目录
1.安装(vmware 15.01环境下安装):
2.vuzzer使用说明
3.vuzzer原理
3.1权重文件以及有着cmp信息的文件生成
3.2 vuzzer种子生成,变异原理
3.2.1 runfuzz.py
3.2.2.gautils.py:
1.安装(vmware 15.01环境下安装):
由于vuzzer是比较久远的项目,且无人更新,所以使用的环境比较老,我们需要安装ubuntu14.04版本的linu系统,并将ubuntu14.04系统内核降到3.13.0-24。具体做法如下:
#下载3.13.0-24版的内核
sudo apt-get install linux-image-3.13.0-24-generic
#重启
sudo reboot
然后我们在进入初始界面时按“esc”进入内核选择界面,选择3.13.0-24进入(注意这时界面显示存在一些问题,全屏会导致系统黑屏,所以以小窗口显示,该问题至今未解决),进入后我们可以使用uname -r查看内核版本,然后将原先的内核卸载
sudo apt-get purge linux-image-版本
sudo apt-get purge linux-headers-版本
接下来我们安装vuzzer
#下载vuzzer源码
git clone https://github.com/vusec/vuzzer
gcc --version
g++ --version
#查询gcc和g++版本,若不为4.8则用以下命令安装
sudo apt-get install gcc-4.8
sudo apt-get install g++-4.8
#在官网上下载pin-2.14版本的pin,并在vuzzer中创建到pin的链接,回到vuzzer文件夹下
ln -s /path-to-pin-homes pin
python --version
#检查是否带有带有python2.7,如果未安装执行以下命令安装
sudo apt-get install python-2.7
#下载EWAHBoolArray源码
git clone https://github.com/lemire/EWAHBoolArray
#将EWAHBoolArray中headers文件夹下的4个头文件拷贝到/usr/include/目录下
sudo cp headers/* /usr/include/
#安装BitMagic
sudo apt-get install bmagic
#安装BitVector,可在https://engineering.purdue.edu/kak/dist/BitVector-2.2.html下载,解压后在BitVector目录下执行以下命令
sudo python setup.py install
#安装vuzzer,首先回到vuzzer文件夹下
export PIN_ROOT=$(pwd)/pin
cd ./support/libdft/src
make clean
#再回到vuzzer文件夹下
make support-libdft
make
make -f mymakefile
#当我们可以找到obj-ia32/dtracker.so和obj-i32/bbcounts2.so,则说明我们已经安装成功
2.vuzzer使用说明
vuzzer的入口文件是runfuzzer.py,我们运行python runfuzzer.py -h,运行结果如下

其中-s:后的参数位被测试程序命令行,例如-s '/bin/a %s',注意要将转入文件的位置改为%s,使vuzzer以此处输入为基础进行漏洞挖掘
-i后的参数为初始种子所在文件夹,例如-i 'datatemp/a/',注意初始种子文件要有三个或三个以上
-w后的参数为该程序生成的.pkl文件(即程序块权重文件),-n后的参数为该程序生成的.names文件(即cmp指令信息文件)
-l后的参数为需要监测的二进制文件数量,-o后的参数为程序或库的起始地址,-b 后的参数为要监测的库名,下面将介绍vuzzer如何对一个二进制程序做测试
首先我们先写一个c程序,代码如下:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main(int argc,char** argv)
{
char s[30];
FILE* fp;
fp=fopen(argv[1],"r+");
if(fp==NULL)
{
exit(1);
}
fscanf(fp,"%29s",s);
if(s[0]=='W')
{
if(s[10]=='A')
{
fscanf(fp,"%s",s);
printf("%s\n",s);
}
else
{
printf("wrong");
}
}
else
{
printf("wrong");
}
return 0;
}
使用gcc a.c -o a编译生成32位文件(由于vuzzer只能借助命令行测试且只能使用文件输入,所以程序写成上面那个样子,我们发现在第二个fscanf有溢出风险)
我们使用ida打开二进制程序a,在file下选择script file选项,之后选择BB-weightv4.py脚本文件,ida会运行该脚本生成程序块权重文件.pkl和cmp指令信息文件.names,将新生成的文件放在vuzzer/idafiles下,将程序a放在vuzzer/bin文件下,在vuzzer/datatemp下新建一个文件夹a,放入三个初始种子文件。运行命令python runfuzzer.py -s './bin/a %s' -i 'datatemp/a/' -w 'idafiles/a.pkl' -n idafiles/a.names即可正常使用vuzzer。运行结果如下图所示

其中,测试中用到的所有种子文件都放在data目录下,可以引发crash的种子放在outd/crashInputs目录下,一些crash记录会记在error.log中,每一代的信息都放在status.log内,对cmp的分析结果放在cmp.out中。
3.vuzzer原理
3.1权重文件以及有着cmp信息的文件生成
- def findCMPopnds():使用ida的接口寻找cmp指令,并将cmp指令中的立即数读取出来,并将其转为[set(字符串),set(字符)]返回
- def get_children(BB):借助广度优先算法将某函数所有从BB块出发能够到达的子块首地址组合成列表返回
def calculate_weight(func, fAddr):根据马尔可夫模型和程序控制流图计算每一块到达的概率
def calculate_weight(func, fAddr):
''' This function calculates weight for each BB, in the given function func.
此函数借助广度优先算法计算给定函数func中每个bb的权重。
'''
# We start by iterating all BBs and assigning weights to each outgoing edges.
# we assign a weight 0 to loopback edge because it does not point (i.e., leading) to "new" BB.
edges.clear()
temp = deque([]) # 工作队列
rootFound= False
visited=[] # 已计算权重的程序快
shadow=[]
noorphan=True
#先计算每个程序块到下一程序块的概率
for block in func:
pLen=len(list(block.succs()))
if pLen == 0: # exit BB
continue
eProb=1.0/pLen #查找某程序块之后连接程序块个数n,那么每个程序块到下一程序块的概率1/n
#print "probability = %3.1f"%(eProb,), eProb
for succBB in block.succs():
if (succBB.startEA <= block.startEA) and (len(list(succBB.preds()))>1):
#this is for backedge. this is not entirely correct as BB which are shared or are at lower
#addresses are tagged as having zero value!! TO FIX.,
#在控制流图中国前一个程序块首地址比后一个程序块首地址大,说明可能存在循环,重新给定该程序块到下一程序块概率
edges[(block.startEA,succBB.startEA)]=1.0
else:
edges[(block.startEA,succBB.startEA)]=eProb
print "[*] Finished edge probability calculation"
#for edg in edges:
#print " %x -> %x: %3.1f "%(edg[0],edg[1],edges[edg])
# lets find the root BB
#orphanage=[]#home for orphan BBs
orphID=[]
for block in func:
if len(list(block.preds())) == 0:
#Note: this only check was not working as there are orphan BB in code. Really!!!
#注意:由于代码中有孤立BB,所以此唯一检查不起作用。真的?!!!\
if block.startEA == fAddr:
rootFound=True
root = block
else:
if rootFound==True:
noorphan=False
break
pass
#now, all the BBs should be children of root node and those that are not children are orphans. This check is required only if we have orphans.
#现在,所有bbs都应该是根节点的子级,而那些不是子级的bbs都是孤立的。只有当我们有孤儿时才需要这张支票。
if noorphan == False:
rch=get_children(root)
rch.append(fAddr)# add root also as a non-orphan BB
for blk in func:
if blk.startEA not in rch:
weight[blk.startEA]=(1.0,blk.endEA)
visited.append(blk.id)
orphID.append(blk.id)
#print "[*] orphanage calculation done."
del rch
#程序块概率计算,为其前置程序块概率乘以从前置程序块到该程序块的概率求和
if rootFound==True:
#print "[*] found root BB at %x"%(root.startEA,)
weight[root.startEA] = (1.0,root.endEA)
visited.append(root.id)
print "[*] Root found. Starting weight calculation."
for sBlock in root.succs():
#if sBlock.id not in shadow:
#print "Pushing successor %x"%(sBlock.startEA,)
temp.append(sBlock)
shadow.append(sBlock.id)
loop=dict()# this is a temp dictionary to avoid get_children() call everytime a BB is analysed.
while len(temp) > 0:
current=temp.popleft()
shadow.remove(current.id)
print "current: %x"%(current.startEA,)
if current.id not in loop:
loop[current.id]=[]
# we check for orphan BB and give them a lower score
# by construction and assumptions, this case should not hit!
#我们检查孤立的BB并通过构造和假设给他们一个较低的分数,这种情况不应该发生!
if current.id in orphID:
#weight[current.startEA]=(0.5,current.endEA)
#visited.append(current.id)
continue
tempSum=0.0
stillNot=False
chCalculated=False
for pb in current.preds():
#print "[*] pred of current %x"%(pb.startEA,)
if pb.id not in visited:
if edges[(pb.startEA,current.startEA)]==0.0:
weight[pb.startEA]=(0.5,pb.endEA)
#artificial insertion
#print "artificial insertion branch"
#人工插入分支
continue
#当前置程序块没有概率,那么查找其是不是在该程序块之后会运行到,如果是,说明存在循环,则提升其概率为0.5
if pb.id not in [k[0] for k in loop[current.id]]:
if chCalculated == False:
chCurrent=get_children(current)
chCalculated=True
if pb.startEA in chCurrent:
# this BB is in a loop. we give less score to such BB
weight[pb.startEA]=(0.5,pb.endEA)
loop[current.id].append((pb.id,True))
#print "loop branch"
continue
else:
loop[current.id].append((pb.id,False))
else:
if (pb.id,True) in loop[current.id]:
weight[pb.startEA]=(0.5,pb.endEA)
continue
#print "not pred %x"%(pb.startEA,)
if current.id not in shadow:
temp.append(current)
#print "pushed back %x"%(current.startEA,)
shadow.append(current.id)
stillNot=True
break
#计算程序块概率,为其前置程序块概率乘以从前置程序块到该程序块的概率求和,
if stillNot == False:
# as we sure to get weight for current, we push its successors
for sb in current.succs():
if sb.id in visited:
continue
if sb.id not in shadow:
temp.append(sb)
shadow.append(sb.id)
for pb in current.preds():
tempSum = tempSum+ (weight[pb.startEA][0]*edges[(pb.startEA,current.startEA)])
weight[current.startEA] = (tempSum,current.endEA)
visited.append(current.id)
del loop[current.id]
print "completed %x"%(current.startEA,)
def analysis():将程序按函数切分,并对每个函数生成控制流图,进入def calculate_weight(func, fAddr)中计算权重
def main()
def main():
strings=[]
start = timeit.default_timer()
#获得么个程序块的概率
analysis()
#获得cmp的信息
strings=findCMPopnds()
stop = timeit.default_timer()
#每个程序块的权重=1/概率,返回(程序块开始指令位置:(程序块权重,程序块结束后一条指令位置)
for bb in weight:
fweight[bb]=(1.0/weight[bb][0],weight[bb][1])
print"[**] Printing weights..."
for bb in fweight:
print "BB [%x-%x] -> %3.2f"%(bb,fweight[bb][1],fweight[bb][0])
print " [**] Total Time: ", stop - start
print "[**] Total functions analyzed: %d"%(fCount,)
print "[**] Total BB analyzed: %d"%(len(fweight),)
outFile=GetInputFile() # name of the that is being analysed
strFile=outFile+".names"
outFile=outFile+".pkl"
fd=open(outFile,'w')
#将程序权重放在.pkl文件中
pickle.dump(fweight,fd)
fd.close()
strFD=open(strFile,'w')
#将程序cmp信息放在.name文件中
pickle.dump(strings,strFD)
strFD.close()
print "[*] Saved results in pickle files: %s, %s"%(outFile,strFile)
3.2 vuzzer种子生成,变异原理
这一部分功能主要由runfuzz.py,gautils.py,operators.py实现,下面我们将看一下其中的原理
3.2.1 runfuzz.py
def main():
check_env()
将命令行的指令拆解放入配置的变量中
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='VUzzer options')
parser.add_argument('-s','--sut', help='SUT commandline',required=True)
parser.add_argument('-i','--inputd', help='seed input directory (relative path)',required=True)
parser.add_argument('-w','--weight', help='path of the pickle file(s) for BB wieghts (separated by comma, in case there are two) ',required=True)
#
parser.add_argument('-n','--name', help='Path of the pickle file(s) containing strings from CMP inst (separated by comma if there are two).',required=True)
parser.add_argument('-l','--libnum', help='Nunber of binaries to monitor (only application or used libraries)',required=False, default=1)
parser.add_argument('-o','--offsets',help='base-address of application and library (if used), separated by comma', required=False, default='0x00000000')
parser.add_argument('-b','--libname',help='library name to monitor',required=False, default='')
args = parser.parse_args()
config.SUT=args.sut
config.INITIALD=os.path.join(config.INITIALD, args.inputd)
config.LIBNUM=int(args.libnum)
config.LIBTOMONITOR=args.libname
config.LIBPICKLE=[w for w in args.weight.split(',')]
config.NAMESPICKLE=[n for n in args.name.split(',')]
config.LIBOFFSETS=[o for o in args.offsets.split(',')]
ih=config.PINCMD.index("#") # this is just to find the index of the placeholder in PINCMD list to replace it with the libname,这只是为了在pincmd列表中找到占位符的索引,用libname替换它。
config.PINCMD[ih]=args.libname
###################################
config.minLength=get_min_file(config.INITIALD)
#对文件中清空操作
try:
shutil.rmtree(config.KEEPD)
except OSError:
pass
os.mkdir(config.KEEPD)
try:
os.mkdir("outd")
except OSError:
pass
try:
os.mkdir("outd/crashInputs")
except OSError:
gau.emptyDir("outd/crashInputs")
crashHash=[]
try:
os.mkdir(config.SPECIAL)
except OSError:
gau.emptyDir(config.SPECIAL)
try:
os.mkdir(config.INTER)
except OSError:
gau.emptyDir(config.INTER)
###### open names pickle files,打开名称pickle文件
将.pkl和.names文件的内容读入
gau.prepareBBOffsets()
if config.PTMODE:
pt = simplept.simplept()
else:
pt = None
if config.ERRORBBON==True:
#检查程序中错误处理的程序块
gbb,bbb=dry_run()
else:
gbb=0
# gau.die("dry run over..")
import timing
#selftest()
noprogress=0
currentfit=0
lastfit=0
config.CRASHIN.clear()
stat=open("stats.log",'w')
stat.write("**** Fuzzing started at: %s ****\n"%(datetime.now().isoformat('+'),))
stat.write("**** Initial BB for seed inputs: %d ****\n"%(gbb,))
stat.flush()
os.fsync(stat.fileno())
stat.write("Genaration\t MINfit\t MAXfit\t AVGfit MINlen\t Maxlen\t AVGlen\t #BB\t AppCov\t AllCov\n")
stat.flush()
os.fsync(stat.fileno())
starttime=time.clock()
allnodes = set()
alledges = set()
try:
shutil.rmtree(config.INPUTD)
except OSError:
pass
shutil.copytree(config.INITIALD,config.INPUTD)
# fisrt we get taint of the intial inputs
在data目录下生成初始种子文件
get_taint(config.INITIALD)
print "MOst common offsets and values:", config.MOSTCOMMON
#gg=raw_input("press enter to continue..")
config.MOSTCOMFLAG=True
crashhappend=False
filest = os.listdir(config.INPUTD)
filenum=len(filest)
if filenum < config.POPSIZE:
gau.create_files(config.POPSIZE - filenum)
if len(os.listdir(config.INPUTD)) != config.POPSIZE:
gau.die("something went wrong. number of files is not right!")
efd=open(config.ERRORS,"w")
gau.prepareBBOffsets()
writecache = True
genran=0
bbslide=10 # this is used to call run_error_BB() functions
keepslide=3
keepfilenum=config.BESTP
使用遗传变异的算法生成种子并运行fuzz
while True:
print "[**] Generation %d\n***********"%(genran,)
del config.SPECIALENTRY[:]
del config.TEMPTRACE[:]
del config.BBSEENVECTOR[:]
config.SEENBB.clear()
config.TMPBBINFO.clear()
config.TMPBBINFO.update(config.PREVBBINFO)
fitnes=dict()
execs=0
config.cPERGENBB.clear()
config.GOTSTUCK=False
if config.ERRORBBON == True:
if genran > config.GENNUM/5:
bbslide = max(bbslide,config.GENNUM/20)
keepslide=max(keepslide,config.GENNUM/100)
keepfilenum=keepfilenum/2
#config.cPERGENBB.clear()
#config.GOTSTUCK=False
if 0< genran < config.GENNUM/5 and genran%keepslide == 0:
copy_files(config.INPUTD,config.KEEPD,keepfilenum)
#lets find out some of the error handling BBs,让我们找出一些错误处理bbs
if genran >20 and genran%bbslide==0:
stat.write("\n**** Error BB cal started ****\n")
stat.flush()
os.fsync(stat.fileno())
run_error_bb(pt)
copy_files(config.KEEPD,config.INPUTD,len(os.listdir(config.KEEPD))*1/10)
#copy_files(config.INITIALD,config.INPUTD,1)
files=os.listdir(config.INPUTD)
#将种子文件代入程序中运行,看是否有bug产生且计算每个种子文件的权重
for fl in files:
将种子文件逐个加入命令行运行,并将运行结果返回
tfl=os.path.join(config.INPUTD,fl)
iln=os.path.getsize(tfl)
args = (config.SUT % tfl).split(' ')
progname = os.path.basename(args[0])
#print ''
#print 'Input file sha1:', sha1OfFile(tfl)
#print 'Going to call:', ' '.join(args)
(bbs,retc)=execute(tfl)
#计算权重
if config.BBWEIGHT == True:
fitnes[fl]=gau.fitnesCal2(bbs,fl,iln)
else:
fitnes[fl]=gau.fitnesNoWeight(bbs,fl,iln)
execs+=1
#当种子文件引发程序漏洞执行后面的程序
if retc < 0 and retc != -2:
print "[*]Error code is %d"%(retc,)
efd.write("%s: %d\n"%(tfl, retc))
efd.flush()
os.fsync(efd)
tmpHash=sha1OfFile(config.CRASHFILE)
#将种子文件放入crashInputs文件夹和special文件夹中
if tmpHash not in crashHash:
crashHash.append(tmpHash)
tnow=datetime.now().isoformat().replace(":","-")
nf="%s-%s.%s"%(progname,tnow,gau.splitFilename(fl)[1])
npath=os.path.join("outd/crashInputs",nf)
shutil.copyfile(tfl,npath)
shutil.copy(tfl,config.SPECIAL)
config.CRASHIN.add(fl)
#打开STOPONCRASH选项,fuzz会在第一次发现bug的时候崩溃
if config.STOPONCRASH == True:
#efd.close()
crashhappend=True
break
计算种子文件大小和分数的一些信息
fitscore=[v for k,v in fitnes.items()]
maxfit=max(fitscore)
avefit=sum(fitscore)/len(fitscore)
mnlen,mxlen,avlen=gau.getFileMinMax(config.INPUTD)
print "[*] Done with all input in Gen, starting SPECIAL. \n"
#### copy special inputs in SPECIAL directory and update coverage info ###
spinputs=os.listdir(config.SPECIAL)
#将上轮中覆盖率小于本轮的新种子的种子文件删除
for sfl in spinputs:
if sfl in config.PREVBBINFO and sfl not in config.TMPBBINFO:
tpath=os.path.join(config.SPECIAL,sfl)
os.remove(tpath)
if sfl in config.TAINTMAP:
del config.TAINTMAP[sfl]
config.PREVBBINFO=copy.deepcopy(config.TMPBBINFO)
spinputs=os.listdir(config.SPECIAL)
将本次覆盖率更高的种子文件放入
for inc in config.TMPBBINFO:
config.SPECIALENTRY.append(inc)
if inc not in spinputs:
incp=os.path.join(config.INPUTD,inc)
shutil.copy(incp,config.SPECIAL)
#del fitnes[incp]
计算本次fuzz的代码覆盖率
appcov,allcov=gau.calculateCov()
stat.write("\t%d\t %d\t %d\t %d\t %d\t %d\t %d\t %d\t %d\t %d\n"%(genran,min(fitscore),maxfit,avefit,mnlen,mxlen,avlen,len(config.cPERGENBB),appcov,allcov))
stat.flush()
os.fsync(stat.fileno())
print "[*] Wrote to stat.log\n"
if crashhappend == True:
break
#lets find out some of the error handling BBs
#if genran >20 and genran%5==0:
# run_error_bb(pt)
genran += 1
#this part is to get initial fitness that will be used to determine if fuzzer got stuck.
#查看种子的分数是否提升,如果二十轮都没有改变则说明种子卡死
lastfit=currentfit
currentfit=maxfit
if currentfit==lastfit:#lastfit-config.FITMARGIN < currentfit < lastfit+config.FITMARGIN:
noprogress +=1
else:
noprogress =0
if noprogress > 20:
config.GOTSTUCK=True
stat.write("Heavy mutate happens now..\n")
noprogress =0
if (genran >= config.GENNUM) and (config.STOPOVERGENNUM == True):
break
# copy inputs to SPECIAL folder (if they do not yet included in this folder
#spinputs=os.listdir(config.SPECIAL)
#for sfl in spinputs:
# if sfl in config.PREVBBINFO and sfl not in config.TMPBBINFO:
# tpath=os.path.join(config.SPECIAL,sfl)
# os.remove(tpath)
#config.PREVBBINFO=copy.deepcopy(config.TMPBBINFO)
#spinputs=os.listdir(config.SPECIAL)
#for inc in config.TMPBBINFO:
# config.SPECIALENTRY.append(inc)
# if inc not in spinputs:
# incp=os.path.join(config.INPUTD,inc)
# shutil.copy(incp,config.SPECIAL)
# #del fitnes[incp]
#使用special中的种子文件查看cmp指令比较信息的结果
if len(os.listdir(config.SPECIAL))>0:
if len(os.listdir(config.SPECIAL))<config.NEWTAINTFILES:
get_taint(config.SPECIAL)
else:
try:
os.mkdir("outd/tainttemp")
except OSError:
gau.emptyDir("outd/tainttemp")
if conditional_copy_files(config.SPECIAL,"outd/tainttemp",config.NEWTAINTFILES) == 0:
get_taint("outd/tainttemp")
#print "MOst common offsets and values:", config.MOSTCOMMON
#gg=raw_input("press any key to continue..")
print "[*] Going for new generation creation.\n"
#生成新一代的种子
gau.createNextGeneration3(fitnes,genran)
#raw_input("press any key...")
efd.close()
stat.close()
libfd_mm.close()
libfd.close()
endtime=time.clock()
print "[**] Totol time %f sec."%(endtime-starttime,)
print "[**] Fuzzing done. Check %s to see if there were crashes.."%(config.ERRORS,)
def dry_run():
''' this function executes the initial test set to determine error handling BBs in the SUT. Such BBs are given zero weights during actual fuzzing.
此函数执行初始测试集以确定SUT中的错误处理BBS。这种BBS在实际过程中被赋予零权重。
'''
'''将程序正常运行和程序不正常运行时候经过的程序块输出。'''
print "[*] Starting dry run now..."
tempbad=[]
dfiles=os.listdir(config.INITIALD)
if len(dfiles) <3:
gau.die("not sufficient initial files")
'''基于初始种子运行程序,标记正常运行的一些程序块'''
for fl in dfiles:
tfl=os.path.join(config.INITIALD,fl)
try:
f=open(tfl, 'r')
f.close()
except:
gau.die("can not open our own input %s!"%(tfl,))
(bbs,retc)=execute(tfl)
if retc < 0:
gau.die("looks like we already got a crash!!")
config.GOODBB |= set(bbs.keys())
print "[*] Finished good inputs (%d)"%(len(config.GOODBB),)
#now lets run SUT of probably invalid files. For that we need to create them first.
#现在让我们运行可能无效文件的SUT。为此,我们需要先创建它们。
print "[*] Starting bad inputs.."
lp=0
badbb=set()
while lp <2:
try:
shutil.rmtree(config.INPUTD)
except OSError:
pass
os.mkdir(config.INPUTD)
#生成一些随机字符作为一些种子文件作为测试
gau.create_files_dry(30)
dfiles=os.listdir(config.INPUTD)
#当运行到一些之前没有经过的程序块,那么就是错误处理的程序块
for fl in dfiles:
tfl=os.path.join(config.INPUTD,fl)
(bbs,retc)=execute(tfl)
if retc < 0:
gau.die("looks like we already got a crash!!")
tempbad.append(set(bbs.keys()) - config.GOODBB)
tempcomn=set(tempbad[0])
for di in tempbad:
tempcomn.intersection_update(set(di))
badbb.update(tempcomn)
lp +=1
#else:
# tempcomn = set()
###print "[*] finished bad inputs (%d)"%(len(tempbad),)
config.ERRORBBALL=badbb.copy()
print "[*] finished common BB. TOtal such BB: %d"%(len(badbb),)
for ebb in config.ERRORBBALL:
print "error bb: 0x%x"%(ebb,)
time.sleep(5)
if config.LIBNUM == 2:
baseadr=config.LIBOFFSETS[1]
for ele in tempcomn:
if ele < baseadr:
config.ERRORBBAPP.add(ele)
else:
config.ERRORBBLIB.add(ele-baseadr)
del tempbad
del badbb
#del tempgood
将正确的程序块首地址写入GOODBB中,将错误的程序块首地址写入ERRORBBALL中,返回
return len(config.GOODBB),len(config.ERRORBBALL)
- def read_taint(fpath):返回当前种子文件遇到的cmp信息
- def get_taint(dirin):获取该种子在程序运行时经过cmp指令的信息,放入config.TAINTMAP,并将每个种子文件都有的cmp指令的信息放入config.MAXOFFSET
3.2.2.gautils.py
- def create_files_dry(num):使用datatemp目录下最初的种子文件作为初始文件,借助类ga中的totally_random函数生成随机长度的字符串,函数的参数并没有用
- def create_files(num):第一代生成
def create_files(num):
''' This function creates num number of files in the input directory. This is called if we do not have enough initial population.
Addition: once a new file is created by mutation/cossover, we query MOSTCOMMON dict to find offsets that replace values at those offsets in the new files. Int he case of mutation, we also use taintmap of the parent input to get other offsets that are used in CMP and change them. For crossover, as there are two parents invlived, we cannot query just one, so we do a random change on those offsets from any of the parents in resulting children.
此函数在输入目录中创建num个文件。如果没有足够的初始数量将会被调用。
另外:一旦mutation/cossover创建了一个新文件,我们将查询mostcommon dict以查找在新文件中替换这些偏移值的偏移量。在突变的情况下,我们还使用父输入的污染图来获取CMP中使用的其他偏移并更改它们。对于交叉,因为有两个父对象是反向的,所以我们不能只查询一个,所以我们对这些偏移量从产生子对象的任何父对象进行随机更改。
'''
#files=os.listdir(config.INPUTD)
files=os.listdir(config.INITIALD)
#初始化operators类,注意这里将cmp比较信息,即config.ALLSTRINGS作为参数传入
ga=operators.GAoperator(random.Random(),config.ALLSTRINGS)
while (num != 0):
当满足该条件,将选择两个种子文件做交叉
if random.uniform(0.1,1.0)>(1.0 - config.PROBCROSS) and (num >1):
#we are going to use crossover, so we get two parents.
par=random.sample(files, 2)
bn, ext = splitFilename(par[0])
#fp1=os.path.join(config.INPUTD,par[0])
#fp2=os.path.join(config.INPUTD,par[1])
fp1=os.path.join(config.INITIALD,par[0])
fp2=os.path.join(config.INITIALD,par[1])
p1=readFile(fp1)
p2=readFile(fp2)
#完成交叉
ch1,ch2 = ga.crossover(p1,p2)
# now we make changes according to taintflow info.
#将一些污染的信息加入
ch1=taint_based_change(ch1,par[0])
ch2=taint_based_change(ch2,par[1])
np1=os.path.join(config.INPUTD,"ex-%d.%s"%(num,ext))
np2=os.path.join(config.INPUTD,"ex-%d.%s"%(num-1,ext))
writeFile(np1,ch1)
writeFile(np2,ch2)
num -= 2
#当满足该条件时,将对单个文件做变异
else:
fl=random.choice(files)
bn, ext = splitFilename(fl)
#fp=os.path.join(config.INPUTD,fl)
fp=os.path.join(config.INITIALD,fl)
p1=readFile(fp)
#随机选择一种策略对种子做变异
ch1= ga.mutate(p1,fl)
ch1=taint_based_change(ch1,fl)
np1=os.path.join(config.INPUTD,"ex-%d.%s"%(num,ext))
writeFile(np1,ch1)
num -= 1
return 0
- def prepareBBOffsets(): 将.names中比较信息加入到config.ALLSTRINGS,将.pkl中的权重加入到config.ALLBB,config.cAPPBB
- def fitnesCal2(bbdict, cinput,ilen): 将能过发现新程序块的种子记录在TMPBBINFO,并将所有探索到的程序块记录在cPERGENBB,计算种子评分:score=该种子发现的程序块个数*
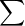 log(程序块权重)*log(该种子运行中经过该程序块次数)
log(程序块权重)*log(该种子运行中经过该程序块次数) - def calculateCov():覆盖率计算
- def createNextGeneration3(fit,gn):下一代生成
def createNextGeneration3(fit,gn):
''' this funtion generates new generation. This is the implemntation of standard ilitism approach. We are also addressing "input bloating" issue by selecting inputs based on its length. the idea is to select inputs for crossover their lenths is less than the best input's length. Oterwise, such inputs directly go for mutation whereby having a chance to reduce their lengths.'''
'''产生新一代'''
files=os.listdir(config.INPUTD)
#初始化operators类
ga=operators.GAoperator(random.Random(),config.ALLSTRINGS)
sfit=sorted(fit.items(),key=itemgetter(1),reverse=True)
bfp=os.path.join(config.INPUTD,sfit[0][0])
bestLen=os.path.getsize(bfp)
fitnames=[k for k,v in sfit]
# as our selection policy requires that each input that trigerred a new BB must go to the next generation, we need to find a set of BEST BBs and merge it with this set of inputs.
best=set(fitnames[:config.BESTP])#.union(set(config.SPECIALENTRY))
#best.update(config.CRASHIN)
#print "best",best, len(best)
if len(best)%2 !=0:
for nm in fitnames:
if nm not in best:
best.add(nm)
break
if config.GOTSTUCK==True:
heavyMutate(config.INPUTD,ga,best)
#here we check for file length and see if we can reduce lengths of some.
#降低种子字符长度
if gn%config.skipGen ==0:
mn,mx,avg=getFileMinMax(config.INPUTD)
filesTrim(config.INPUTD,avg,bestLen,config.minLength,ga, best)
i=0
bn, ext = splitFilename(sfit[i][0])
#limit=config.POPSIZE - config.BESTP
limit=config.POPSIZE - len(best)
#print "nextgen length %d - %d\n"%(limit, len(best))
#raw_input("enter key")
crashnum=0 #this variable is used to count new inputs generated with crashing inputs.
emptyDir(config.INTER)
copyd2d(config.SPECIAL,config.INTER)
if config.ERRORBBON==True:
copyd2d(config.INITIALD,config.INTER)
while i< limit:
#选择进入遗传的上一代种子
cutp=int(random.uniform(0.4,0.8)*len(fitnames))
#we are going to use crossover s.t. we want to choose best parents frequently, but giving chance to less fit parents also to breed. the above cut gives us an offset to choose parents from. Note that last 10% never get a chance to breed.
#print "crossover"
par=random.sample(fitnames[:cutp], 2)
fp1=os.path.join(config.INPUTD,par[0])
fp2=os.path.join(config.INPUTD,par[1])
inpsp=os.listdir(config.INTER)
#if len(config.SPECIALENTRY)>0 and random.randint(0,9) >6:
# fp1=os.path.join(config.INPUTD,random.choice(config.SPECIALENTRY))
#if len(config.CRASHIN)>0 and random.randint(0,9) >4 and crashnum<5:
# fp2=os.path.join(config.INPUTD,random.choice(config.CRASHIN))
# crashnum += 1
sin1='xxyy'
sin2='yyzz'
if len(inpsp)>0:
if random.randint(0,9) >config.SELECTNUM:
sin1=random.choice(inpsp)
fp1=os.path.join(config.INTER,sin1)
if random.randint(0,9) >config.SELECTNUM:
sin2=random.choice(inpsp)
fp2=os.path.join(config.INTER,sin2)
np1=os.path.join(config.INPUTD,"new-%d-g%d.%s"%(i,gn,ext))
np2=os.path.join(config.INPUTD,"new-%d-g%d.%s"%(i+1,gn,ext))
p1=readFile(fp1)
p2=readFile(fp2)
#当上一代种子长度过长,将不做交叉,直接使用create中优秀的种子做变异
if (len(p1) > bestLen) or (len(p2) > bestLen):
#print "no crossover"
#mch1= ga.mutate(p1)
if sin1 != 'xxyy':
mch1= ga.mutate(p1,sin1)
mch1=taint_based_change(mch1,sin1)
else:
mch1= ga.mutate(p1,par[0])
mch1=taint_based_change(mch1,par[0])
#mch2= ga.mutate(p2)
if sin2 !='yyzz':
mch2= ga.mutate(p2,sin2)
mch2=taint_based_change(mch2,sin2)
else:
mch2= ga.mutate(p2,par[1])
mch2=taint_based_change(mch2,par[1])
if len(mch1)<3 or len(mch2)<3:
die("zero input created")
writeFile(np1,mch1)
writeFile(np2,mch2)
i+=2
#continue
#先对选出的两个种子做交叉,然后使用create中优秀的种子做变异
else:
#print "crossover"
ch1,ch2 = ga.crossover(p1,p2)
#now we do mutation on these children, one by one
if random.uniform(0.1,1.0)>(1.0 - config.PROBMUT):
#mch1= ga.mutate(ch1)
if sin1 !='xxyy':
mch1= ga.mutate(ch1,sin1)
mch1=taint_based_change(mch1,sin1)
else:
mch1= ga.mutate(ch1,par[0])
mch1=taint_based_change(mch1,par[0])
if len(mch1)<3:
die("zero input created")
writeFile(np1,mch1)
else:
if sin1 != 'xxyy':
ch1=taint_based_change(ch1,sin1)
else:
ch1=taint_based_change(ch1,par[0])
writeFile(np1,ch1)
if random.uniform(0.1,1.0)>(1.0 - config.PROBMUT):
#mch2= ga.mutate(ch2)
if sin2 !='yyzz':
mch2= ga.mutate(ch2,sin2)
mch2=taint_based_change(mch2,sin2)
else:
mch2= ga.mutate(ch2,par[1])
mch2=taint_based_change(mch2,par[1])
if len(mch2)<3:
die("zero input created")
writeFile(np2,mch2)
else:
if sin2 != 'yyzz':
ch2=taint_based_change(ch2,sin2)
else:
ch2=taint_based_change(ch2,par[1])
writeFile(np2,ch2)
i += 2
# now we need to delete last generation inputs from INPUTD dir, preserving BEST inputs.
#best=[k for k,v in sfit][:config.BESTP]
#print "gennext loop ",i
#raw_input("enterkey..")
for fl in files:
if fl in best:
continue
os.remove(os.path.join(config.INPUTD,fl))
#lets check if everything went well!!!
if len(os.listdir(config.INPUTD))!=config.POPSIZE:
die("Something went wrong while creating next gen inputs.. check it!")
return 0
3.2.3.operators.py
- def get_cut():将cmp污染获得的信息加入到种子中
- def mutate():对单个种子做变异
mutators = [eliminate_random, change_bytes, change_bytes,add_random, add_random, change_random,single_change_random, lower_single_random, raise_single_random, eliminate_null, eliminate_double_null, totally_random, int_slide, double_fuzz,change_random_full,change_random_full,eliminate_random,add_random, change_random]:变异策略
def mutate(self, original,fl):
result=self.r.choice(self.mutators)(self, original,fl)
while len(result)<3:
result= self.r.choice(self.mutators)(self, original,fl)
assert len(result)>2, "elimination failed to reduce size %d" % (len(result),)
return result
- def crossover(self, original1, original2):对两个种子做交叉
crossovers=[single_crossover, double_crossover]#交叉策略
def crossover(self, original1, original2):
minlen=min(len(original1), len(original2))
if minlen <20:
return original1, original2 # we don't do any crossover as parents are two young to have babies ;)
return self.r.choice(self.crossovers)(self, original1,original2)
本文内容由网友自发贡献,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有涉嫌抄袭侵权的内容,请联系:hwhale#tublm.com(使用前将#替换为@)