ROS中使用A星算法进行路径规划
- 前言
- python编写A星算法
-
- ROS结合A星算法
-
- 实现结果
前言
由于本人这学期修了一门《智能工程》的课程,课程的大作业要求大家自主编写机器人导航程序,包括:路径规划、轨迹规划、控制器、机器人建模等相关程序,因此特在此写下一篇博客,记录开发过程。
这是第一篇博客,用于记录如何将自己编写的A星算法用于ROS中。
python编写A星算法
描述
先声明:在使用Python编写A*算法的过程中,深深的体会到了C++的链表、指针的便利性,但奈何已经1年多没使用C++写过程序了,所以还是用了Python来完成的。我编写的A星算法的时间复杂度和空间复杂度肯定都很高,希望大家看了轻喷。
由于要用在ROS的map中寻找路径,所以我把A星算法写成了一个类,只需要传进去三个参数,一个是二维的List(ROS中规定:可走区域的数值为0,障碍物数值为100,未知领域数值为-1),一个是起始点的坐标,一个是终点的坐标。
最后程序会返回一个List,里面的内容是从终点到起点的最短路径,用每一个点的坐标表示。
比如下面是一张地图:
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
规定起点为[2,2],终点为[2,4],则返回的内容为:[(2,4),(1,4),(0,3),(1,2),(2,2)]
具体实现
对于地图中每一个像素点,如果这个像素点可到达,那就计算当前的G代价(self.cost_g),H代价(self.cost_h),F代价(self.cost_f)
这个类,相当于C++中的struct
class map_node():
def __init__(self):
self.x = 0
self.y = 0
self.cost_f = 0
self.cost_g = 0
self.cost_h = 0
self.parent = [0,0]
主要类:
class find_path():
类初始化函数:
-
extend_map函数是将地图扩展一圈,加一圈障碍物(像素值为1)
-
声明一个state_map用于保存map中每一个像素点的状态:
- 2代表已经在open表中
- 3代表已经在close表中
- 0代表还没有处理过
-
起点和终点自然横纵坐标都+=1
-
初始化一些变量 openlist、closelist
def __init__(self, map, start, goal):
self.map = self.extend_map(map)
self.state_map = np.zeros([len(map) + 2, len(map[0]) + 2])
self.start = start
self.start[0] += 1
self.start[1] += 1
self.goal = goal
self.goal[0] += 1
self.goal[1] += 1
self.open_list = []
self.cloase_list = []
self.path = []
self.if_reach = False
扩展地图边界的函数
def extend_map(self, map):
new_row = np.ones(len(map[0]))
new_col = np.ones(len(map) + 2)
x = np.insert(map, 0, new_row, axis=0)
x = np.insert(x, len(map) + 1, new_row, axis=0)
x = np.insert(x, 0 , new_col, axis=1)
x = np.insert(x, len(map[0]) + 1 , new_col, axis=1)
return x
主要的寻找路径的函数
- 如果设置的起始点和终点不可达,print 提示,然后直接退出
- append_around_open函数是把该点周围的8个点加到open表中
- 把起始点加到close表中
- 进入循环,利用find_min_cost_f每次寻找open表中最小的cost_f,把它周围的8个点加到open表中,然后把这个节点加到close表,直到找到了到终点的路径,然后利用append_path函数回溯父节点直到回溯到起点。
def start_find(self):
if self.map[self.start[0]][self.start[1]] != 0:
print "\033[0;31m[E] : Please set the valid start point\033[0m"
print "value = ", self.map[self.start[0]][self.start[1]]
return "None"
if self.map[self.goal[0]][self.goal[1]] != 0:
print "\033[0;31m[E] : Please set the valid goal point\033[0m"
return "None"
self.append_around_open(self.start, cost_g=0)
temp = map_node()
temp.x = self.start[0]
temp.y = self.start[1]
self.append_close(temp)
while True:
min_cost, index_min_cost = self.find_min_cost_f()
current_node = self.open_list[index_min_cost]
if current_node.x == self.goal[0] and current_node.y == self.goal[1]:
self.append_path(current_node)
break
self.append_around_open([current_node.x, current_node.y], cost_g=current_node.cost_g)
self.append_close(current_node)
self.open_list.remove(current_node)
return self.path
利用循环遍历该点周围的8个点
注意:如果cost_f有更小的,要更新cost_f和父节点
def append_around_open(self, coordinate, cost_g):
for i in [-1, 0, 1]:
for j in [-1, 0, 1]:
if i == 0 and j == 0:
continue
if self.map[coordinate[0] + i][coordinate[1] + j] == 0 \
and self.state_map[coordinate[0] + i][coordinate[1] + j] != 3:
temp = map_node()
temp.cost_g = 10 + cost_g
temp.cost_h = (abs(self.goal[0] - (coordinate[0] + i)) + abs(self.goal[1] - (coordinate[1] + j))) * 10
temp.cost_f = temp.cost_g + temp.cost_h
temp.x = coordinate[0] + i
temp.y = coordinate[1] + j
temp.parent[0] = coordinate[0]
temp.parent[1] = coordinate[1]
if self.state_map[coordinate[0] + i][coordinate[1] + j] == 2:
current_index = self.find_index(coordinate[0] + i, coordinate[1] + j)
if self.open_list[current_index].cost_f > temp.cost_f:
self.open_list[current_index] = temp
else:
self.state_map[coordinate[0] + i][coordinate[1] + j] = 2
self.open_list.append(temp)
回溯父节点,然后把每一个节点的坐标append到self.path这变量中
def append_path(self, node):
while True:
self.path.append([node.x - 1, node.y - 1])
if node.x == self.start[0] and node.y == self.start[1]:
break
current_index = self.find_close_index(node.parent[0], node.parent[1])
node = self.cloase_list[current_index]
寻找open表中的最小的cost_f
def find_min_cost_f(self):
min_cost = 100000
index_min_cost = 0
for i in range(len(self.open_list)):
if self.open_list[i].cost_f < min_cost:
min_cost = self.open_list[i].cost_f
index_min_cost = i
return min_cost, index_min_cost
其它函数
def find_close_index(self, x, y):
for i in range(len(self.cloase_list)):
if self.cloase_list[i].x == x and self.cloase_list[i].y == y:
return i
def find_index(self, x, y):
for i in range(len(self.open_list)):
if self.open_list[i].x == x and self.open_list[i].y == y:
return i
def append_close(self, node):
self.state_map[node.x][node.y] = 3
self.cloase_list.append(node)
ROS结合A星算法
描述
由于本人ROS学的并不是很深入,目前只掌握了topic这一种消息传输机制,因此,程序中只包括利用topic传输消息。
通过ROS中的Topic订阅"/map"、"/initialpose"、"/move_base_simple/goal"这三个话题,然后通过计算,将path发布出去("/path_my_A_star")
具体实现
类初始化函数
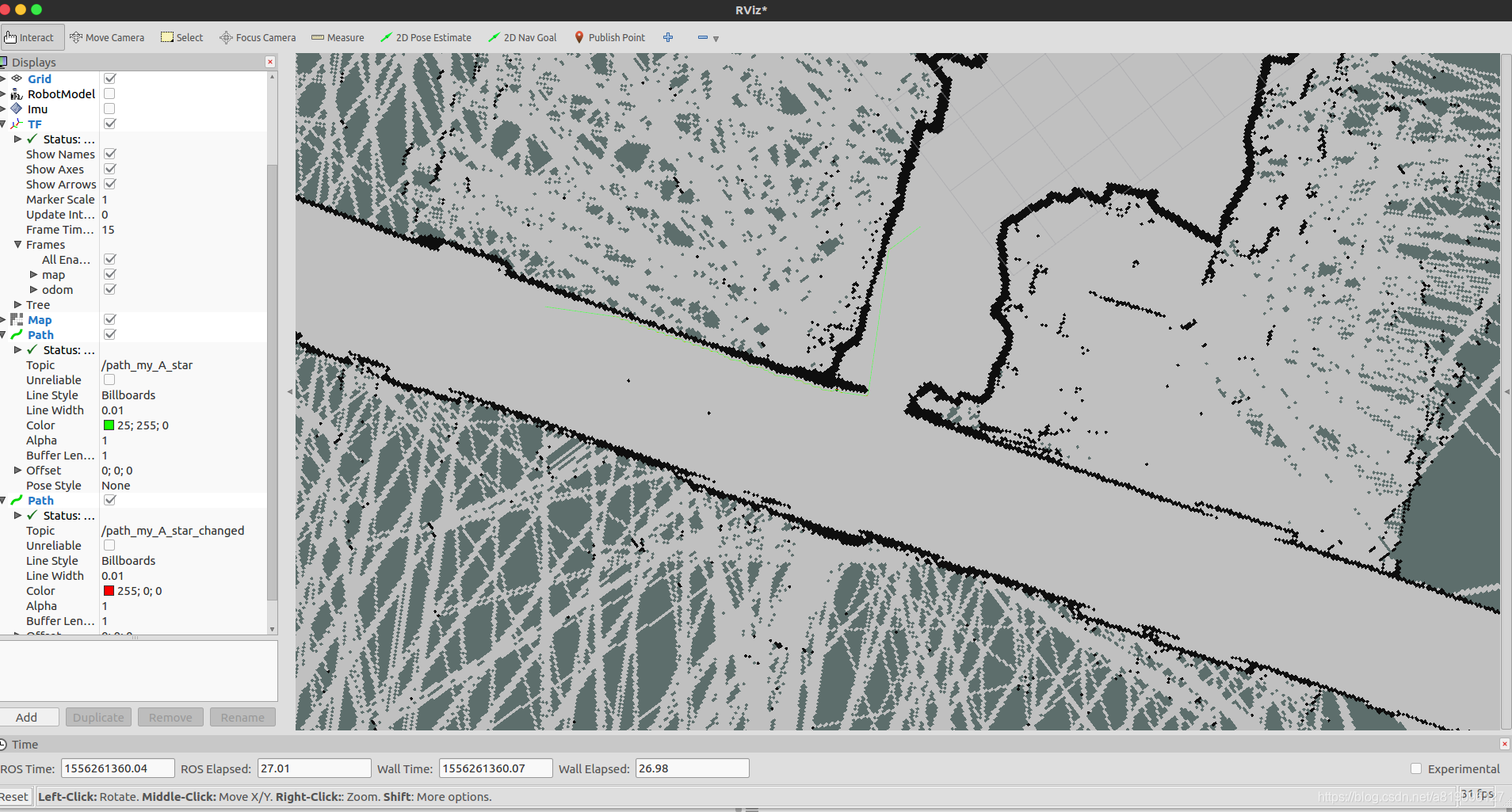
- “/path_my_A_star"是未进行平滑处理的路径,有直角等,”/path_my_A_star_changed"是平滑处理的
def __init__(self):
rospy.init_node("path_pub")
self.path_pub = rospy.Publisher("/path_my_A_star", Path, queue_size=15)
self.path_pub_changed = rospy.Publisher("/path_my_A_star_changed", Path, queue_size=15)
self.origin_x = 0
self.origin_y = 0
self.resolution = 0
self.width = 0
self.height = 0
self.map_sub = rospy.Subscriber("/map", OccupancyGrid, self.map_callback)
self.current_path = Path()
self.current_path_changed = Path()
rospy.sleep(1)
self.start_map_point = []
self.goal_map_point = []
self.path_map = []
self.path_world = []
self.if_start_find_path = False
self.goal_pose = PoseStamped()
self.init_pose = PoseWithCovarianceStamped()
self.init_pose_sub = rospy.Subscriber("/initialpose", PoseWithCovarianceStamped, self.init_pose_callback)
self.goal_pose_sub = rospy.Subscriber("/move_base_simple/goal", PoseStamped, self.goal_pose_callback)
self.last_time = rospy.get_rostime()
self.start_find_path()
rospy.Rate(1)
rospy.spin()
起始点回调函数
def init_pose_callback(self, msg):
self.init_pose = msg
self.start_map_point = self.WorldTomap(msg.pose.pose.position.x, msg.pose.pose.position.y)
print "----------------start point----------------",self.start_map_point
print "value = ", self.map[self.start_map_point[0]][self.start_map_point[1]]
if self.start_map_point == [-1, -1]:
print "\033[0;31m[E] : Please set the valid goal point\033[0m"
终点回调函数
def goal_pose_callback(self, msg):
self.path_map = []
self.goal_pose = msg
self.if_start_find_path = True
self.goal_map_point = self.WorldTomap(msg.pose.position.x, msg.pose.position.y)
print "-----------------goal point---------------",self.goal_map_point
if self.goal_map_point == [-1, -1]:
print "\033[0;30m[Kamerider E] : Please set the valid goal point\033[0m"
return
else:
self.start_find_path()
地图回调函数
def map_callback(self, msg):
print msg.header
print "------"
print msg.info
print "------"
print len(msg.data)
self.origin_x = msg.info.origin.position.x
self.origin_y = msg.info.origin.position.y
self.resolution = msg.info.resolution
self.width = msg.info.width
self.height = msg.info.height
print "-------",self.width
raw = np.array(msg.data, dtype=np.int8)
self.map = raw.reshape((self.height, self.width))
self.map_sub.unregister()
将起始点和终点的topic里的World坐标系的数值转化为map上的像素坐标,用于world坐标系映射到map下的离散的像素点
def WorldTomap(self, wx, wy):
if wx < self.origin_x or wy < self.origin_y:
return [-1, -1]
mx = (int)((wx - self.origin_x) / self.resolution)
my = (int)((wy - self.origin_y) / self.resolution)
if mx < self.width and my < self.height:
return [my, mx]
return [-1, -1]
调用A星算法寻找路径
def start_find_path(self):
if self.if_start_find_path:
print ('\033[0;32m[I] : Start find path with A* \033[0m')
temp = A_star.find_path(self.map, self.start_map_point, self.goal_map_point)
self.path_map = temp.start_find()
print self.path_map
self.publisher_path()
else:
rospy.sleep(1)
print ('\033[0;33m[W] : Please set goal pose\033[0m')
return
发布两种不同的路径,一种是原始路径,一种是利用插值平滑处理过的
def publisher_path(self):
time = 1
y1 = []
y2 = []
for i in range(len(self.path_map)):
current_time = rospy.get_rostime()
current_pose = PoseStamped()
current_pose.pose.position.x, current_pose.pose.position.y= self.mapToWorld(self.path_map[i][1], self.path_map[i][0])
y1.append(self.mapToWorld(self.path_map[i][1], self.path_map[i][0])[0])
y2.append(self.mapToWorld(self.path_map[i][1], self.path_map[i][0])[1])
current_pose.pose.position.z = 0.0
current_pose.pose.orientation.x = 0.0
current_pose.pose.orientation.y = 0.0
current_pose.pose.orientation.z = 0.0
current_pose.pose.orientation.w = 1.0
time += 1
self.current_path.header.stamp = current_time
self.current_path.header.frame_id = "odom"
self.current_path.poses.append(current_pose)
self.path_pub.publish(self.current_path)
self.last_time = current_time
length = len(self.path_map)
x = np.array([num for num in range(length)])
xnew = np.arange(0,length - 1, 0.1)
func1 = interpolate.interp1d(x, y1, kind='cubic')
func2 = interpolate.interp1d(x, y2, kind='cubic')
ynew1 = func1(xnew)
ynew2 = func2(xnew)
for i in range(len(ynew1)):
current_time = rospy.get_rostime()
current_pose = PoseStamped()
current_pose.pose.position.x = ynew1[i]
current_pose.pose.position.y = ynew2[i]
current_pose.pose.position.z = 0.0
current_pose.pose.orientation.x = 0.0
current_pose.pose.orientation.y = 0.0
current_pose.pose.orientation.z = 0.0
current_pose.pose.orientation.w = 1.0
time += 1
self.current_path_changed.header.stamp = current_time
self.current_path_changed.header.frame_id = "odom"
self.current_path_changed.poses.append(current_pose)
self.path_pub_changed.publish(self.current_path_changed)
self.last_time = current_time
实现结果
设置起点
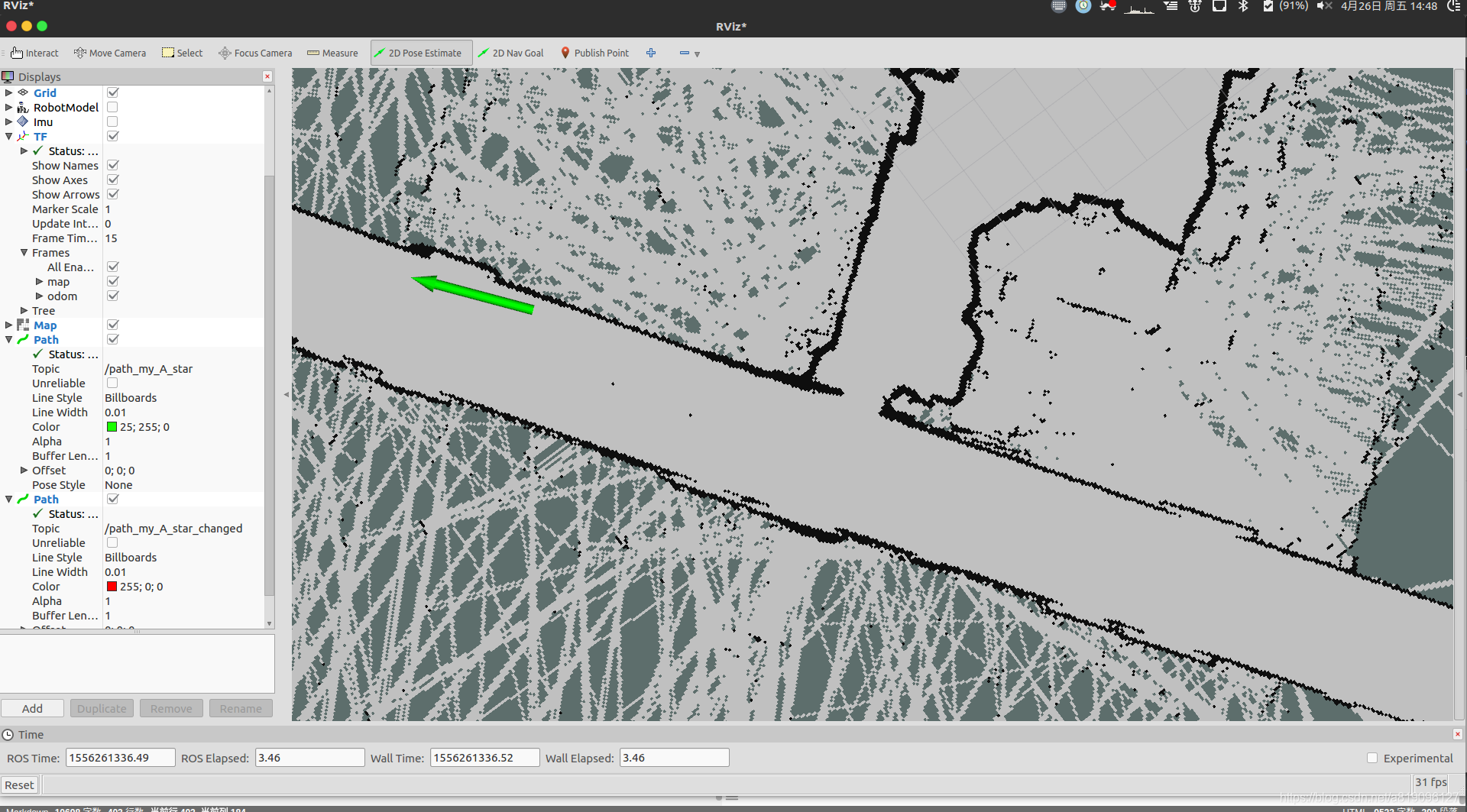
设置终点
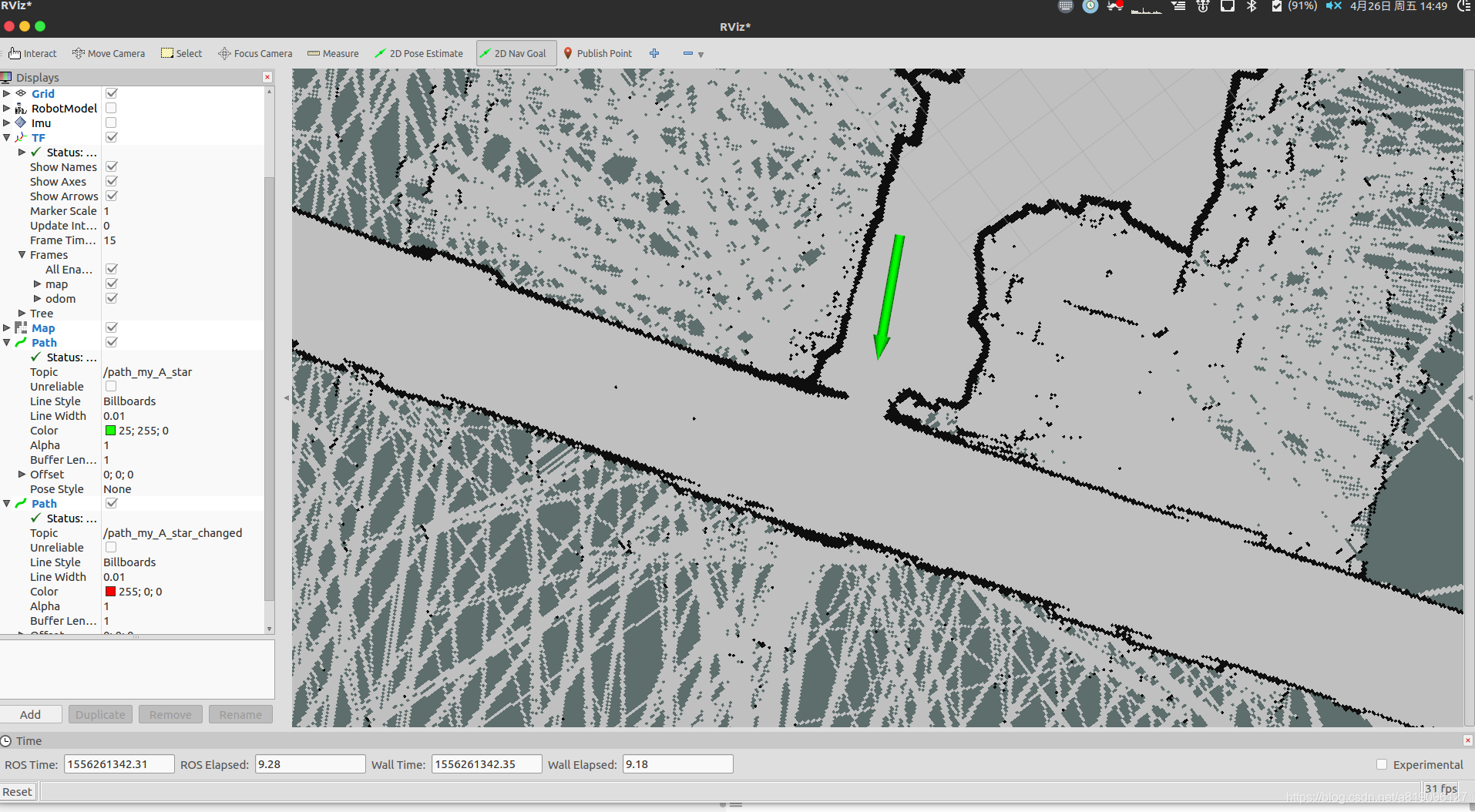
生成的路径
本文内容由网友自发贡献,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有涉嫌抄袭侵权的内容,请联系:hwhale#tublm.com(使用前将#替换为@)