C++ Primer(第五版)|练习题答案与解析(第三章:字符串、向量和数组)
本博客主要记录C++ Primer(第五版)中的练习题答案与解析。
参考:C++ Primer
C++ Primer
练习题3.2
编写程序,从标准输入中一次读入一整行,然后修改该程序使其一次读入一个词。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::string;
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
int main()
{
string line;
while(getline(cin, line)){
cout<<line<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
测试:
abasasddasd dasd dasdasd
abasasddasd dasd dasdasd
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::string;
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
int main()
{
string word;
while(cin>>word){
cout<<word<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
测试:
abc efg
abc
efg
练习题3.3
说明string类的输入运算符和getline函数分别是如何处理空白字符的。
- string对象会自动忽略开头的空白(即空格符、制表符、换行符等等)并从第一个真正的字符开始,直到遇到下一个空白为止。(P77)
- 如果需要字符串中保留输入时的空白符,这时应该用getline代替原来的>>运算符,直到遇见换行符结束。(P78)
练习题3.4
编写程序,读入两个字符串,比较其是否相等并输出结果。如果不相等,输出较大的那个字符串。改写上述程序,比较输入的两个字符串是否等长,如果不等长,输出长度较大的那个字符串。
测试一:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::string;
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
int main()
{
string str1, str2;
while (cin >> str1 >> str2)
{
if (str1 == str2)
cout << "The two strings are equal." << endl;
else
cout << "The larger string is " << ((str1 > str2) ? str1 : str2);
}
return 0;
}
abc
aBc
The larger string is abc
abc
abc
The two strings are equal.
测试二:
using std::string;
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
int main()
{
for (string str1, str2; cin >> str1 >> str2;)
{
if (str1.size() == str2.size())
cout << "The two strings have the same length." << endl;
else
cout << "The longer string is " << ((str1.size() > str2.size()) ? str1 : str2) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
abcde
abcdef
The larger string is abcdef
练习题3.5
编写一段程序,从标准输入中读入多个字符串并将它们连接在一起,输出连接成的大字符串。然后修改程序,用空格把输入的多个字符串分割开来。
测试一:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::string;
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
int main()
{
string word;
string concatenated;
while (getline (cin, word)) {
concatenated += word;
cout <<"The concatenated string is "<< concatenated << endl;
}
return 0;
}
abcd
The concatenated string is abcd
abcd 123 efg 789
The concatenated string is abcdabcd 123 efg 789
xyz
The concatenated string is abcdabcd 123 efg 789xyz
测试二:
using std::string;
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
int main()
{
string word;
string str;
while (getline(cin, word)) {
str += (word + " ");
cout <<"The concatenated string is " << str << endl;
}
return 0;
}
abc efg 123
The concatenated string is abc efg 123
xyz 789
The concatenated string is abc efg 123 xyz 789
练习题3.6
编写程序,使用范围for语句将字符串内的所有字符用X代替。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::string;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
int main()
{
string str("a simple string");
for (auto &c : str) c = 'X';
cout << str << endl;
return 0;
}
练习题3.7
将上一题循环控制变量的类型设为char将发生什么?估计结果,并验证。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::string;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
int main()
{
string str("a simple string");
for (char &c : str) c = 'X';
cout << str << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:XXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
可以运行,每个元素是char类型。
练习题3.8
分别用while循环和for循环重写第一题,哪种形式更好呢?
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::string;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
int main()
{
string str("a simple string");
decltype(str.size()) i = 0;
while (i < str.size()) str[i++] = 'X';
cout << str << endl;
for (i = 0; i < str.size(); str[i++] = 'Y');
cout << str << endl;
return 0;
}
其实差不多。
练习题3.9
下面的程序有何作用?它合法吗?如果不合法,为什么?
string s;
cout << s[0] << endl;
- 不合法,使用超出范围的下标将引发不可预知的结果,以此推断,使用下标访问空string也会引发不可预知的结果。(P84)
练习题3.10
编写程序,读入一个包含标点符号的字符串,将标点符号去除后输出字符串剩余的部分。
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::string;
using std::cout;
using std::cin;
using std::endl;
int main()
{
cout << "Enter a string of characters including punctuation." << endl;
for (string s; getline(cin, s); cout << endl)
for (auto i : s)
if (!ispunct(i)) cout << i;
return 0;
}
Enter a string of characters including punctuation.
hello,word! todat is a nice day!
helloword todat is a nice day
练习题3.11
下面的范围for语句合法吗?如果合法,c的类型是什么?
const string s = "Keep out!";
for (auto &c : s) { }
- 如果不使用c修改原string的内容,则合法。
- 如果要修改,则不合法。这是因为设置一个auto类型的引用时,初始值中的顶层const依旧保留,c的类型为const string&。
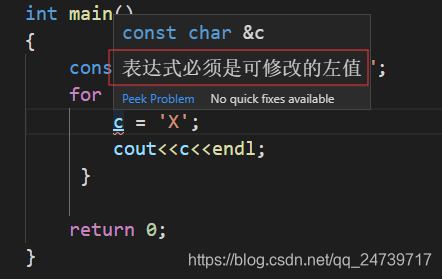
练习题3.12
下列vector对象的定义是否正确?说明原因
( a )vector<vector<int>> ivec; 合法,创建的类型为,(P87)
( b )vector<string> svec = ivec; 不合法,创建的svec是string类型, 而ivec是vector<int>类型(P88)
( c )vector<string>svec(10, "null"); 合法,创建10个string类型的元素,每个都被初始化为null
练习题3.13
下列vector对象各包含多少个元素?值分别是多少?
( a )vector<int> v1; 不包含元素,初始状态为空,P88。
( b )vector<int> v2(10); 包含10个元素,都初始化为0,P89。
( c )vector<int> v3(10, 42); 包含10个元素,都初始化为42
( d )vector<int> v4{10}; 包含1个元素,值为10。
( e )vector<int> v5{10, 42};包含2个元素,值分别是10和42。
( f )vector<string> v6{10}; 10个默认初始化的元素,P89。
( g )vector<string> v7{10, "hi"};10个值为hi的元素,P89。
练习题3.14
编写一段程序,用cin读入一组整数并把它们存入vector对象。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
int main()
{
std::vector<int> vec;
for (int i; std::cin >> i; vec.push_back(i));
return 0;
}
练习题3.15
改写上题程序,读入字符串
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
int main()
{
std::vector<std::string> vec;
for (std::string buffer; std::cin >> buffer; vec.push_back(buffer));
return 0;
}
练习题3.16
编写程序,将13题中的vector对象容量和值输出。检验之前的回答是否正确
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using std::vector;
using std::string;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
int main()
{
vector<int> v1;
cout << "{\n \"v1\":{\"size\":\"" << v1.size() << "\",\"value\":[";
for (auto i : v1)
cout << i << ",";
if (!v1.empty()) cout << "\b";
cout << "]}" << endl;
vector<int> v2(10);
cout << " \"v2\":{\"size\":\"" << v2.size() << "\",\"value\":[";
for (auto i : v2)
cout << i << ",";
if (!v2.empty()) cout << "\b";
cout << "]}" << endl;
vector<int> v3(10, 42);
cout << " \"v3\":{\"size\":\"" << v3.size() << "\",\"value\":[";
for (auto i : v3)
cout << i << ",";
if (!v3.empty()) cout << "\b";
cout << "]}" << endl;
vector<int> v4{ 10 };
cout << " \"v4\":{\"size\":\"" << v4.size() << "\",\"value\":[";
for (auto i : v4)
cout << i << ",";
if (!v4.empty()) cout << "\b";
cout << "]}" << endl;
vector<int> v5{ 10, 42 };
cout << " \"v5\":{\"size\":\"" << v5.size() << "\",\"value\":[";
for (auto i : v5)
cout << i << ",";
if (!v5.empty()) cout << "\b";
cout << "]}" << endl;
vector<string> v6{ 10 };
cout << " \"v6\":{\"size\":\"" << v6.size() << "\",\"value\":[";
for (auto i : v6)
if (i.empty()) cout << "(null)" << ",";
else cout << i << ",";
if (!v6.empty()) cout << "\b";
cout << "]}" << endl;
vector<string> v7{ 10, "hi" };
cout << " \"v7\":{\"size\":\"" << v7.size() << "\",\"value\":[";
for (auto i : v7)
if (i.empty()) cout << "(null)" << ",";
else cout << i << ",";
if (!v7.empty()) cout << "\b";
cout << "]}\n}" << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
{
"v1":{"size":"0","value":[]}
"v2":{"size":"10","value":[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]}
"v3":{"size":"10","value":[42,42,42,42,42,42,42,42,42,42]}
"v4":{"size":"1","value":[10]}
"v5":{"size":"2","value":[10,42]}
"v6":{"size":"10","value":[(null),(null),(null),(null),(null),(null),(null),(null),(null),(null)]}
"v7":{"size":"10","value":[hi,hi,hi,hi,hi,hi,hi,hi,hi,hi]}
}
练习题3.17
从cin读入一组词并把它们存入一个vector对象,然后设法把所有词都改为大写。输出改变后的结果,每个词占一行。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::vector;
using std::string;
int main()
{
vector<string> vec;
for (string word; cin >> word; vec.push_back(word));
for (auto &str : vec) for (auto &c : str) c = toupper(c);
for (string::size_type i = 0; i != vec.size(); ++i)
{
if (i != 0 && i % 8 == 0) cout << endl;
cout << vec[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
练习题3.18
下面的程序合法吗?该如何修改?
vector<int> ivec;
ivec[0] = 42;
不合法,ivec为空,不包含任何元素,不能通过下标去访问元素。P94。
修改为:ivec.push_back(42);
练习题3.19
如果想定义一个含有10个元素的vector元素,所有元素值都为42,请列举三种不同的方式,哪种更好?原因?
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using std::vector;
int main()
{
vector<int> ivec1(10, 42);
vector<int> ivec2{ 42, 42, 42, 42, 42, 42, 42, 42, 42, 42 };
vector<int> ivec3;
for (int i = 0; i != 10; ++i) ivec3.push_back(42);
std::cout << "The first approach is better!" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
练习题3.20
读入一组整数并把它们存入一个vector对象,将每对相邻整数的和输出出来,改写程序,这次要求先输出第一个和最后一个之和,接着输出第二个和倒数第二个之和,依次类推。
测试一
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using std::vector; using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::cin;
int main()
{
vector<int> ivec;
for (int i; cin >> i; ivec.push_back(i));
if (ivec.empty())
{
cout << "input at least one integer." << endl;
return -1;
}
if (ivec.size() == 1)
{
cout << "only one integer " << ivec[0] << ", it doesn't have any adjacent elements." << endl;
return -1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < ivec.size() - 1; ++i)
cout << ivec[i] + ivec[i + 1] << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
输出一
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9^Z
3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17
测试二
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using std::vector;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::cin;
int main()
{
vector<int> ivec;
for (int i; cin >> i; ivec.push_back(i));
if (ivec.empty())
{
cout << "input at least one integer." << endl;
return -1;
}
auto size = (ivec.size() + 1) / 2;
for (int i = 0; i != size; ++i)
cout << ivec[i] + ivec[ivec.size() - i - 1] << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
输出二
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9^Z
10 10 10 10 10
练习题3.21
请使用迭代器重做3.16题。
测试:
#include <vector>
#include <iterator>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using std::vector;
using std::string;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
void check_and_print(const vector<int>& vec)
{
cout << "size: " << vec.size() << " content: [";
for (auto it = vec.begin(); it != vec.end(); ++it)
cout << *it << (it != vec.end() - 1 ? "," : "");
cout << "]\n" << endl;
}
void check_and_print(const vector<string>& vec)
{
cout << "size: " << vec.size() << " content: [";
for (auto it = vec.begin(); it != vec.end(); ++it)
cout << *it << (it != vec.end() - 1 ? "," : "");
cout << "]\n" << endl;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> v1;
vector<int> v2(10);
vector<int> v3(10, 42);
vector<int> v4{ 10 };
vector<int> v5{ 10, 42 };
vector<string> v6{ 10 };
vector<string> v7{ 10, "hi" };
check_and_print(v1);
check_and_print(v2);
check_and_print(v3);
check_and_print(v4);
check_and_print(v5);
check_and_print(v6);
check_and_print(v7);
return 0;
}
输出:
size: 0 content: []
size: 10 content: [0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]
size: 10 content: [42,42,42,42,42,42,42,42,42,42]
size: 1 content: [10]
size: 2 content: [10,42]
size: 10 content: [,,,,,,,,,]
size: 10 content: [hi,hi,hi,hi,hi,hi,hi,hi,hi,hi]
练习题3.23
创建一个含有10个整数的vector对象,使用迭代器将所有元素的值都变为之前的两倍。并输出内容,检测是否正确。
测试
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
using std::vector; using std::iterator; using std::cout;
int main()
{
vector<int> v{ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
for (auto it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); ++it)
*it *= 2;
for (auto i : v)
cout << i << " ";
return 0;
}
输出:
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18
练习题3.24
使用迭代器重做3.20题。
测试:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using std::vector; using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::cin;
int main()
{
vector<int> v;
for (int buffer; cin >> buffer; v.push_back(buffer));
if (v.size() < 2)
{
cout << " please enter at least two integers";
return -1;
}
for (auto it = v.cbegin(); it + 1 != v.cend(); ++it)
cout << *it + *(it + 1) << " ";
cout << endl;
for (auto lft = v.cbegin(), rht = v.cend() - 1; lft <= rht; ++lft, --rht)
cout << *lft + *rht << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9^Z
3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17
10 10 10 10 10
练习题3.25
使用迭代器划分成绩(93页)
测试
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
using std::vector; using std::cout; using std::cin; using std::endl;
int main()
{
vector<unsigned> scores(11, 0);
for (unsigned grade; cin >> grade;)
if (grade <= 100)
++*(scores.begin() + grade / 10);
for (auto s : scores)
cout << s << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
1 11 21 31 21 41 51 61 71 81^Z
1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0
练习题3.26
二分搜索中,为什么用的是mid=beg+(end-beg)/2,而非mid=(beg+end)/2;?
end成员返回的迭代器是尾后迭代器,是指向尾元素的下一个位置P(95)
练习题3.27
假设txt_size是一个无参数的函数,返回值为int,下面定义是否合法?说明原因
unsigned buf_size = 1024;
(a )int ia[buf_size]; 不合法,buf_size不是常量
(b )int ia[4*7-14]; 合法的,4*7-14是个常量。
(c )int ia[txt_size()]; 不合法,函数返回值不是常量
(d )char str[11] = "fundamental"; 不合法,没有空间可放空字符
练习题3.28
下列数组中元素的值是什么?
string sa[10];
int ia[10];
int main()
{
string sa2[10];
int ia2[10];
for (auto i : ia2) {
cout << i << " ";
}
}
练习题3.29
相比vector来说,数组有哪些缺点?
大小固定,不够灵活。(P101)
练习题3.30
指出下面代码中索引的错误
constexpr size_t array_size = 10;
int ia[array_size];
for (size_t ix = 1; ix <= array_size; ix ++) {
ia[ix] = ix;
}
练习题3.31
编写程序,定义一个长度为10的int数组,令每个元素的值就是其下标值。
测试
#include <iostream>
using std::cout; using std::endl;
int main()
{
int arr[10];
for (auto i = 0; i < 10; ++i) arr[i] = i;
for (auto i : arr) cout << i << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
练习题3.32
将上题创建的数组拷贝给另一个数组,使用vector重新程序。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::vector;
int main()
{
int arr[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) arr[i] = i;
int arr2[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; ++i) arr2[i] = arr[i];
vector<int> v(10);
for (int i = 0; i != 10; ++i) v[i] = arr[i];
vector<int> v2(v);
for (auto i : v2) cout << i << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
练习题3.33
对于P10页程序而言,如果不初始化scores将会发生什么?
如果不初始化scores,则其中内容未知,可能为空,也可能有别的数据。
练习题3.34
假定p1和p2指向同一数组中的元素,则下面程序的功能是什么?什么情况下该程序是非法的?
(1)p1 += p2 - p1; p2-p1为p1与p2之间的距离,p1+(p1和p2之间的距离),即最后得到p2的值。当p1或p2不在同一数组内,则程序非法。(P108)
练习题3.35
编写一段程序,利用指针将数组中的元素置为0.
测试
#include <iostream>
using std::cout; using std::endl;
int main()
{
const int size = 10;
int arr[size];
for (auto ptr = arr; ptr != arr + size; ++ptr) *ptr = 0;
for (auto i : arr) cout << i << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
练习题3.36
编写一段程序,比较两个数组是否相等。再写一段程序,比较两个vector对象是否相等。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <iterator>
using std::begin; using std::end; using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::vector;
bool compare(int* const pb1, int* const pe1, int* const pb2, int* const pe2)
{
if ((pe1 - pb1) != (pe2 - pb2))
return false;
else
{
for (int* i = pb1, *j = pb2; (i != pe1) && (j != pe2); ++i, ++j)
if (*i != *j) return false;
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
int arr1[3] = { 0, 1, 2 };
int arr2[3] = { 0, 2, 4 };
if (compare(begin(arr1), end(arr1), begin(arr2), end(arr2)))
cout << "The two arrays are equal." << endl;
else
cout << "The two arrays are not equal." << endl;
cout << "==========" << endl;
vector<int> vec1 = { 0, 1, 2 };
vector<int> vec2 = { 0, 1, 2 };
if (vec1 == vec2)
cout << "The two vectors are equal." << endl;
else
cout << "The two vectors are not equal." << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
The two arrays are not equal.
==========
The two vectors are equal.
练习题3.37
下面的程序是何含义,输出结果是什么?
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <iterator>
#include <string.h>
using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::vector;
int main()
{
const char s[] = {'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'};
const char* p = s;
while (*p) {
cout << *p << " ";
++ p;
}
cout << strlen(s) << endl;
return 0;
}
输出
h e l l o ?
s初始化时,并未加‘\0’,因此其长度未知,while循环会一直继续知道遇见’\0’。输出“hello+未知字符”。
练习题3.38
两个指针相加不仅是非法的,并且没什么意义,请问为什么没有意义?
两个指针相加,相当于两个地址值相加,没有意义。
练习题3.39
写一段程序,比较两个string对象,再编写一段程序,比较两个c风格字符串的内容。
测试
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::string;
int main()
{
string s1("Test"), s2("Train");
if (s1 == s2)
cout << "same string." << endl;
else if (s1 > s2)
cout << "Test > Train" << endl;
else
cout << "Test < Train" << endl;
cout << "=========" << endl;
const char* cs1 = "Test";
const char* cs2 = "Train";
auto result = strcmp(cs1, cs2);
if (result == 0)
cout << "same string." << endl;
else if (result < 0)
cout << "Test < Train" << endl;
else
cout << "Test > Train" << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
Test < Train
=========
Test < Train
练习题3.40
编写一段程序,定义两个字符数组并用字符串字面值初始化它们,接着再定义一个字符数组,存放前两个数组连接后的结果。使用strcpy和strcat把前两个数组的内容拷贝到第三个数组中
测试:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
const char cstr1[]="Hello";
const char cstr2[]="world!";
int main()
{
constexpr size_t new_size = strlen(cstr1) + strlen(" ") + strlen(cstr2) +1;
char cstr3[new_size];
strcpy(cstr3, cstr1);
strcat(cstr3, " ");
strcat(cstr3, cstr2);
std::cout << cstr3 << std::endl;
}
输出:
Hello world!
练习题3.41
编写一段程序,用整型数组初始化一个vector对象。
测试
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using std::vector; using std::cout; using std::endl; using std::begin; using std::end;
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
vector<int> v(begin(arr), end(arr));
for (auto i : v) cout << i << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
练习题3.43
编写三个不同版本的程序,令其均能输出ia元素,版本1使用范围for语句管理迭代过程,版本2和3都使用普通for语句,其中版本2要求使用下标运算符,版本3要求使用指针。此外,三个版本都要直接写出数据类型,而不能使用类型别名,auto关键字和decltype。
测试
#include <iostream>
using std::cout; using std::endl;
int main()
{
int arr[3][4] =
{
{ 0, 1, 2, 3 },
{ 4, 5, 6, 7 },
{ 8, 9, 10, 11 }
};
for (const int(&row)[4] : arr)
for (int col : row) cout << col << " ";
cout << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i != 3; ++i)
for (size_t j = 0; j != 4; ++j) cout << arr[i][j] << " ";
cout << endl;
for (int(*row)[4] = arr; row != arr + 3; ++row)
for (int *col = *row; col != *row + 4; ++col) cout << *col << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
输出
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
练习题3.44
改写上一个练习中的程序,使用类型别名来代替循环控制变量的类型。
#include <iostream>
using std::cout; using std::endl;
int main()
{
int ia[3][4] = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 };
using int_array = int[4];
for (int_array& p : ia)
for (int q : p)
cout << q << " ";
cout << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i != 3; ++i)
for (size_t j = 0; j != 4; ++j)
cout << ia[i][j] << " ";
cout << endl;
for (int_array* p = ia; p != ia + 3; ++p)
for (int *q = *p; q != *p + 4; ++q)
cout << *q << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
输出
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
练习题3.45
再次改写程序,这次使用auto关键字。
#include <iostream>
using std::cout; using std::endl;
int main()
{
int ia[3][4] = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 };
for (auto& p : ia)
for (int q : p)
cout << q << " ";
cout << endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i != 3; ++i)
for (size_t j = 0; j != 4; ++j)
cout << ia[i][j] << " ";
cout << endl;
for (auto p = ia; p != ia + 3; ++p)
for (int *q = *p; q != *p + 4; ++q)
cout << *q << " ";
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
输出:
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11
本文内容由网友自发贡献,版权归原作者所有,本站不承担相应法律责任。如您发现有涉嫌抄袭侵权的内容,请联系:hwhale#tublm.com(使用前将#替换为@)