.
If g is True, it will return the data in g
If g is False, it will return the data in m/s^2
Returns a dictionary with the measurement results.
"""
# Read the data from the MPU-6050
x = self.read_i2c_word(self.ACCEL_XOUT0)
y = self.read_i2c_word(self.ACCEL_YOUT0)
z = self.read_i2c_word(self.ACCEL_ZOUT0)
accel_scale_modifier = None
accel_range = self.read_accel_range(True)
if accel_range == self.ACCEL_RANGE_2G:
accel_scale_modifier = self.ACCEL_SCALE_MODIFIER_2G
elif accel_range == self.ACCEL_RANGE_4G:
accel_scale_modifier = self.ACCEL_SCALE_MODIFIER_4G
elif accel_range == self.ACCEL_RANGE_8G:
accel_scale_modifier = self.ACCEL_SCALE_MODIFIER_8G
elif accel_range == self.ACCEL_RANGE_16G:
accel_scale_modifier = self.ACCEL_SCALE_MODIFIER_16G
else:
print("Unkown range - accel_scale_modifier set to self.ACCEL_SCALE_MODIFIER_2G")
accel_scale_modifier = self.ACCEL_SCALE_MODIFIER_2G
x = x / accel_scale_modifier
y = y / accel_scale_modifier
z = z / accel_scale_modifier
if g is True:
return {'x': x, 'y': y, 'z': z}
elif g is False:
x = x * self.GRAVITIY_MS2
y = y * self.GRAVITIY_MS2
z = z * self.GRAVITIY_MS2
return {'x': x, 'y': y, 'z': z}
def set_gyro_range(self, gyro_range):
"""Sets the range of the gyroscope to range.
gyro_range -- the range to set the gyroscope to. Using a pre-defined
range is advised.
"""
# First change it to 0x00 to make sure we write the correct value later
self.bus.write_byte_data(self.address, self.GYRO_CONFIG, 0x00)
# Write the new range to the ACCEL_CONFIG register
self.bus.write_byte_data(self.address, self.GYRO_CONFIG, gyro_range)
def read_gyro_range(self, raw=False):
"""Reads the range the gyroscope is set to.
If raw is True, it will return the raw value from the GYRO_CONFIG
register.
If raw is False, it will return 250, 500, 1000, 2000 or -1. If the
returned value is equal to -1 something went wrong.
"""
# Get the raw value
raw_data = self.bus.read_byte_data(self.address, self.GYRO_CONFIG)
if raw is True:
return raw_data
elif raw is False:
if raw_data == self.GYRO_RANGE_250DEG:
return 250
elif raw_data == self.GYRO_RANGE_500DEG:
return 500
elif raw_data == self.GYRO_RANGE_1000DEG:
return 1000
elif raw_data == self.GYRO_RANGE_2000DEG:
return 2000
else:
return -1
def get_gyro_data(self):
"""Gets and returns the X, Y and Z values from the gyroscope.
Returns the read values in a dictionary.
"""
# Read the raw data from the MPU-6050
x = self.read_i2c_word(self.GYRO_XOUT0)
y = self.read_i2c_word(self.GYRO_YOUT0)
z = self.read_i2c_word(self.GYRO_ZOUT0)
gyro_scale_modifier = None
gyro_range = self.read_gyro_range(True)
if gyro_range == self.GYRO_RANGE_250DEG:
gyro_scale_modifier = self.GYRO_SCALE_MODIFIER_250DEG
elif gyro_range == self.GYRO_RANGE_500DEG:
gyro_scale_modifier = self.GYRO_SCALE_MODIFIER_500DEG
elif gyro_range == self.GYRO_RANGE_1000DEG:
gyro_scale_modifier = self.GYRO_SCALE_MODIFIER_1000DEG
elif gyro_range == self.GYRO_RANGE_2000DEG:
gyro_scale_modifier = self.GYRO_SCALE_MODIFIER_2000DEG
else:
print("Unkown range - gyro_scale_modifier set to self.GYRO_SCALE_MODIFIER_250DEG")
gyro_scale_modifier = self.GYRO_SCALE_MODIFIER_250DEG
x = x / gyro_scale_modifier
y = y / gyro_scale_modifier
z = z / gyro_scale_modifier
return {'x': x, 'y': y, 'z': z}
def get_all_data(self):
"""Reads and returns all the available data."""
temp = self.get_temp()
accel = self.get_accel_data()
gyro = self.get_gyro_data()
return [accel, gyro, temp]
if __name__ == "__main__":
mpu = mpu6050(0x68)
mpu.set_accel_range(mpu.ACCEL_RANGE_2G)
mpu.set_gyro_range(mpu.GYRO_RANGE_1000DEG)
print(mpu.get_temp())
while 1:
accel_data = mpu.get_accel_data()
ax = 2*9.8*accel_data['x']/32768
ay = 2*9.8*accel_data['y']/32768
az = 2 * 9.8 * accel_data['z'] / 32768
ax = round(ax, 2)
ay = round(ay, 2)
az = round(az, 2)
print("accel_data:" + " " + str(ax) + " " +
str(ay) + " " + str(az))
gyro_data = mpu.get_gyro_data()
# 角速度
gx = 1000*gyro_data['x']/32768
gy = 1000 * gyro_data['y'] / 32768
gz = 1000 * gyro_data['z'] / 32768
gx = round(gx, 2)
gy = round(gy, 2)
gz = round(gz, 2)
print("jiao rate:" + " " + str(gx) + " " +
str(gy) + " " + str(gz))
time.sleep(1)
PCA9685代码案例:
在原基础上增加了用于控制电机pwm的函数,
setMotoPluse(channel, pulse)
#参数1:通道 参数2:高电平时间(0-4095)
#!/usr/bin/python
import time
import math
import smbus
# ============================================================================
# Raspi PCA9685 16-Channel PWM Servo Driver
# ============================================================================
class PCA9685:
# Registers/etc.
__SUBADR1 = 0x02
__SUBADR2 = 0x03
__SUBADR3 = 0x04
__MODE1 = 0x00
__PRESCALE = 0xFE
__LED0_ON_L = 0x06
__LED0_ON_H = 0x07
__LED0_OFF_L = 0x08
__LED0_OFF_H = 0x09
__ALLLED_ON_L = 0xFA
__ALLLED_ON_H = 0xFB
__ALLLED_OFF_L = 0xFC
__ALLLED_OFF_H = 0xFD
def __init__(self, address=0x40, debug=False):
self.bus = smbus.SMBus(1)
self.address = address
self.debug = debug
if (self.debug):
print("Reseting PCA9685")
self.write(self.__MODE1, 0x00)
def write(self, reg, value):
"Writes an 8-bit value to the specified register/address"
self.bus.write_byte_data(self.address, reg, value)
if (self.debug):
# print("I2C: Write 0x%02X to register 0x%02X" % (value, reg))
pass
def read(self, reg):
"Read an unsigned byte from the I2C device"
result = self.bus.read_byte_data(self.address, reg)
if (self.debug):
print("I2C: Device 0x%02X returned 0x%02X from reg 0x%02X" % (self.address, result & 0xFF, reg))
return result
def setPWMFreq(self, freq):
"Sets the PWM frequency"
prescaleval = 25000000.0 # 25MHz
prescaleval /= 4096.0 # 12-bit
prescaleval /= float(freq)
prescaleval -= 1.0
if (self.debug):
print("Setting PWM frequency to %d Hz" % freq)
print("Estimated pre-scale: %d" % prescaleval)
prescale = math.floor(prescaleval + 0.5)
if (self.debug):
print("Final pre-scale: %d" % prescale)
oldmode = self.read(self.__MODE1)
newmode = (oldmode & 0x7F) | 0x10 # sleep
self.write(self.__MODE1, newmode) # go to sleep
self.write(self.__PRESCALE, int(math.floor(prescale)))
self.write(self.__MODE1, oldmode)
time.sleep(0.005)
self.write(self.__MODE1, oldmode | 0x80)
def setPWM(self, channel, on, off):
"Sets a single PWM channel"
self.write(self.__LED0_ON_L + 4 * channel, on & 0xFF)
self.write(self.__LED0_ON_H + 4 * channel, on >> 8)
self.write(self.__LED0_OFF_L + 4 * channel, off & 0xFF)
self.write(self.__LED0_OFF_H + 4 * channel, off >> 8)
if (self.debug):
# print("channel: %d LED_ON: %d LED_OFF: %d" % (channel, on, off))
pass
def setServoPulse(self, channel, pulse):
"Sets the Servo Pulse,The PWM frequency must be 50HZ"
pulse = int(pulse * 4096 / 20000) # PWM frequency is 50HZ,the period is 20000us
self.setPWM(channel, 0, pulse)
def setMotoPluse(self, channel, pulse):
if pulse > 3000:
self.setPWM(channel, 0, 3000)
else:
self.setPWM(channel, 0, pulse)
if __name__ == '__main__':
pwm = PCA9685(0x40, debug=True)
pwm.setPWMFreq(50)
print("start the control")
while True:
for i in range(500, 2500, 10):
pwm.setServoPulse(0, i)
time.sleep(0.02)
#
# for i in range(2500, 500, -10):
# pwm.setServoPulse(0, i)
# time.sleep(0.02)
代码参考:
MPU6050
PCA9685
本文内容由网友自发贡献,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有涉嫌抄袭侵权的内容,请联系:hwhale#tublm.com(使用前将#替换为@)